Question: An agent has preferences defined over a consumption good and leisure. His utility functionis U=(c y )2 I, where c is the amount of consumption
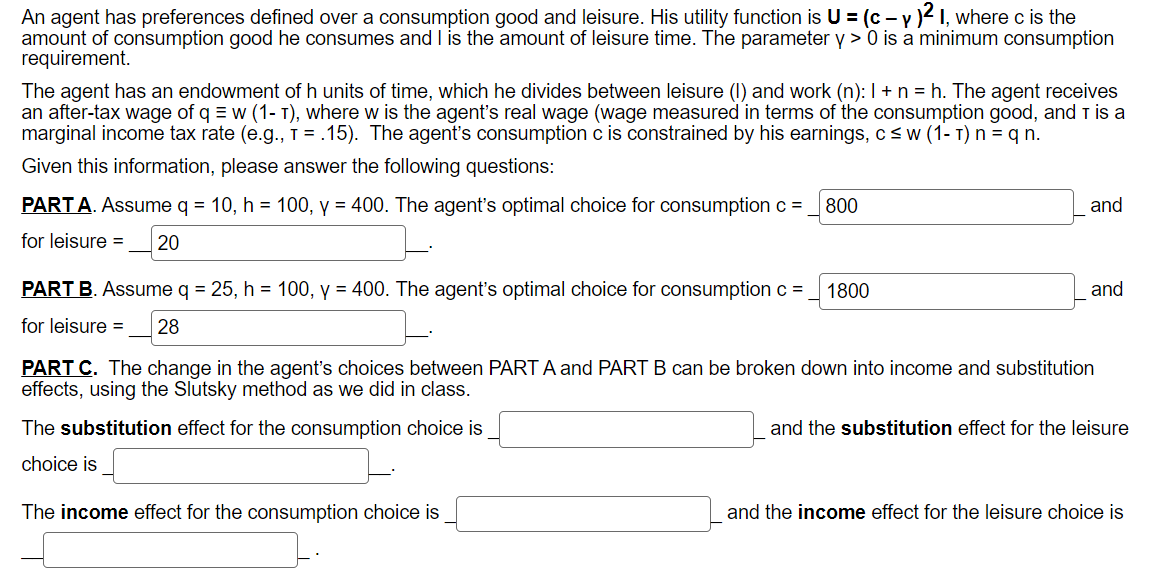
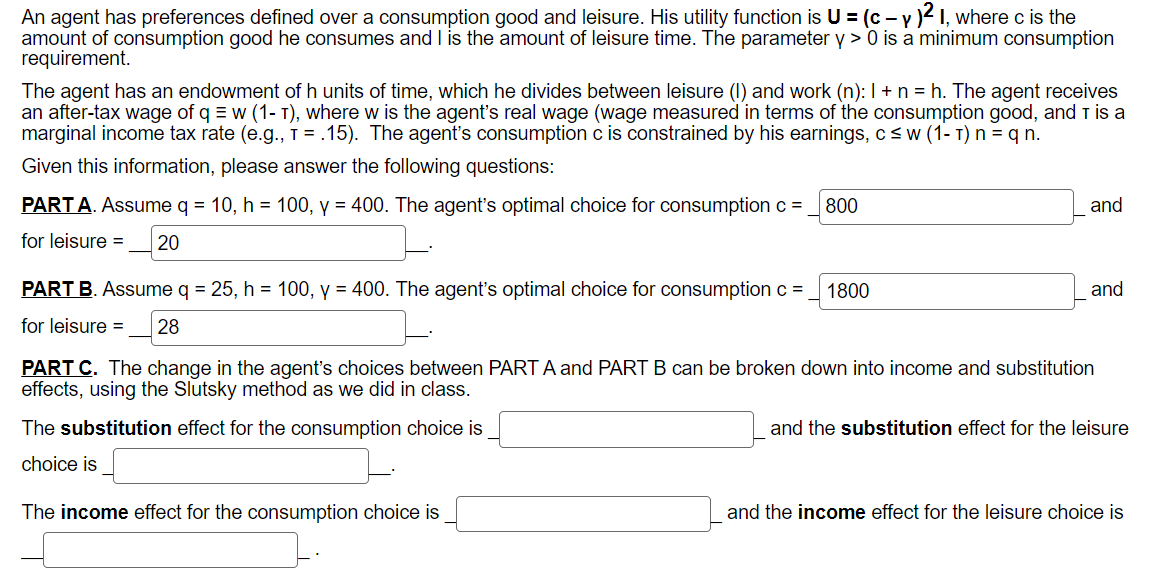
An agent has preferences defined over a consumption good and leisure. His utility functionis U=(c y )2 I, where c is the amount of consumption good he consumes and | is the amount of leisure time. The parameter y > 0 is a minimum consumption requirement. The agent has an endowment of h units of time, which he divides between leisure (1) and work (n): | + n = h. The agent receives an after-tax wage of g = w (1- 1), where w is the agent's real wage (wage measured in terms of the consumption good, and Tis a marginal income tax rate (e.g., T = .15). The agent's consumption c is constrained by his earnings, csw (1-1)n=qn. Given this information, please answer the following questions: PARTA. Assume q = 10, h =100, y = 400. The agent's optimal choice for consumption = for leisure = | 20 L PART B. Assume q = 25, h = 100, y = 400. The agent's optimal choice for consumption = for leisure = _|28 | 800 (1800 | and | and PART C. The change in the agent's choices between PART A and PART B can be broken down into income and substitution effects, using the Slutsky method as we did in class. The substitution effect for the consumption choice is J choice is J B The income effect for the consumption choice is J = 3 L and the substitution effect for the leisure L and the income effect for the leisure choice is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


