Question: Adverse Selection Insurance Model: (Challenging) Again consider the insurance model of adverse selection described in class. Suppose that consumers types have a density f(1) =
Adverse Selection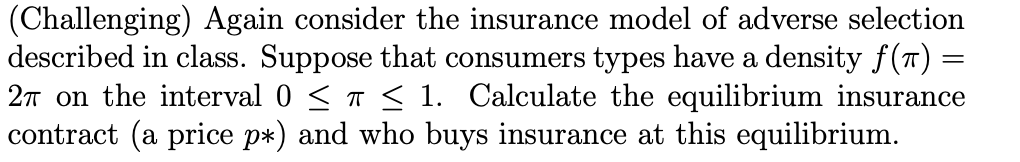
Insurance Model:


(Challenging) Again consider the insurance model of adverse selection described in class. Suppose that consumers types have a density f(1) = 27 on the interval 0 h(P) = 1- (1-(P/W) 1/2 1-(1-(L/w))1/2 Whether individuals buy or not also depends on the price: P=0 then h(P)=0/(1-(1-(L/w))1/2) everyone buys When P=L then h(P)=1. no-one buys. Price is determined by the average riskiness of a customer. Profit from an average customer = P-L[1+h(P)]/2 Perfect competition gives zero profit L[1+h(P)]/2 P=0 or L[1+h(P)]/2 =P Expected Cost = Revenue This is the equation we will solve to find the equilibrium. (Challenging) Again consider the insurance model of adverse selection described in class. Suppose that consumers types have a density f(1) = 27 on the interval 0 h(P) = 1- (1-(P/W) 1/2 1-(1-(L/w))1/2 Whether individuals buy or not also depends on the price: P=0 then h(P)=0/(1-(1-(L/w))1/2) everyone buys When P=L then h(P)=1. no-one buys. Price is determined by the average riskiness of a customer. Profit from an average customer = P-L[1+h(P)]/2 Perfect competition gives zero profit L[1+h(P)]/2 P=0 or L[1+h(P)]/2 =P Expected Cost = Revenue This is the equation we will solve to find the equilibrium
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


