Question: A pond drains through a pipe as shown below. Under a number of simplifying assumptions, the following differential equation describes how depth changes with time:
A pond drains through a pipe as shown below. Under a number of simplifying assumptions, the following differential equation describes how depth changes with time:
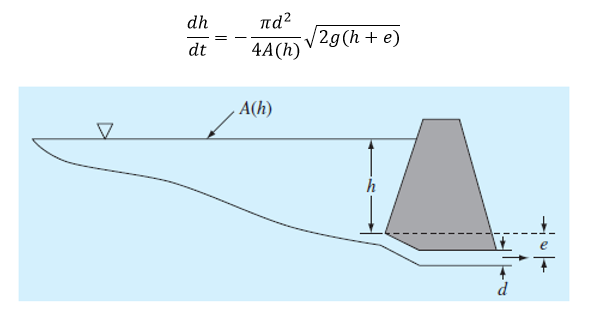
Where h = depth (m), t = time (s), d = pipe diameter (m), A(h) = pond surface area as afunction of depth (m2), g =gravitational constant (= 9.81 m/s2), and e = depth of pipeoutlet below the pond bottom (m). Based on the following area-depth table, solve this differential equation to determine how long it takes for the pond to empty, given that:
h(0) = 6 m, d = 0.25 m, e = 1 m.
| h (m) | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| A(h) x 104 m2 | 1.17 | 0.97 | 0.67 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.18 |
|
Hint:
1. Fit a fifth-order polynomial with a zero intercept for the area-depth data [Note that the Excel curve-fitting equation is not accepted];
2. Substitute the derived polynomial into the differential equation given above;
3. Solve (integrate) the derived equation at step 2 numerically (using Eulers method Modified Eulers method, and Runge-Kutta method and h=0.025). Details of three steps for each method are required then a computer code can be developed for the rest of iterations.
Develop a computer code (MATLAB) for step 3. Terminate the program running when a negative area is detected.
dh d2 dt 4A(h) ATh5V2g(h +e) A(h) e T t-fd Td h- It
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


