Question: A soil sample 10 cm in diameter is placed in a tube 1 m long. A constant supply of water is allowed to flow

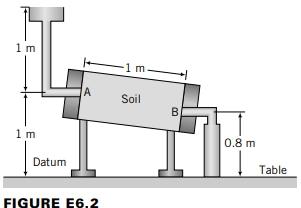
A soil sample 10 cm in diameter is placed in a tube 1 m long. A constant supply of water is allowed to flow into one end of the soil at A, and the outflow at B is collected by a beaker (Figure E6.2). The average amount of water collected is 1cm for every 10 seconds. The tube is inclined as shown in Figure E6.2. Determine the (a) hydraulic gradient, (b) flow rate, (c) average velocity, (d) seepage velocity if e = 0.6, and (e) hydraulic conductivity. Strategy: In flow problems, you must define a datum position. So your first task is to define the datum position and then find the difference in total head between A and B. Use the head difference to calculate the hydraulic gradient and use Equations (6.7) to (6.9) to solve the problem. Equation (6.7): Vr = kr = kii 22 Equation (6.8): Us = = ki = Equation (6.9): q; = vA = Akji 1 m 1 m Datum A FIGURE E6.2 -1 m Soil B 0.8 m Table
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
T Datum a The hydralic gradie... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


