Question: An ordinary differential equation with a Neumann boundary condition. Let's consider a simple diffusion and simultaneous first - order reaction in a reactor with a
An ordinary differential equation with a Neumann boundary condition.
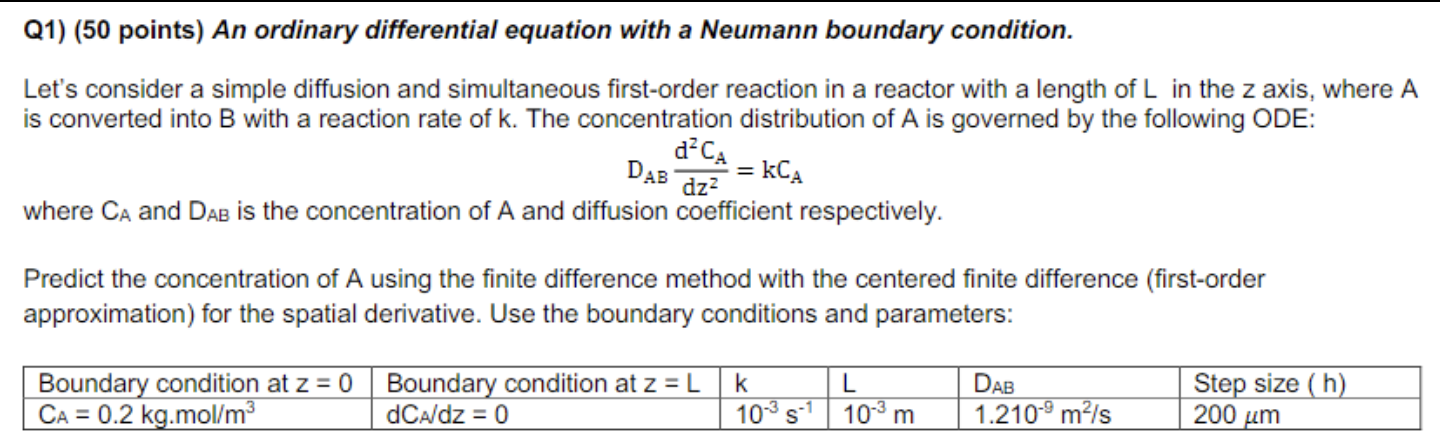
Let's consider a simple diffusion and simultaneous firstorder reaction in a reactor with a length of in the axis, where is converted into with a reaction rate of The concentration distribution of is governed by the following ODE:
where and is the concentration of A and diffusion coefficient respectively.
Predict the concentration of A using the finite difference method with the centered finite difference firstorder approximation for the spatial derivative. Use the boundary conditions and parameters:
tableBoundary condition at Boundary condition at Step size
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


