Question: Please answer all the above questions correctly providing necessary formulae, equations, expressions, diagrams, charts, graphs, tables and plots. A tubular chemical reactor (plug flow reactor
Please answer all the above questions correctly providing necessary formulae, equations, expressions, diagrams, charts, graphs, tables and plots.
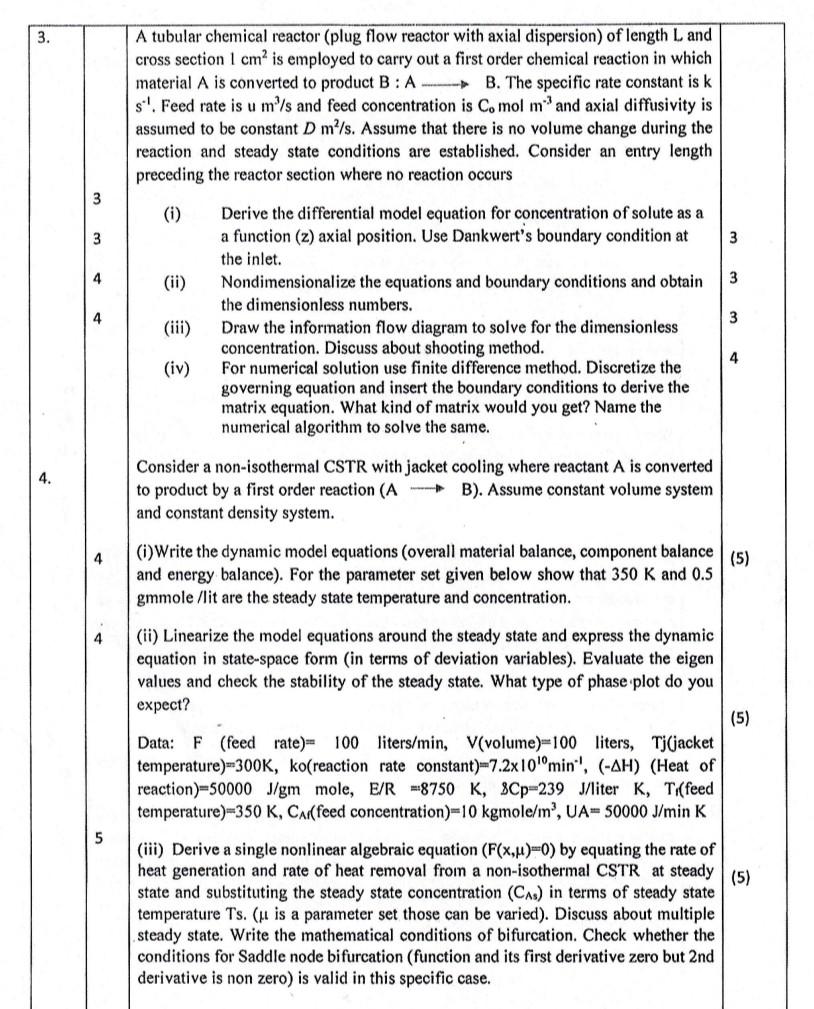
A tubular chemical reactor (plug flow reactor with axial dispersion) of length L and cross section 1cm2 is employed to carry out a first order chemical reaction in which material A is converted to product B:A B. The specific rate constant is k s1. Feed rate is um3/s and feed concentration is C0molmm3 and axial diffusivity is assumed to be constant Dm2/s. Assume that there is no volume change during the reaction and steady state conditions are established. Consider an entry length preceding the reactor section where no reaction occurs (i) Derive the differential model equation for concentration of solute as a a function (z) axial position. Use Dankwert's boundary condition at the inlet. (ii) Nondimensionalize the equations and boundary conditions and obtain the dimensionless numbers. (iii) Draw the information flow diagram to solve for the dimensionless concentration. Discuss about shooting method. (iv) For numerical solution use finite difference method. Discretize the governing equation and insert the boundary conditions to derive the matrix equation. What kind of matrix would you get? Name the numerical algorithm to solve the same. Consider a non-isothermal CSTR with jacket cooling where reactant A is converted to product by a first order reaction (AB ). Assume constant volume system and constant density system. (i) Write the dynamic model equations (overall material balance, component balance and energy balance). For the parameter set given below show that 350K and 0.5 gmmole /lit are the steady state temperature and concentration. (ii) Linearize the model equations around the steady state and express the dynamic equation in state-space form (in terms of deviation variables). Evaluate the eigen values and check the stability of the steady state. What type of phase plot do you expect? Data: F (feed rate =100 liters /min,V( volume )=100 liters, Tj (jacket temperature) =300K,ko (reaction rate constant )=7.21010min1,(H) (Heat of reaction) =50000J/gm mole, E/R=8750K,8Cp=239J/ iter K,Tif (feed temperature )=350K,CAr( feed concentration )=10kgmole/m3,UA=50000J/minK (iii) Derive a single nonlinear algebraic equation (F(x,)=0) by equating the rate of heat generation and rate of heat removal from a non-isothermal CSTR at steady state and substituting the steady state concentration (CAs) in terms of steady state temperature Ts. ( is a parameter set those can be varied). Discuss about multiple steady state. Write the mathematical conditions of bifurcation. Check whether the conditions for Saddle node bifurcation (function and its first derivative zero but 2nd derivative is non zero) is valid in this specific case. A tubular chemical reactor (plug flow reactor with axial dispersion) of length L and cross section 1cm2 is employed to carry out a first order chemical reaction in which material A is converted to product B:A B. The specific rate constant is k s1. Feed rate is um3/s and feed concentration is C0molmm3 and axial diffusivity is assumed to be constant Dm2/s. Assume that there is no volume change during the reaction and steady state conditions are established. Consider an entry length preceding the reactor section where no reaction occurs (i) Derive the differential model equation for concentration of solute as a a function (z) axial position. Use Dankwert's boundary condition at the inlet. (ii) Nondimensionalize the equations and boundary conditions and obtain the dimensionless numbers. (iii) Draw the information flow diagram to solve for the dimensionless concentration. Discuss about shooting method. (iv) For numerical solution use finite difference method. Discretize the governing equation and insert the boundary conditions to derive the matrix equation. What kind of matrix would you get? Name the numerical algorithm to solve the same. Consider a non-isothermal CSTR with jacket cooling where reactant A is converted to product by a first order reaction (AB ). Assume constant volume system and constant density system. (i) Write the dynamic model equations (overall material balance, component balance and energy balance). For the parameter set given below show that 350K and 0.5 gmmole /lit are the steady state temperature and concentration. (ii) Linearize the model equations around the steady state and express the dynamic equation in state-space form (in terms of deviation variables). Evaluate the eigen values and check the stability of the steady state. What type of phase plot do you expect? Data: F (feed rate =100 liters /min,V( volume )=100 liters, Tj (jacket temperature) =300K,ko (reaction rate constant )=7.21010min1,(H) (Heat of reaction) =50000J/gm mole, E/R=8750K,8Cp=239J/ iter K,Tif (feed temperature )=350K,CAr( feed concentration )=10kgmole/m3,UA=50000J/minK (iii) Derive a single nonlinear algebraic equation (F(x,)=0) by equating the rate of heat generation and rate of heat removal from a non-isothermal CSTR at steady state and substituting the steady state concentration (CAs) in terms of steady state temperature Ts. ( is a parameter set those can be varied). Discuss about multiple steady state. Write the mathematical conditions of bifurcation. Check whether the conditions for Saddle node bifurcation (function and its first derivative zero but 2nd derivative is non zero) is valid in this specific case
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


