Question: algorithm for Part b 2. Write a code to solve Az b by the Gaussian elimination plus the backward substitution (a) Write a MATLAB function
algorithm for Part b
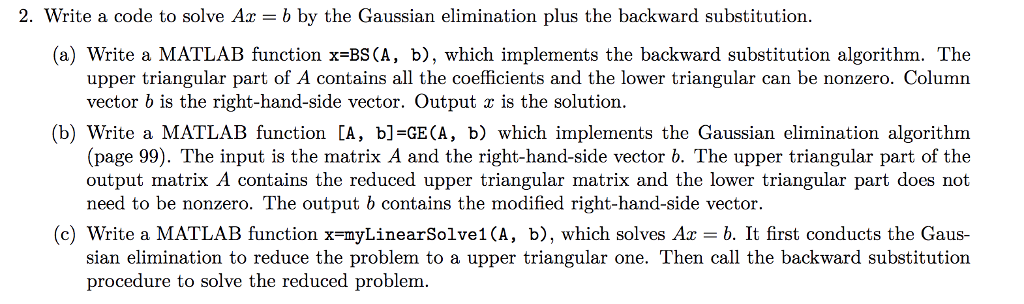
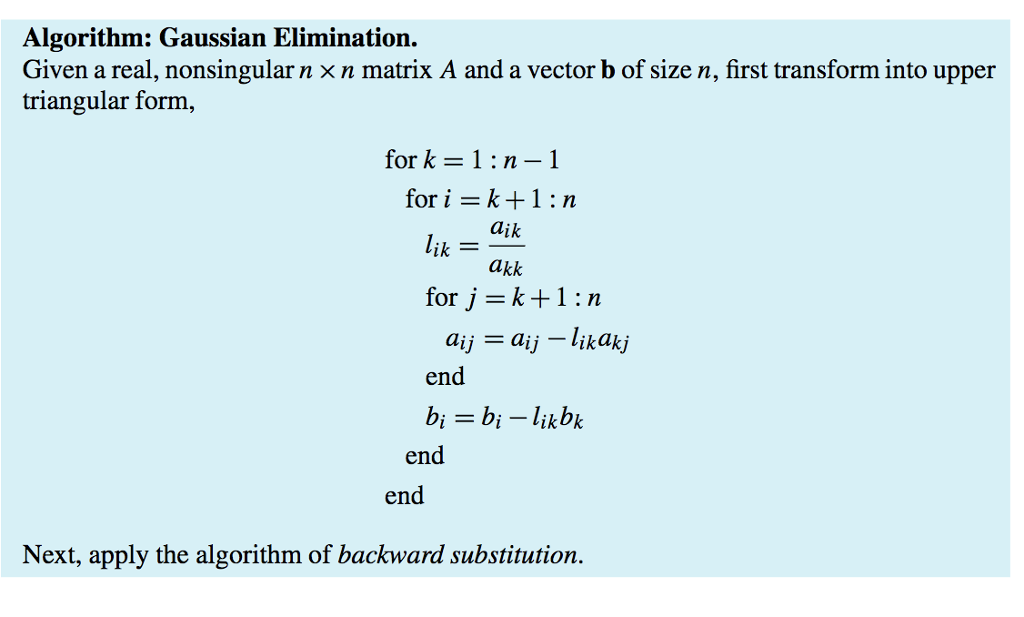
2. Write a code to solve Az b by the Gaussian elimination plus the backward substitution (a) Write a MATLAB function x-BS(A, b), which implements the backward substitution algorithm. The upper triangular part of A contains all the coefficients and the lower triangular can be nonzero. Column vector b is the right-hand-side vector. Output x is the solution. (b) Write a MATLAB function [A, b]=GE (A, b) which implernents the Gaussian elimination algorithm (page 99). The input is the matrix A and the right-hand-side vector b. The upper triangular part of the output matrix A contains the reduced upper triangular matrix and the lower triangular part does not need to be nonzero. The output b contains the modified right-hand-side vector. (c) Write a MATLAB function x=myLinearSolve1(A, b), which solves Ax b. It first conducts the Gaus- sian elimination to reduce the problem to a upper triangular one. Then call the backward substitution procedure to solve the reduced problem. 2. Write a code to solve Az b by the Gaussian elimination plus the backward substitution (a) Write a MATLAB function x-BS(A, b), which implements the backward substitution algorithm. The upper triangular part of A contains all the coefficients and the lower triangular can be nonzero. Column vector b is the right-hand-side vector. Output x is the solution. (b) Write a MATLAB function [A, b]=GE (A, b) which implernents the Gaussian elimination algorithm (page 99). The input is the matrix A and the right-hand-side vector b. The upper triangular part of the output matrix A contains the reduced upper triangular matrix and the lower triangular part does not need to be nonzero. The output b contains the modified right-hand-side vector. (c) Write a MATLAB function x=myLinearSolve1(A, b), which solves Ax b. It first conducts the Gaus- sian elimination to reduce the problem to a upper triangular one. Then call the backward substitution procedure to solve the reduced
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


