Question: A student hangs a 0.125 kg object on a spring, sets it into oscillation, and obtains the data for the position and velocity of
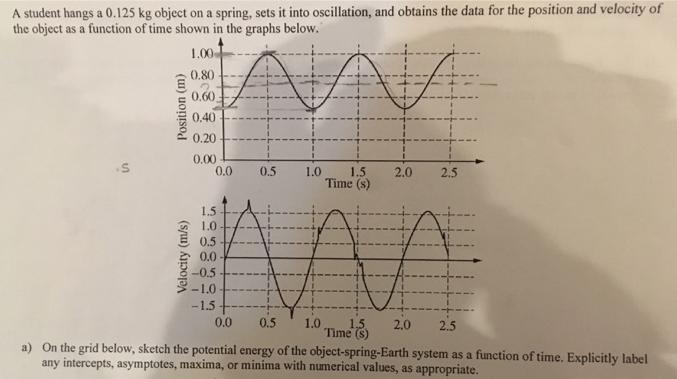

A student hangs a 0.125 kg object on a spring, sets it into oscillation, and obtains the data for the position and velocity of the object as a function of time shown in the graphs below. 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Time (s) 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 -1.5 0.0 0.5 2.5 1.0 Time a) On the grid below, sketch the potential energy of the object-spring-Earth system as a function of time. Explicitly label 2.0 any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. (u) uoisod Velocity (m/s) 2.0 2.5 1.5 Time (s) 0.0 0.5 1.0 (b) On the axes below, sketch the acceleration of the object as a function of time. Explicitly label any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. Potential Energy (J) A student hangs a 0.125 kg object on a spring, sets it into oscillation, and obtains the data for the position and velocity of the object as a function of time shown in the graphs below. 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Time (s) 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 -1.5 0.0 0.5 2.5 1.0 Time a) On the grid below, sketch the potential energy of the object-spring-Earth system as a function of time. Explicitly label 2.0 any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. (u) uoisod Velocity (m/s) 2.0 2.5 1.5 Time (s) 0.0 0.5 1.0 (b) On the axes below, sketch the acceleration of the object as a function of time. Explicitly label any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. Potential Energy (J) A student hangs a 0.125 kg object on a spring, sets it into oscillation, and obtains the data for the position and velocity of the object as a function of time shown in the graphs below. 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Time (s) 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 -1.5 0.0 0.5 2.5 1.0 Time a) On the grid below, sketch the potential energy of the object-spring-Earth system as a function of time. Explicitly label 2.0 any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. (u) uoisod Velocity (m/s) 2.0 2.5 1.5 Time (s) 0.0 0.5 1.0 (b) On the axes below, sketch the acceleration of the object as a function of time. Explicitly label any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. Potential Energy (J) A student hangs a 0.125 kg object on a spring, sets it into oscillation, and obtains the data for the position and velocity of the object as a function of time shown in the graphs below. 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Time (s) 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 -1.5 0.0 0.5 2.5 1.0 Time a) On the grid below, sketch the potential energy of the object-spring-Earth system as a function of time. Explicitly label 2.0 any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. (u) uoisod Velocity (m/s) 2.0 2.5 1.5 Time (s) 0.0 0.5 1.0 (b) On the axes below, sketch the acceleration of the object as a function of time. Explicitly label any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. Potential Energy (J) A student hangs a 0.125 kg object on a spring, sets it into oscillation, and obtains the data for the position and velocity of the object as a function of time shown in the graphs below. 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Time (s) 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 -1.5 0.0 0.5 2.5 1.0 Time a) On the grid below, sketch the potential energy of the object-spring-Earth system as a function of time. Explicitly label 2.0 any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. (u) uoisod Velocity (m/s) 2.0 2.5 1.5 Time (s) 0.0 0.5 1.0 (b) On the axes below, sketch the acceleration of the object as a function of time. Explicitly label any intercepts, asymptotes, maxima, or minima with numerical values, as appropriate. Potential Energy (J)
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (142 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
SO LUTIONS OO As we know the potenti enengy of a is given as Spring U 3 kx2 where ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


