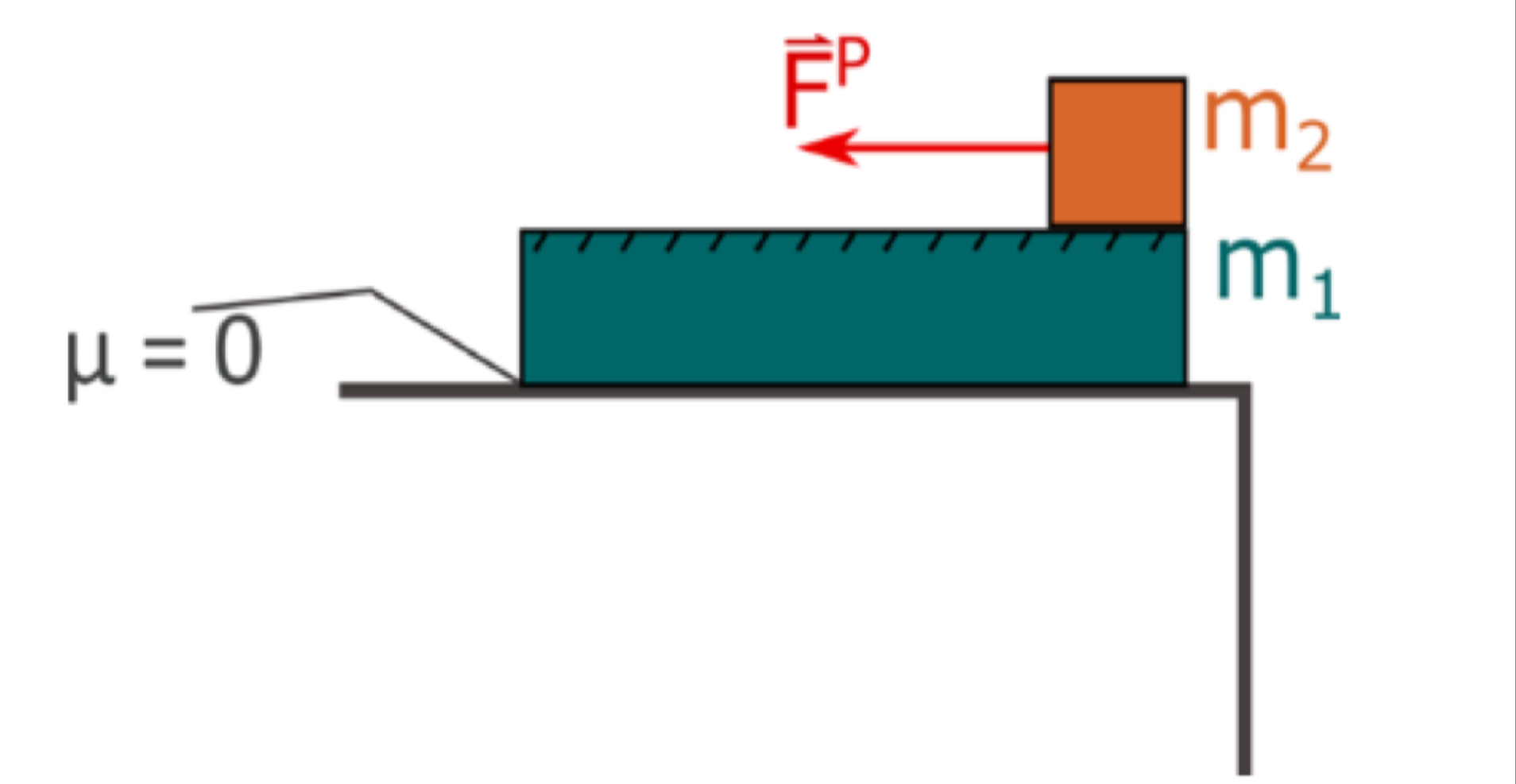
Question: A square 4 - kg - box lies on the righthand side of a bigger 1 1 . 0 - kg rectangular box. Both objects
A square kgbox lies on the righthand side of a bigger kg rectangular box. Both objects start from
rest. The only friction occurs on the interface between the boxes. The coefficient of kinetic friction between
the two is The rectangular box is meters in length. A constant horizontal force pulls on the square
box to the left. It takes s for the square box to get to the other side of the rectangular box. Note though,
the rectangular box may also move during this time.
a Draw a freebody diagram for both objects and label each
force using the notation used in this course.
b Symbolically write out Newtons nd law for both objects.
Dont put in numbers, only use the variables and notation
used in this course.
c Identify all Newtons rd law force pairs.
d Use sign sensemaking to determine the direction of accelera
tion of the rectangular box. Explain why you believe it will be
in that direction.
Now input numbers and find the following quantities.
e What is the magnitude of the force applied to the top box?
f How far does the bottom box travel? Hint: use a nonmovingnonaccelerating reference frame,
ie static origin on the right side of the table for both blocks.
g What is the final velocity of the top and bottom block?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


