Question: A sorting algorithm that uses a binary tree to sort a list of positive integers a1, a2, . . . , an from largest to
A sorting algorithm that uses a binary tree to sort a list of positive integers a1, a2, . . . , an from largest to smallest can be described as follows. In the first step, we construct the binary tree. The elements a1, a2, . . . , an are the leaves of the tree, and we build up the tree one level at a time from there. From left to right, compare the elements in pairs, and put the larger of the two as the parent vertex. Do this at each level until reaching the root, which will be the largest element. Output the value at the root. For example, if the list to be sorted is 22, 8, 14, 17, 3, 9, 27, 11, the tree would look like this: 22 8 14 17 3 9 27 11 22 22 17 9 27 27 27 Then, in the second step, remove the leaf corresponding to that largest element, and replace it with a leaf labeled 0, which is defined to be smaller than all the other list elements. Recompute the labels of all vertices on the path from this 0 to the root. That is, relabel all vertices on the path from the 0 to the root by choosing the larger of the values of their two children. Then the root will become the second-largest element. Output the value at the root. In our example, the tree would now look like this: 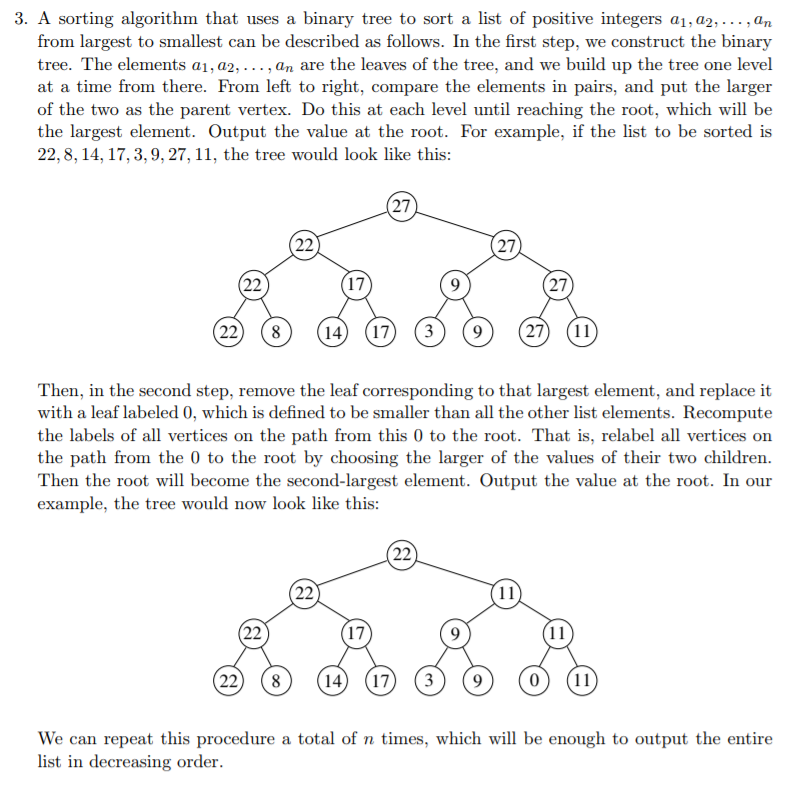

3. A sorting algorithm that uses a binary tree to sort a list of positive integers a1, a2,... ,an from largest to smallest can be described as follows. In the first step, we construct the binary tree. The elements a1, a2,..., an are the leaves of the tree, and we build up the tree one level at a time from there. From left to right, compare the elements in pairs, and put the larger of the two as the parent vertex. Do this at each level until reaching the root, which will be the largest element. Output the value at the root. For example, if the list to be sorted is 22,8,14,17,3,9,27, 11, the tree would look like this 27 27 17 27 22) (8 14 17 (3 9 27 11 Then, in the second step, remove the leaf corresponding to that largest element, and replace it with a leaf labeled 0, which is defined to be smaller than all the other list elements. Recompute the labels of all vertices on the path from this 0 to the root. That is, relabel all vertices on the path from the 0 to the root by choosing the larger of the values of their two children Then the root wll become the second-largest element. Output the value at the root. In our example, the tree would now look like this: 17 22) (8 14 17 39 We can repeat this procedure a total of n times, which will be enough to output the entire list in decreasing order
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


