Question: Algebraic Problem - Addressing Negative Externalities A refinery produces one unit of waste for each unit of refined product. The firm disposes of the waste
Algebraic Problem - Addressing Negative Externalities
A refinery produces one unit of waste for each unit of refined product. The firm disposes of the waste in the nearby lake. The inverse demand curve for the refined product (which is also the private marginal benefit curve PMB) is Pd = 24 - Q, where Q is the quantity consumed when the price consumers pay is Pd. The inverse supply curve (also the private marginal cost curve) for refining is PMC = 2 + Q, where PMC is the private marginal cost when the industry produces Q units. The marginal external cost is MEC = 0.5Q, where MEC is the marginal external cost when the refinery releases Q units of waste.
(i) Solve for the private market equilibrium (insert price and quantity combination).
(ii) Obtain the socially efficient equilibrium (insert new price and quantity combination).
(iii) What is the value of the deadweight loss from the negative externality (in $)?
(iv) Find the (Pigouvian) per-unit carbon tax $ that should be imposed to erase the negative externality, i.e. shift the equilibrium from the privately optimal to the socially efficient one.
HINT:
The graph below shows the marginal social cost, marginal private cost/market supply, marginal external cost and demand curves of chemical manufacturer emitting pollution.
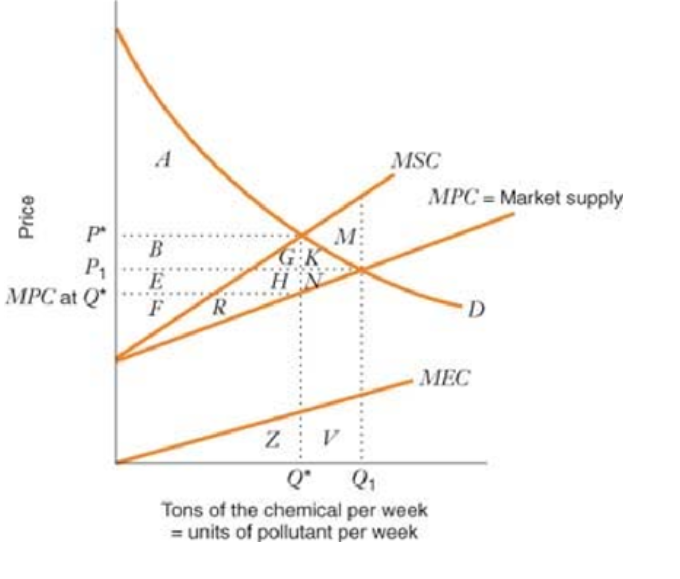
A MSC MPC = Market supply Price M B H N MPC at Q R D . ....... ............... MEC Z ...... Q" Q1 Tons of the chemical per week = units of pollutant per week
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


