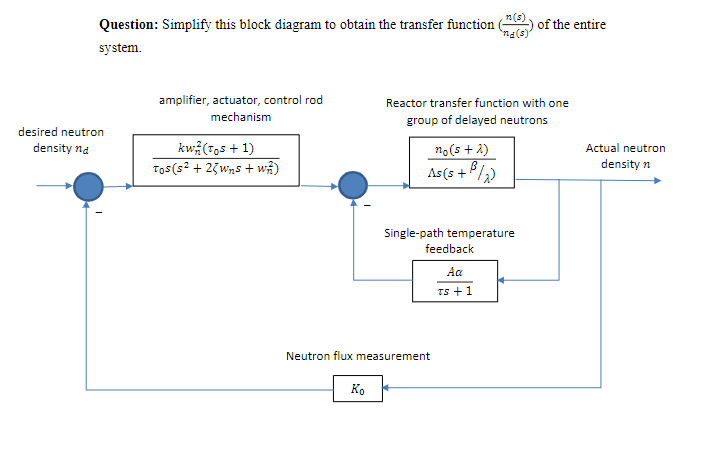
Question: amplifier, actuator, control rod Reactor transfer function with on A simplified block diagram is shown below, for a reactor with a single - path temperature
amplifier, actuator, control rod
Reactor transfer function with on
A simplified block diagram is shown below, for a reactor with a singlepath temperature
feedback loop, together with the amplifier, actuator, control rod mechanism and the neutron
flux measurement device.
In this block diagram, the reactor transfer function with one group of delayed neutrons, and
the transfer function for singlepath temperature feedback were derived in the class. The
transfer function for the amplifier, actuator, control rod mechanism is used because it is an
excellent approximation of some of the practical servo systems now used in reactor control
systems, and a quadratic form of this should closely approximate the behavior of almost
any type of physical equipment which might be chosen to drive a control rod.
The meaning of the symbols in the block diagram is as below:
k : gain
wnpi fn
fn : undamped natural resonant frequency of control rod servo system
zeta : damping ratio of servo system
A : a constant depending on power level, moderator and coolant
alpha : lumped temperature coefficient
tau : time constant dependent upon mass and specific heat capacity of the moderator
K : proportional gain of the neutron flux detector
n : original neutron density
lambda : precursor decay constant
Lambda lkeff
l : effective time between succeeding generations
keffDelta nn
n :neutron density
B : fraction of delayed neutrons
Question: Simplify this block diagram to obtain the transfer function nsnds of the entire system.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


