Question: Add suitable code to the code below and then run it Run the provided code first, to load the required function and data into memory,
Add suitable code to the code below and then run it
Run the provided code first, to load the required function and data into memory, then do the calculation in the interactive Python shell.
Feel free to choose the approach you prefer.
Figure 1 charts data about the highest points, i.e. the points with the highest altitudes above sea level, in each of 56 European countries (Wikipedia, 2017).
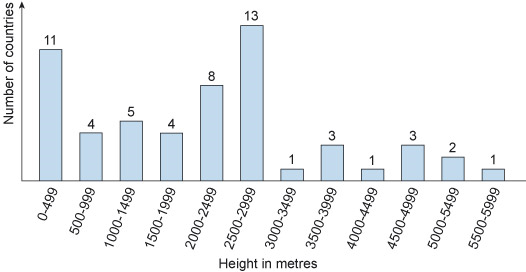
Give the median, correct to the nearest whole number. Also copy and paste the Python code you used and briefly (in one or two sentences) explain how you ran it.
For this list of data the mean is 2185, which is smaller than the median. From looking at Figure 1 briefly suggest a possible reason.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- INITIAL CODE -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Heighest point of 56 European countries, in metres. 08/10/2017 """
from data_stats import median
heights = [2764,2942,3798,4466,345,694,2386,2925,1831,1952,1603,3694,171,318,1324,4810,5201,2962,2919,1014,2110,4810,2658,2656,312,2599,294,560,253,430,163,2534,887,321,2469,2499,2351,1993,1041,2764,2544,5642,749,2169,2655,2864,3718,3479,2104,4634,347,5137,1031,2061,1344,75]
""" You can use one of two approaches -- add suitable code below and then run this file -- run this file first then do the calculation in the Python interactive shell. """
----------------------------------------------------
PROVIDED CODE ----------------------------------------------------
import math
def median(alist): """ Calculates the median of a list of numbers. The list must not be empty. """
number_of_values = len(alist) sorted_list = sorted(alist)
# Two cases, depending on whether the number of values is odd or even. quotient = number_of_values // 2 remainder = number_of_values % 2 if (remainder == 1): result = sorted_list[quotient] else: result = (sorted_list[quotient - 1] + sorted_list[quotient]) / 2 return result def test_median(): assert median([2]) == 2 assert median([4, 3]) == 3.5 assert median([3, 1, 8, 4, 7, 6, 4, 2, 5, 9]) == 4.5 assert median([7, 2, 6, 2, 5, 3, 1, 0, 8, 6, 6, 4, 9]) == 5
# Unit test test_median()
def mean(list): """Return mean of list""" sum = 0 count = 0 for item in list: sum = sum + item count = count + 1 return sum / count
def test_mean(): list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] assert(mean(list) == 3) # Unit test test_mean()
def corr_coef(list_x, list_y): """ Return correlation between values in list_x and list_y.
Lists must be of equal length. """ x_bar = mean(list_x) y_bar = mean(list_y) sxy = 0 sxx = 0 syy = 0 for index in range(len(list_x)): x = list_x[index] y = list_y[index] sxy = sxy + (x - x_bar) * (y - y_bar) sxx = sxx + (x - x_bar) * (x - x_bar) syy = syy + (y - y_bar) * (y - y_bar) return sxy / math.sqrt(sxx * syy)
def test_corr_coef(): # Data from M140 Unit 9 Example 5 list1 = [78.9, 75.8, 77.3, 74.2, 78.1, 72.8, 77.6, 77.9] list2 = [56.7, 53.1, 56.1, 55.9, 54.1, 48.6, 59.4, 54.0] assert round(corr_coef(list1, list2), 2) == 0.64 # Unit test test_corr_coef()
Number of countries 0-499 500-999 1000-1499 1500-1999 2000-2499 2500-2999 3000-3499 3500-3999 4000-4499 4500-4999 5000-5499 5500-5999
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


