Question: (a) How long it will take to perform each activity is estimated. (b) In order to locate the critical path, calculation is performed (the longest
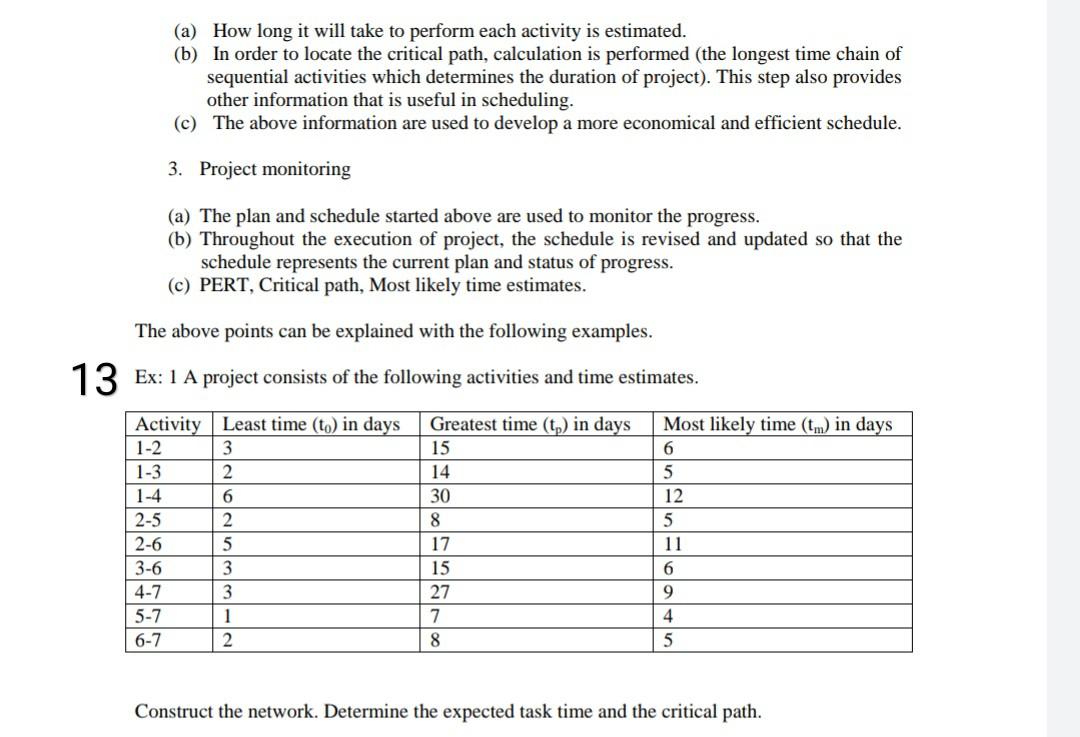
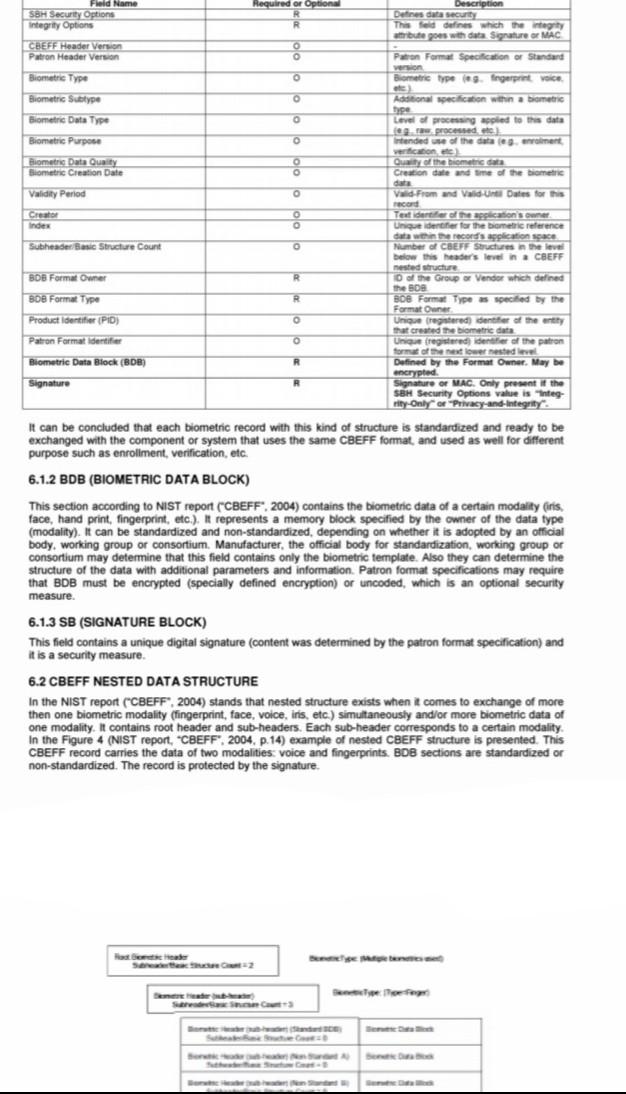
(a) How long it will take to perform each activity is estimated. (b) In order to locate the critical path, calculation is performed (the longest time chain of sequential activities which determines the duration of project). This step also provides other information that is useful in scheduling. (c) The above information are used to develop a more economical and efficient schedule. 3. Project monitoring (a) The plan and schedule started above are used to monitor the progress. (b) Throughout the execution of project, the schedule is revised and updated so that the schedule represents the current plan and status of progress. (c) PERT, Critical path, Most likely time estimates. 1-2 3 2 14 The above points can be explained with the following examples. 13 Ex: 1 A project consists of the following activities and time estimates. Activity Least time (to) in days Greatest time (t) in days Most likely time (tm) in days 15 6 1-3 5 1-4 30 2-5 5 2-6 17 3-6 15 4-7 27 5-7 4 6-7 5 6 12 2 8 5 11 3 6 9 3 7 1 2 8 Construct the network. Determine the expected task time and the critical path. Field Name Required or Options Description SBH Security Options R Detines data security Integrity Options R The eld defines which the integrity attribute goes with data Signature or MAC CBEFF Header Version O Patron Header Version Patron Format Specification of Standard Biometric Type o Biometric type. fingerprint voice Biometric Subtype 0 Additional specification within a biometric type Biometric Data Type o Level of processing applied to this data e processed Biometric Purpose o tended we of the data legeniment verification) Biometr Data Quality 8 Biometric Creation Date Quality of the biometric data Creation date and time of the biometne Validity Period o ValidFrom and valid until Dates for this record Teatro the applications cum Index Unique identifier for the biometric reference data white records application space Subheader Basic Structure Count Number of CBEFF Structures in the level below this header's level in a CHEFF neste structure BOB Format Owner R of the Group or Vender which defined the De BOB FormatType R Boe Format Type as specified by the Format Owner Product Identifier (PID) o Unique registered Identer of the entity that created the biometrice data Patron Format identifier Uhone (registered identifier of the patron form of the next lower nested level Biometrie Data Block (BDR) R Defined by the Format Owner. Maybe encrypted Signature R Signature of MAC Only present the SBH Security Options value ishte rity-Only or Privacy-and-integrity It can be concluded that each biometric record with this kind of structure is standardized and ready to be exchanged with the component or system that uses the same CBEFF format, and used as well for different purpose such as enrollment, verification, etc. 6.1.2 BDB (BIOMETRIC DATA BLOCK) ) This section according to NIST report (CBEFF 2004) contains the biometric data of a certain modality (ins, face, hand print, fingerprint, etc.). It represents a memory block specified by the owner of the data type (modality). It can be standardized and non-standardized, depending on whether it is adopted by an official body, working group or consortium. Manufacturer, the official body for standardization, working group or consortium may determine that this field contains only the biometric template. Also they can determine the structure of the data with additional parameters and information. Patron format specifications may require that BDB must be encrypted (specially defined encryption) or uncoded, which is an optional security measure 6.1.3 SB (SIGNATURE BLOCK) This field contains a unique digital signature content was determined by the patron format specification) and it is a security measure 6.2 CBEFF NESTED DATA STRUCTURE In the NIST report (CBEFF, 2004) stands that nested structure exists when it comes to exchange of more then one biometric modality (fingerprint, face, voice, ins, etc.) simultaneously and/or more biometric data of one modality. It contains root header and sub-headers. Each sub-header corresponds to a certain modality In the Figure 4 (NIST report, CBEFF, 2004, p. 14) example of nested CBEFF structure is presented. This CBEFF record carries the data of two modalities voice and fingerprints. BDB sections are standardized or non-standardized. The record is protected by the signature che
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


