Question: An engineering project requires a temporary excavation through an existing clay embankment. The proposed excavation will be 5 m wide and 6 . 5 m
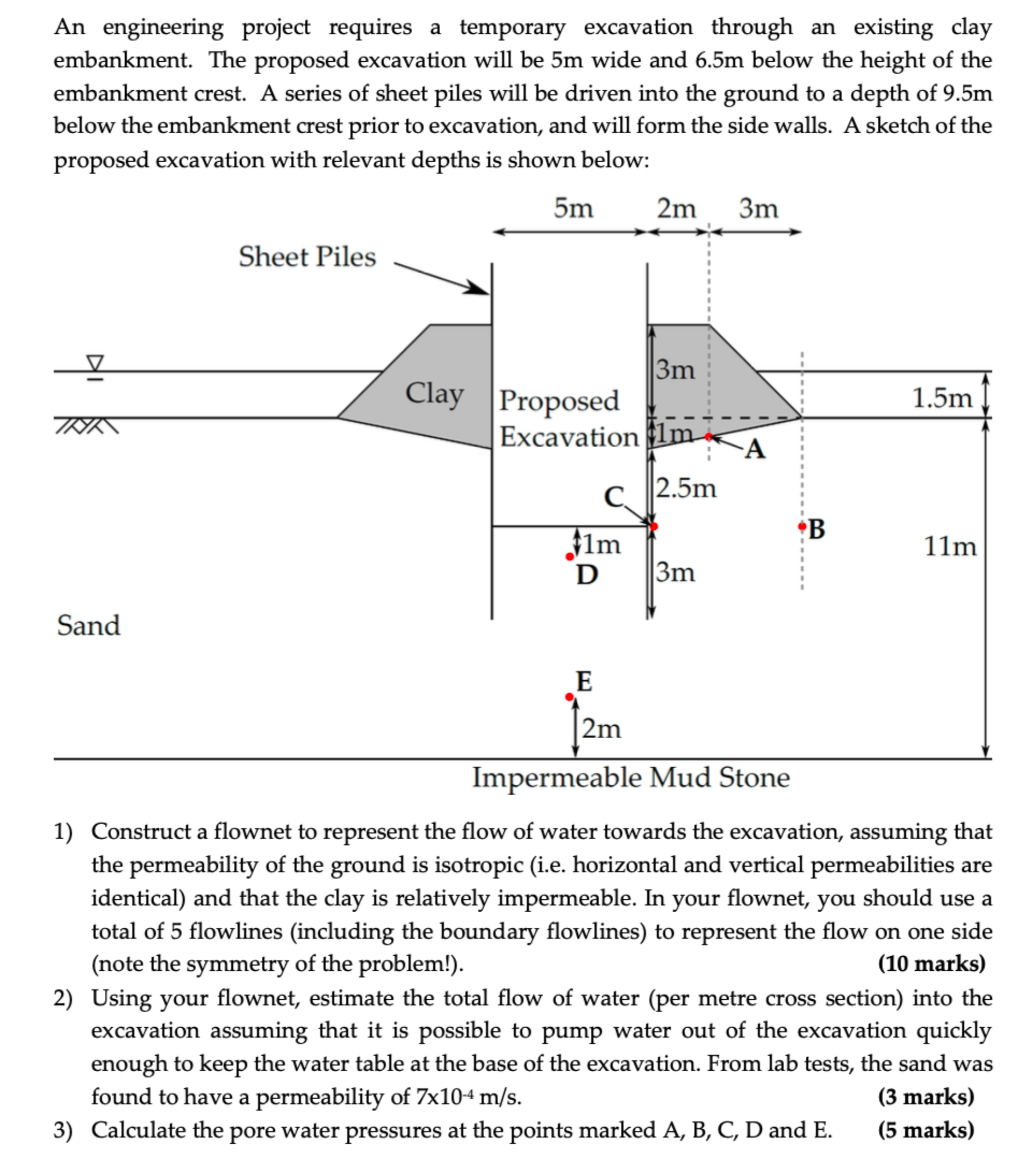
An engineering project requires a temporary excavation through an existing clay
embankment. The proposed excavation will be m wide and m below the height of the
embankment crest. A series of sheet piles will be driven into the ground to a depth of m
below the embankment crest prior to excavation, and will form the side walls. A sketch of the
proposed excavation with relevant depths is shown below:
Sand
Impermeable Mud Stone
Construct a flownet to represent the flow of water towards the excavation, assuming that
the permeability of the ground is isotropic ie horizontal and vertical permeabilities are
identical and that the clay is relatively impermeable. In your flownet, you should use a
total of flowlines including the boundary flowlines to represent the flow on one side
note the symmetry of the problem!
Using your flownet, estimate the total flow of water per metre cross section into the
excavation assuming that it is possible to pump water out of the excavation quickly
enough to keep the water table at the base of the excavation. From lab tests, the sand was
found to have a permeability of
Calculate the pore water pressures at the points marked A B C D and E
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


