Question: (Adapted from Exercise 44 of Chapter 2 from Programming Languages: Build, Prove, Compare (p. 210).) Recall the DEFINEOLDGLOBAL and DEFINENEWGLOBAL rules from the operational semantics
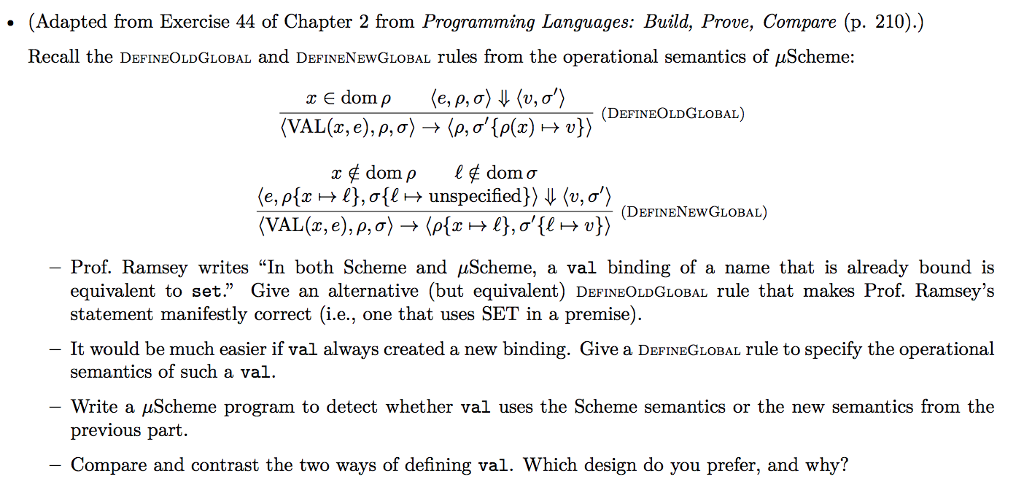
(Adapted from Exercise 44 of Chapter 2 from Programming Languages: Build, Prove, Compare (p. 210).) Recall the DEFINEOLDGLOBAL and DEFINENEWGLOBAL rules from the operational semantics of uScheme: I E dom p (e, p, o) 1 (v, o') (DEFINEOLDGLOBAL) (VAL(x, e), p,o) + (p, o'{p(x) + v}) x dom pl # dom o (e, p{x + l},0{l unspecified}} W (v, o'). (DEFINENEWGLOBAL) (VAL(x, e), P,0) + ({x + l},o'{l + 1}} - Prof. Ramsey writes In both Scheme and puScheme, a val binding of a name that is already bound is equivalent to set Give an alternative (but equivalent) DEFINEOLDGLOBAL rule that makes Prof. Ramsey's statement manifestly correct (i.e., one that uses SET in a premise). - It would be much easier if val always created a new binding. Give a DEFINEGLOBAL rule to specify the operational semantics of such a val. Write a uScheme program to detect whether val uses the Scheme semantics or the new semantics from the previous part. Compare and contrast the two ways of defining val. Which design do you prefer, and why? (Adapted from Exercise 44 of Chapter 2 from Programming Languages: Build, Prove, Compare (p. 210).) Recall the DEFINEOLDGLOBAL and DEFINENEWGLOBAL rules from the operational semantics of uScheme: I E dom p (e, p, o) 1 (v, o') (DEFINEOLDGLOBAL) (VAL(x, e), p,o) + (p, o'{p(x) + v}) x dom pl # dom o (e, p{x + l},0{l unspecified}} W (v, o'). (DEFINENEWGLOBAL) (VAL(x, e), P,0) + ({x + l},o'{l + 1}} - Prof. Ramsey writes In both Scheme and puScheme, a val binding of a name that is already bound is equivalent to set Give an alternative (but equivalent) DEFINEOLDGLOBAL rule that makes Prof. Ramsey's statement manifestly correct (i.e., one that uses SET in a premise). - It would be much easier if val always created a new binding. Give a DEFINEGLOBAL rule to specify the operational semantics of such a val. Write a uScheme program to detect whether val uses the Scheme semantics or the new semantics from the previous part. Compare and contrast the two ways of defining val. Which design do you prefer, and why
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


