Question: An error in a BST implementation may result in a variety of problems. Ex: Key - related problems include: - A node ( X
An error in a BST implementation may result in a variety of problems. Ex: Keyrelated problems include:
A node X in in the left subtree of ancestor Y with X s key Ys key
A node X in in the right subtree of ancestor Y with X s key Y s key
Childrelated problems include:
A node that is a child of two or more distinct nodes
A child pointer that points to an ancestor
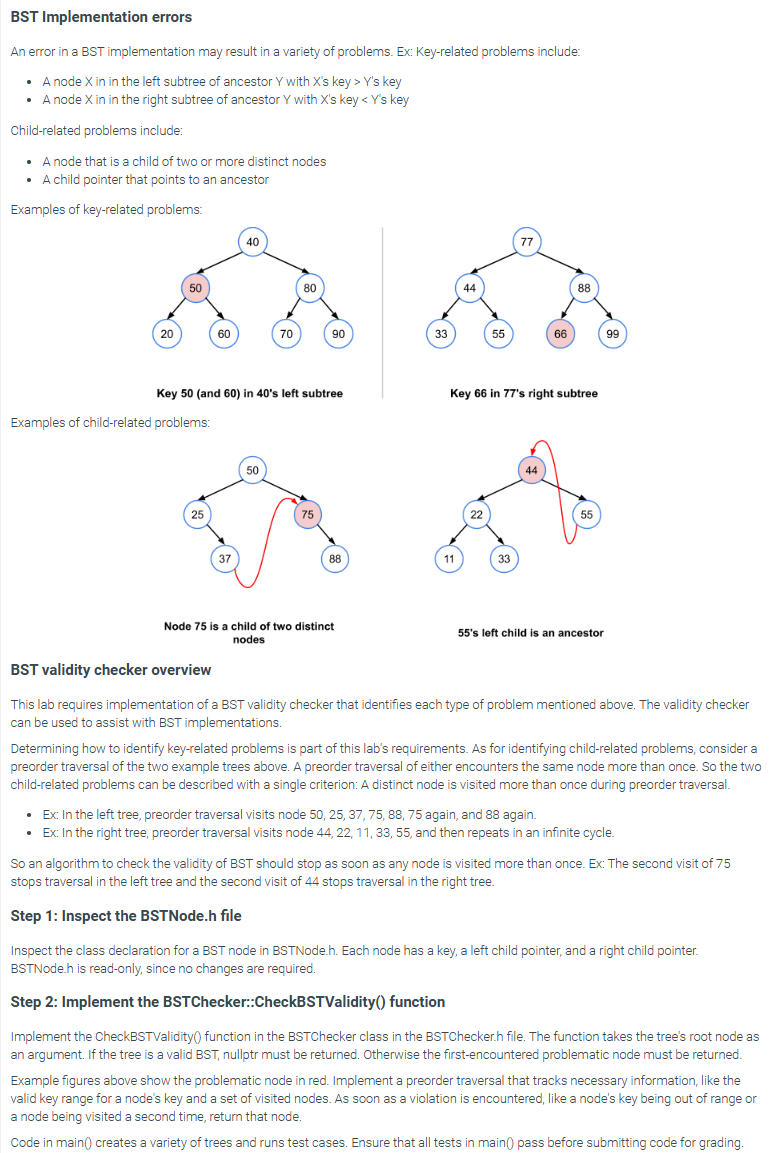
Examples of keyrelated problems:
Key mathbfand in s left subtree
Examples of childrelated problems:
Key in s right subtree
s left child is an ancestor
BST validity checker overview
This lab requires implementation of a BST validity checker that identifies each type of problem mentioned above. The validity checker can be used to assist with BST implementations.
Determining how to identify keyrelated problems is part of this lab's requirements. As for identifying childrelated problems, consider a preorder traversal of the two example trees above. A preorder traversal of either encounters the same node more than once. So the two childrelated problems can be described with a single criterion: A distinct node is visited more than once during preorder traversal.
Ex: In the left tree, preorder traversal visits node again, and again.
Ex: In the right tree, preorder traversal visits node and then repeats in an infinite cycle.
So an algorithm to check the validity of BST should stop as soon as any node is visited more than once. Ex: The second visit of stops traversal in the left tree and the second visit of stops traversal in the right tree.
Step : Inspect the BSTNode.h file
Inspect the class declaration for a BST node in BSTNode.h Each node has a key, a left child pointer, and a right child pointer. BSTNode.h is readonly, since no changes are required.
Step : Implement the BSTChecker::CheckBSTValidity function
Implement the CheckBSTValidity function in the BSTChecker class in the BSTChecker.h file. The function takes the tree's root node as an argument. If the tree is a valid BST nullptr must be returned. Otherwise the firstencountered problematic node must be returned.
Example figures above show the problematic node in red. Implement a preorder traversal that tracks necessary information, like the valid key range for a node's key and a set of visited nodes. As soon as a violation is encountered, like a node's key being out of range or a node being visited a second time, return that node.
Code in main creates a variety of trees and runs test cases. Ensure that all tests in main pass before submitting code for grading.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


