Question: Ammonia, N H 3 , is being selectively removed from an air - N H 3 mixture by absorption into water. In this steady -
Ammonia, is being selectively removed from an air
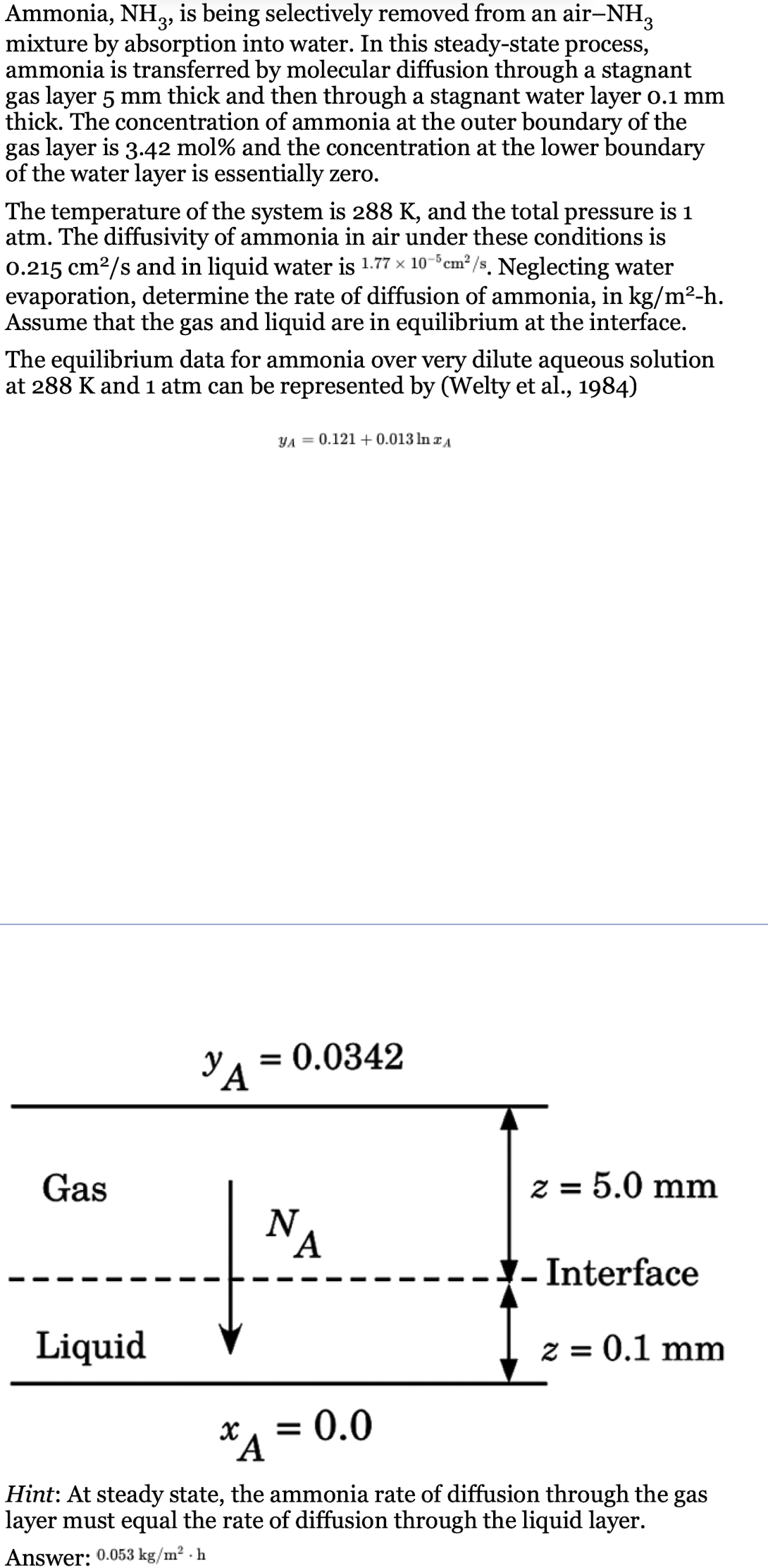
mixture by absorption into water. In this steadystate process,
ammonia is transferred by molecular diffusion through a stagnant
gas layer thick and then through a stagnant water layer
thick. The concentration of ammonia at the outer boundary of the
gas layer is mol and the concentration at the lower boundary
of the water layer is essentially zero.
The temperature of the system is and the total pressure is
atm. The diffusivity of ammonia in air under these conditions is
and in liquid water is Neglecting water
evaporation, determine the rate of diffusion of ammonia, in
Assume that the gas and liquid are in equilibrium at the interface.
The equilibrium data for ammonia over very dilute aqueous solution
at and atm can be represented by Welty et al
Hint: At steady state, the ammonia rate of diffusion through the gas
layer must equal the rate of diffusion through the liquid layer.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


