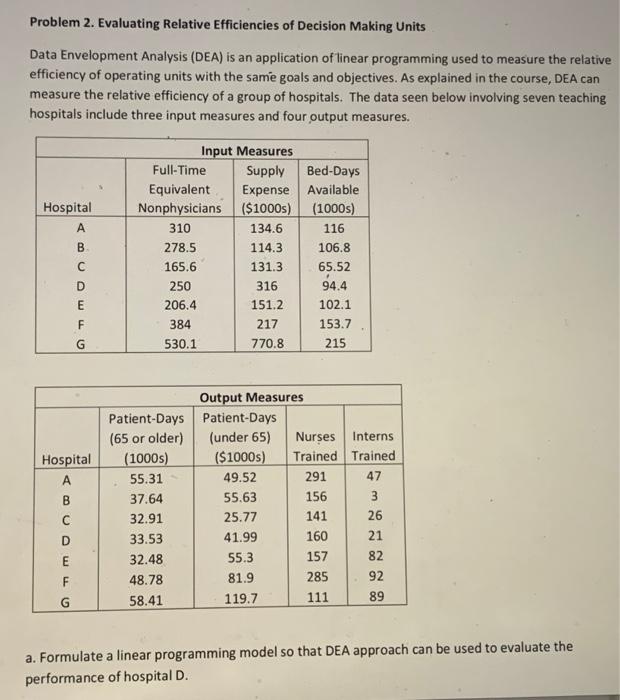
Question: Problem 2. Evaluating Relative Efficiencies of Decision Making Units Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) is an application of linear programming used to measure the relative efficiency
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


