Question: A function can return simplest a unmarried cost, but that price can be a category object with many contributors. This lets in us to efficiently
A function can return simplest a unmarried cost, but that price can be a category object
with many contributors. This lets in us to efficiently return many values. For
example:
Click right here to view code image
struct Entry
string name;
int cost;
;
Entry read_entry(istream& is) // naive read feature (for a
higher model, see §10.Five)
string s;
int i;
is >> s >> i;
return s,i;
car e = read_entry(cin);
cout Here, s,i is used to construct the Entry go back value. Similarly, we are able to
"unpack" an Entry's members into nearby variables:
Click here to view code image
car [n,v] = read_entry(is);
cout The auto [n,v] declares neighborhood variables n and v with their sorts deduced
from read_entry()'s go back kind. This mechanism for giving local names to
members of a class item is known as established binding.
Consider every other example:
Click right here to view code photograph
map
// ... Fill m ...
For (const car [key,value] : m)
cout As common, we will enhance automobile with const and &. For example:
Click right here to view code photo
void incr(map
element of m
for (car& [key,value] : m)
++price;
When structured binding is used for a class without a non-public data, it is easy to
see how the binding is completed: there ought to be the equal range of names defined
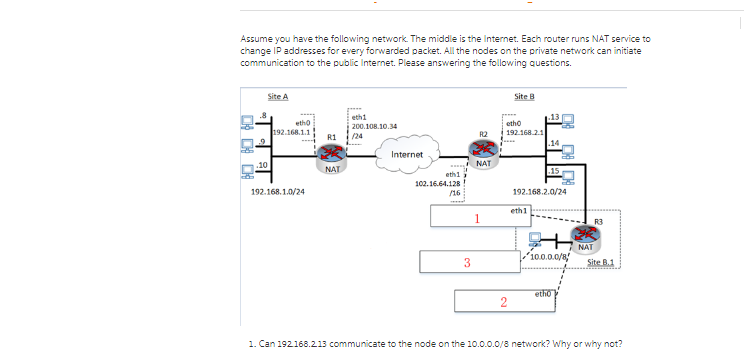

Assume you have the following network. The middle is the Internet. Each router runs NAT service to change IP addresses for every forwarded packet. All the nodes on the private network can initiate communication to the public Internet. Please answering the following questions. 600 40 .10 Site A eth0 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.0/24 eth1 200.108.10.34 R1 /24 NAT Internet eth1 102.16.64.128 /16 3 R2 NAT 1 Site B etho 192.168.2.1 2 .14 192.168.2.0/24 eth1 10.0.0.0/8 etho NAT R3 Site B.1 1. Can 192.168.2.13 communicate to the node on the 10.0.0.0/8 network? Why or why not?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


