Question: advance computer architecture: a quantitative approach 6th E. Ch1 CS6 1.6 [0/00/10/10/201 General-purpose processes are optimized for general-purpose computing. That is, they are optimized for


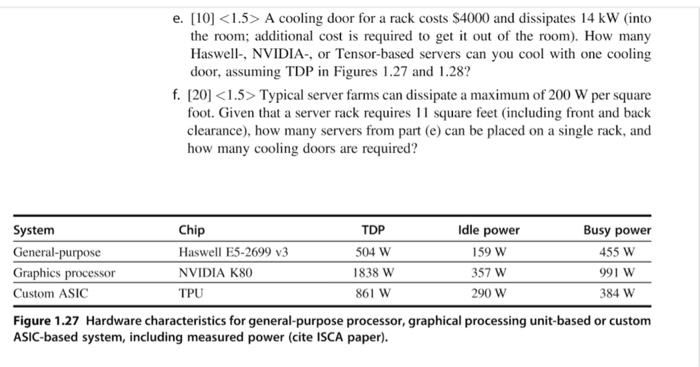
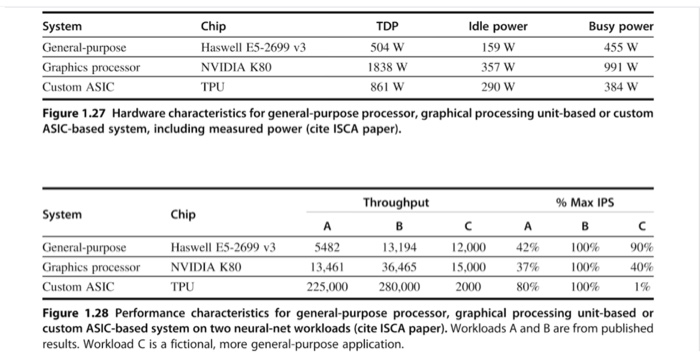
1.6 [0/00/10/10/201 General-purpose processes are optimized for general-purpose computing. That is, they are optimized for behavior that is gener- ally found across a large number of applications. However, once the domain is restricted somewhat, the behavior that is found across a large number of the target applications may be different from general-purpose applications. One such appli cation is deep learning or neural networks. Deep learning can be applied to many different applications, but the fundamental building block of inference-using the learned information to make decisions-is the same across them all. Inference operations are largely parallel, so they are currently performed on graphics proces- sing units, which are specialized more toward this type of computation, and not to inference in particular. In a quest for more performance per watt, Google has cre- ated a custom chip using tensor processing units to accelerate inference operations in deep learning. This approach can be used for speech recognition and image recognition, for example. This problem explores the trade-offs between this pro- cess, a general-purpose processor (Haswell E5-2699 v3) and a GPU (NVIDIA K80), in terms of performance and cooling. If heat is not removed from the com- puter efficiently, the fans will blow hot air back onto the computer, not cold air Note: The differences are more than processor-on-chip memory and DRAM also come into play. Therefore statistics are at a system level, not a chip level
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


