Question: a) Using the expressions given below, calculate the critical radius (r) and energy barrier (G) for the homogeneous nucleation of a solid copper crystal from
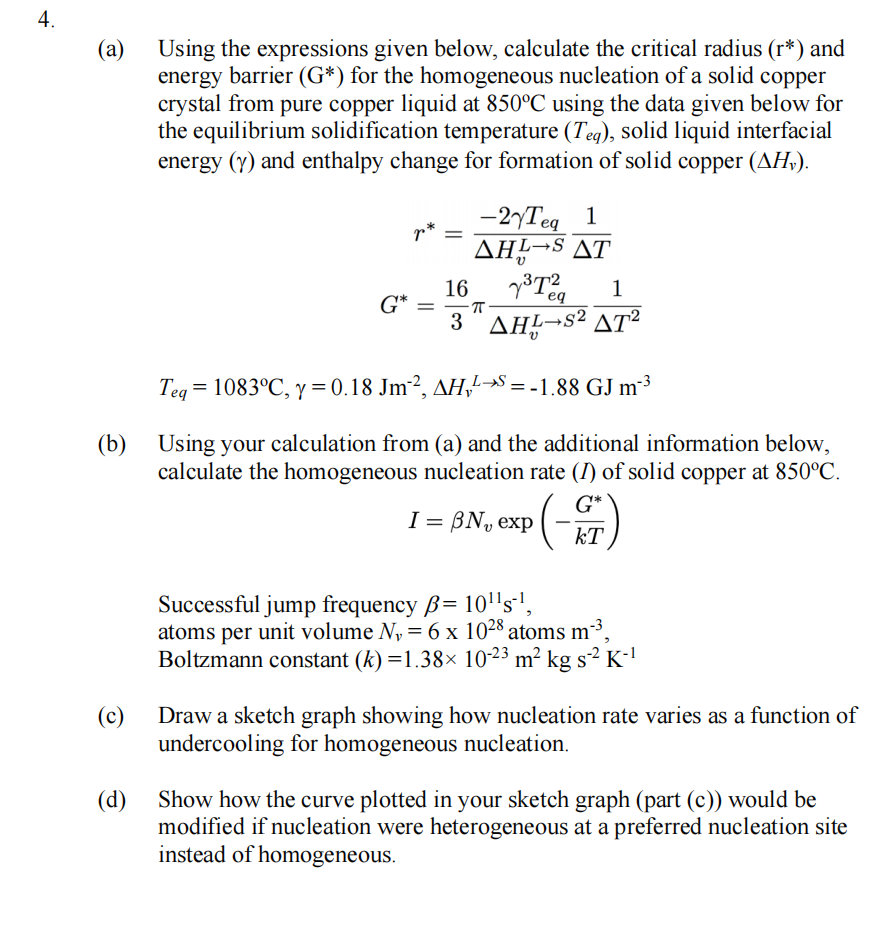
a) Using the expressions given below, calculate the critical radius (r) and energy barrier (G) for the homogeneous nucleation of a solid copper crystal from pure copper liquid at 850C using the data given below for the equilibrium solidification temperature (Teq), solid liquid interfacial energy () and enthalpy change for formation of solid copper (Hv). r=HvLS2TeqT1G=316HvLS23Teq2T21Teq=1083C,=0.18Jm2,HvLS=1.88GJm3 b) Using your calculation from (a) and the additional information below, calculate the homogeneous nucleation rate (I) of solid copper at 850C. I=Nvexp(kTG) Successful jump frequency =1011s1, atoms per unit volume Nv=61028 atoms m3, Boltzmann constant (k)=1.381023m2kgs2K1 c) Draw a sketch graph showing how nucleation rate varies as a function of undercooling for homogeneous nucleation. d) Show how the curve plotted in your sketch graph (part (c)) would be modified if nucleation were heterogeneous at a preferred nucleation site instead of homogeneous. a) Using the expressions given below, calculate the critical radius (r) and energy barrier (G) for the homogeneous nucleation of a solid copper crystal from pure copper liquid at 850C using the data given below for the equilibrium solidification temperature (Teq), solid liquid interfacial energy () and enthalpy change for formation of solid copper (Hv). r=HvLS2TeqT1G=316HvLS23Teq2T21Teq=1083C,=0.18Jm2,HvLS=1.88GJm3 b) Using your calculation from (a) and the additional information below, calculate the homogeneous nucleation rate (I) of solid copper at 850C. I=Nvexp(kTG) Successful jump frequency =1011s1, atoms per unit volume Nv=61028 atoms m3, Boltzmann constant (k)=1.381023m2kgs2K1 c) Draw a sketch graph showing how nucleation rate varies as a function of undercooling for homogeneous nucleation. d) Show how the curve plotted in your sketch graph (part (c)) would be modified if nucleation were heterogeneous at a preferred nucleation site instead of homogeneous
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


