Question: Actual Variance Flex Variance Static/Planning Data U or F Budget U or F Budget Sales in units: 26,300 26,300 25,000 Sales Revenue $605,000 Variable
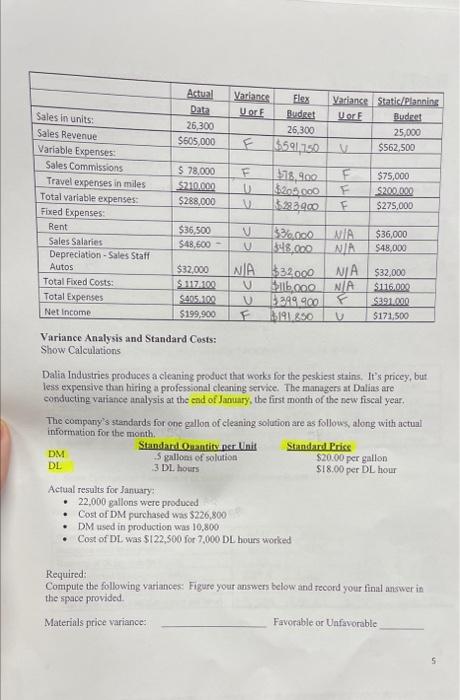

Actual Variance Flex Variance Static/Planning Data U or F Budget U or F Budget Sales in units: 26,300 26,300 25,000 Sales Revenue $605,000 Variable Expenses F $591750 V $562,500 Sales Commissions $ 78,000 F $78,900 F $75,000 Travel expenses in miles $210.000 $205,000 F $200,000 Total variable expenses: $288,000 $283,900 F $275,000 Fixed Expenses: Rent $36,500 2 $3,000 NIA $36,000 Sales Salaries $48,600- V $48,000 N/A $48,000 Depreciation-Sales Staff Autos $32,000 NIA $32.000 NIA $32,000 Total Fixed Costs: $117.100 2 Total Expenses 16,000 $405.100 U $399.900 N/A $116,000 F $391.000 Net Income $199,900 F $191,850 $171,500 Variance Analysis and Standard Costs: Show Calculations Dalia Industries produces a cleaning product that works for the peskiest stains. It's pricey, but less expensive than hiring a professional cleaning service. The managers at Dalias are conducting variance analysis at the end of January, the first month of the new fiscal year. The company's standards for one gallon of cleaning solution are as follows, along with actual information for the month. DM DL Standard Quantity per Unit Actual results for January: 5 gallons of solution 3 DL hours 22,000 gallons were produced Cost of DM purchased was $226,800 DM used in production was 10,800 Standard Price Cost of DL was $122,500 for 7,000 DL hours worked Required: $20.00 per gallon $18.00 per DL hour Compute the following variances: Figure your answers below and record your final answer in the space provided. Materials price variance: Favorable or Unfavorable 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


