Question: alpha 65 beta -0.1 lambda 20 PS = 1Q delta 0.05 Equilibrium Condition: Pd = PS, thus Qe In (a) + pin(Q,) = In(2) +8In(2,)
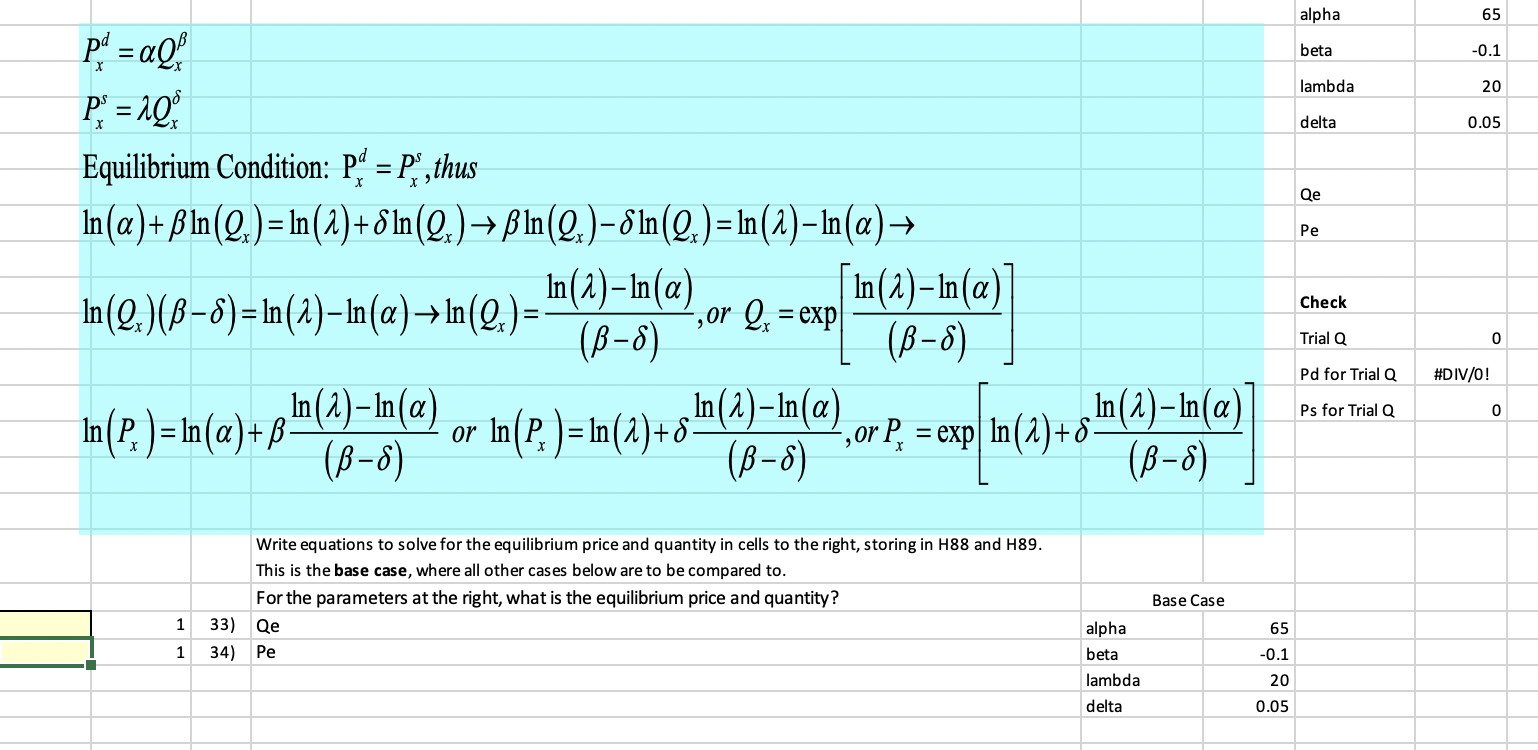
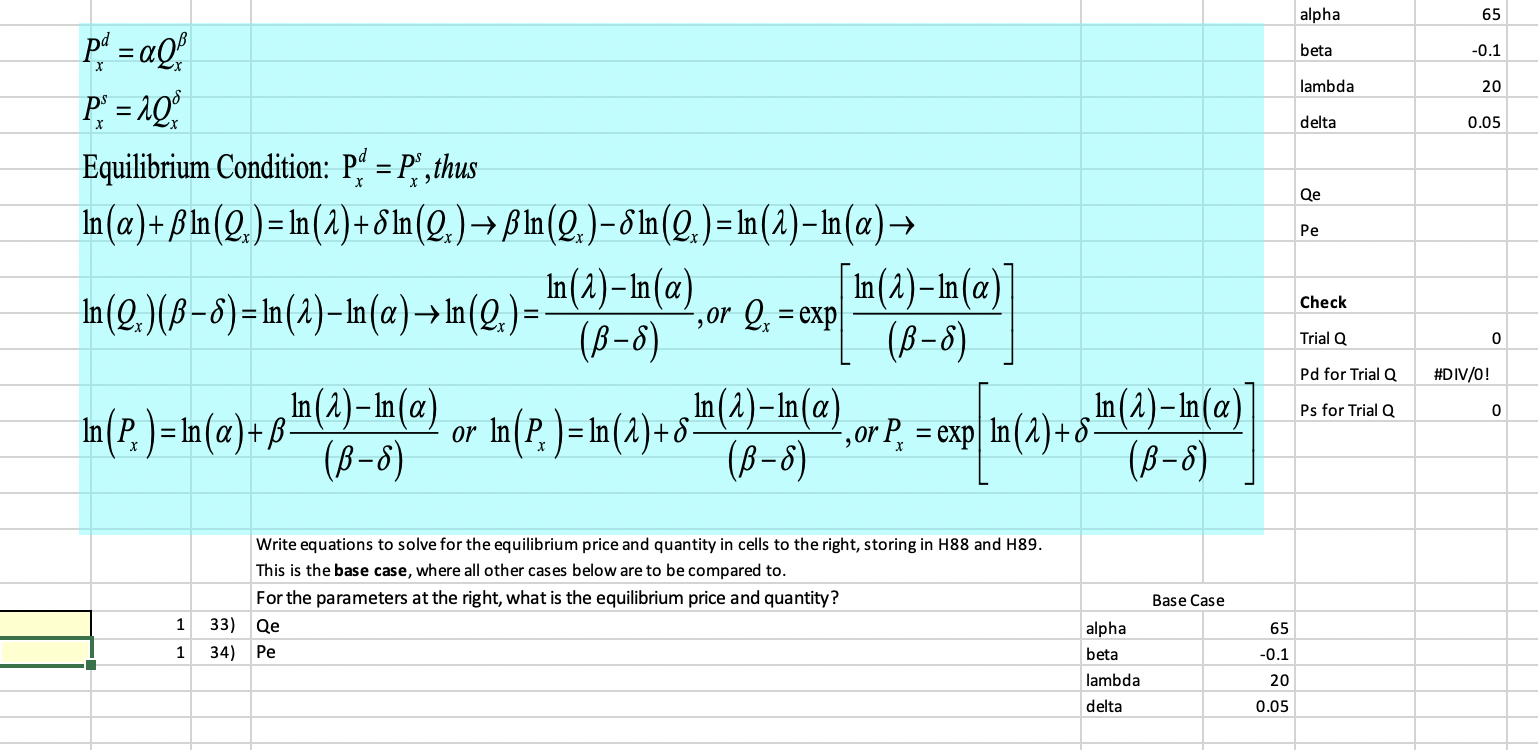
alpha 65 beta -0.1 lambda 20 PS = 1Q delta 0.05 Equilibrium Condition: Pd = PS, thus Qe In (a) + pin(Q,) = In(2) +8In(2,) -> Bin(2)-8In(2) = In(2)-In(a)-> Pe In(Q.) (B -8) = In(2)-In(a) -> In(Q ) = In (2) - In (o) ,or 2x = exp In (1) -In (a ) Check (B-8) (B -8) Trial Q 0 Pd for Trial Q #DIV/O! In (2) -In (a) or In (P )= In (2) +8 In (2) -In(a) Ps for Trial Q 0 In P. = In(a)+ B (B-8) , or P. = exp In (2) +8 In (2) -In(a) ( B-8) ( B-8) Write equations to solve for the equilibrium price and quantity in cells to the right, storing in H88 and H89. This is the base case, where all other cases below are to be compared to. For the parameters at the right, what is the equilibrium price and quantity? Base Case 1 33) Qe alpha 65 1 34) Pe beta -0.1 lambda 20 delta 0.05
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


