Question: Algorithm 1.1 Sequential Search Problem: Is the kay in the stay 5 of ra ksys? inputs (paransis): positive intega 12, array of keys S indazed
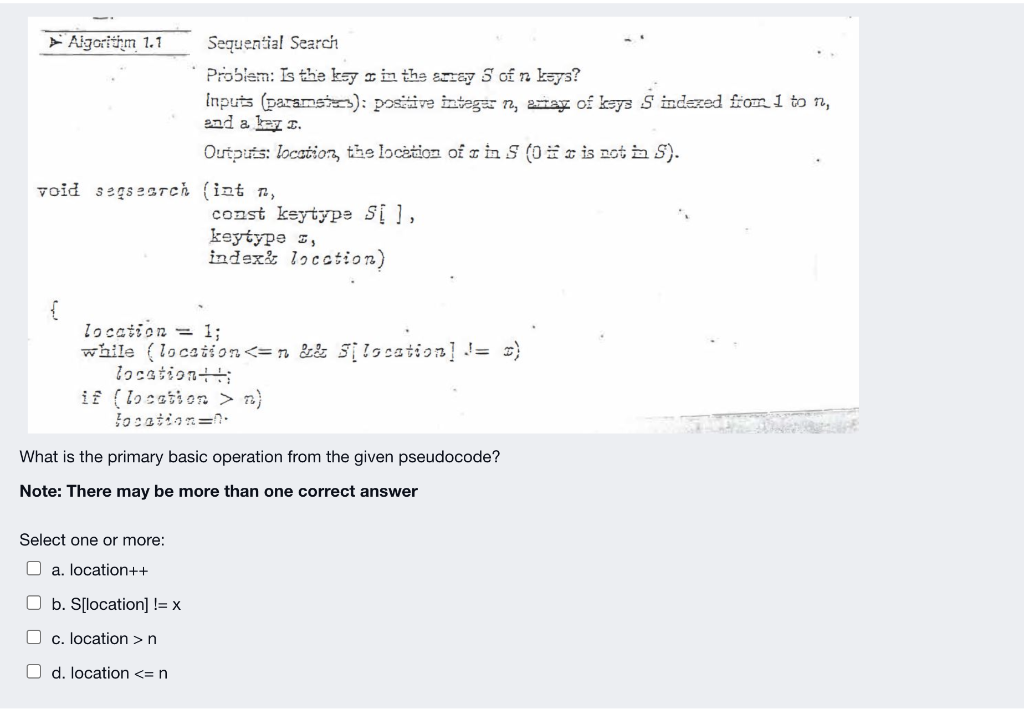
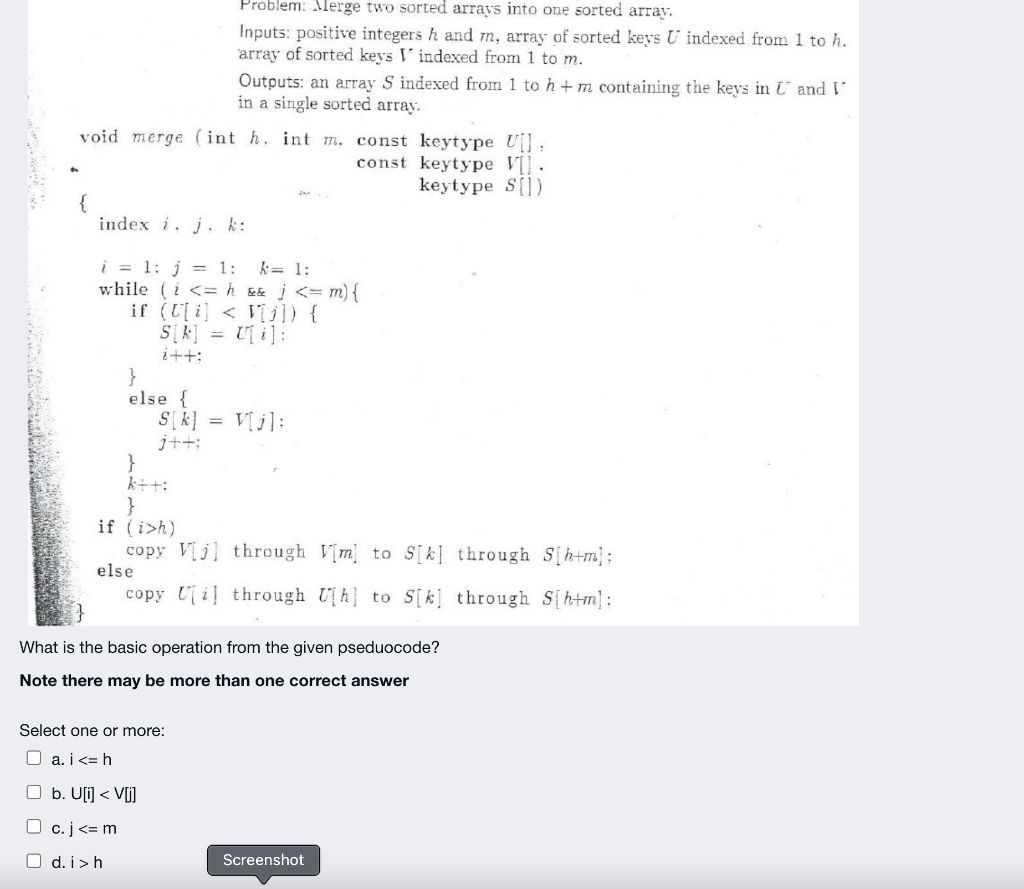
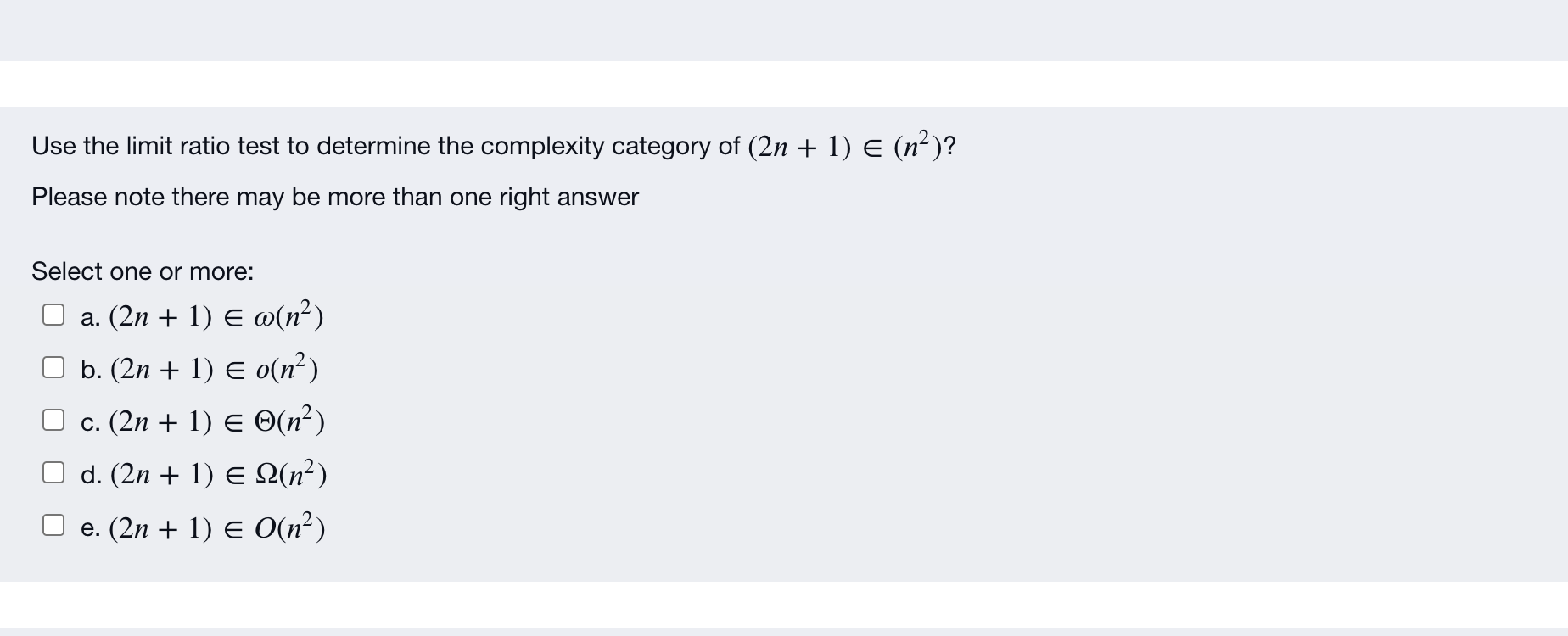
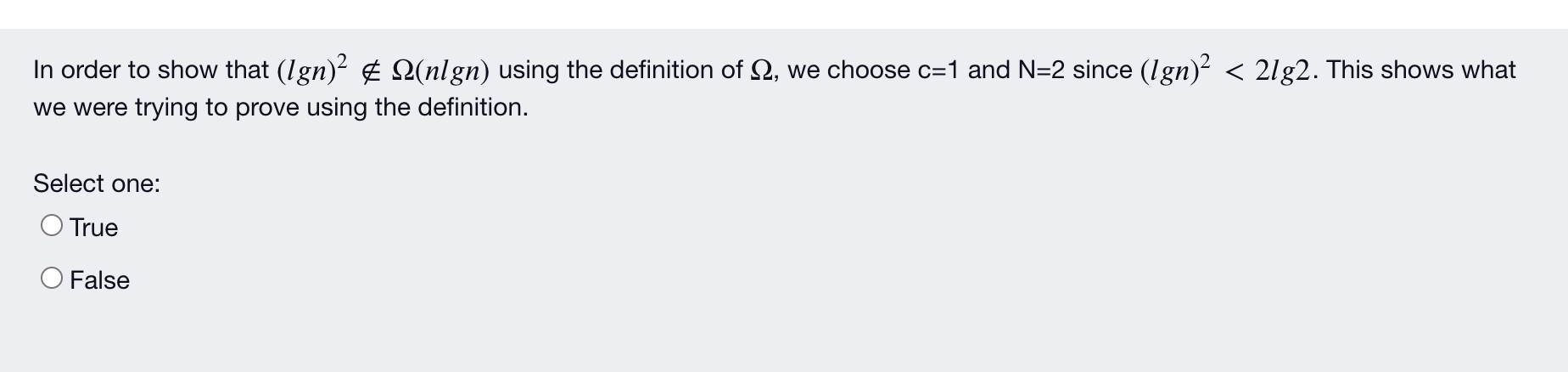
Algorithm 1.1 Sequential Search Problem: Is the kay in the stay 5 of ra ksys? inputs (paransis): positive intega 12, array of keys S indazed from 1 to no, and a STI. Outputs: location, the loction of in s (0*x is not 5). void seasestch (izt tay coast ksytype S l, keytype , index: locations) { location = 1; while (location 2) location=1 What is the primary basic operation from the given pseudocode? Note: There may be more than one correct answer Select one or more: O a. location++ b. S[location] != x O c. location >n O d. location h) copy V[j] through Vim to Sikl through S[h+m); else copy lil through th] to S[k] through S[htm: What is the basic operation from the given pseduocode? Note there may be more than one correct answer Select one or more: O a. i h Screenshot Use the limit ratio test to determine the complexity category of (2n + 1) (n?)? Please note there may be more than one right answer Select one or more: a. (2n + 1) E @(na) b. (2n + 1) E 0(n?) c. (2n + 1) = O(n) d. (2n + 1) E 12(n) e. (2n + 1) = O(na) In order to show that (Ign)2 2(nlgn) using the definition of 12, we choose c=1 and N=2 since (Ign)2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


