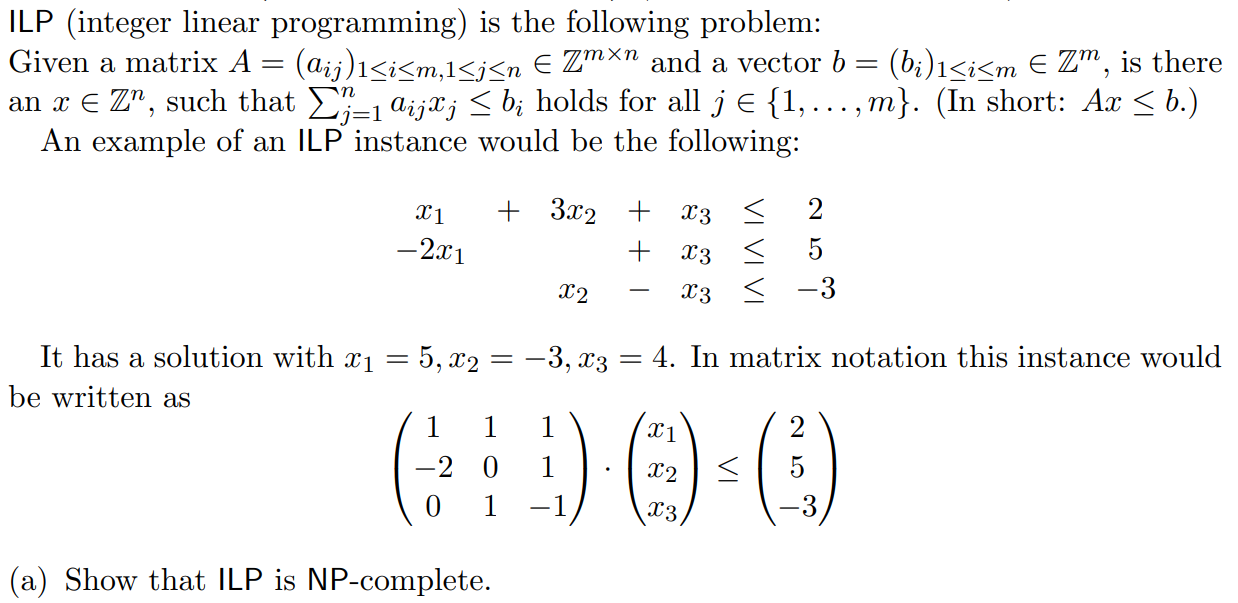
Question: ( a ) Show that ILP is NP - complete. Hint: You may use the following: Let N be the length of the encoding of
a Show that ILP is NPcomplete.
Hint: You may use the following: Let N be the length of the encoding of A and bExample of an encoding: all entries from A and b are encoded in binary and written consecutively with a fitting separator. Then there is a polynomial p such that if there is an with Ax b then there is also an with Ax b and for all j
b RLP is defined similar to ILP: The only difference is that the question is if there is an with Ax b instead of It is known that RLP P Why doesnt the previous reduction show P NP or in other words: why does your reduction from the previous exercise noShow that ILP remains NPcomplete even if we only allow equations instead of inequalities, ie we require Ax b Additionally we require x t work for RLP
Show that ILP remains NPcomplete even if we only allow equations instead of inequalities, ie we require Ax b Additionally we require x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


