Question: and this is problem 4: 5. Repeat problem 4 d) and e) using DSB-SC with d=0 if b; = 0 and d=+2 if b; =
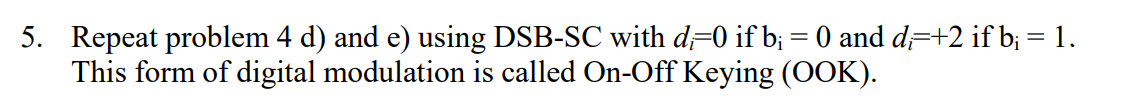 and this is problem 4:
and this is problem 4:
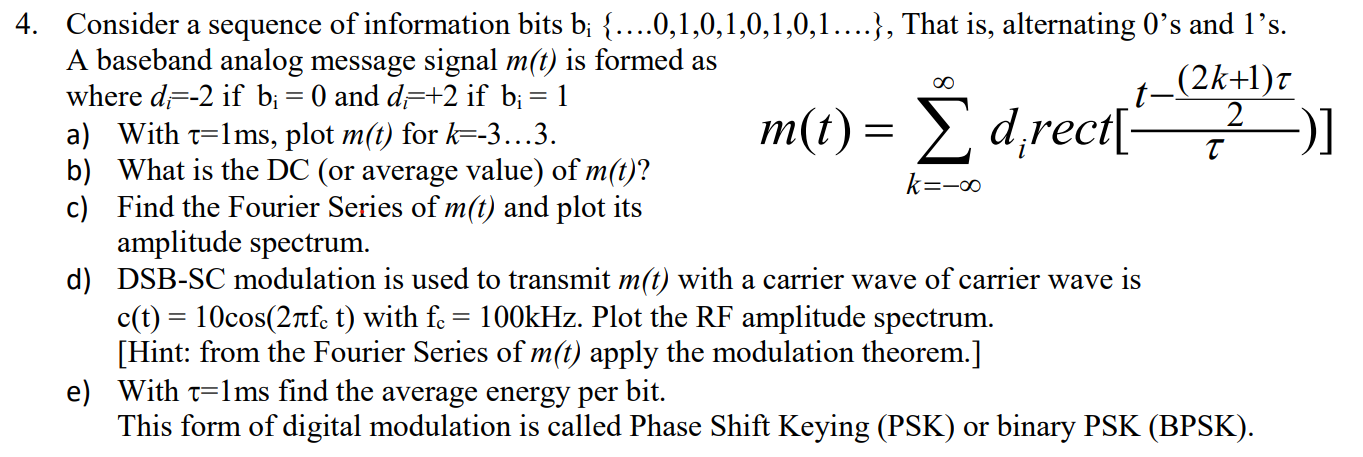
5. Repeat problem 4 d) and e) using DSB-SC with d=0 if b; = 0 and d=+2 if b; = 1. This form of digital modulation is called On-Off Keying (OOK). t-(2k+1) 2 m(t) = direct( 2) 4. Consider a sequence of information bits bi {....0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1....}, That is, alternating 0's and ls. A baseband analog message signal m(t) is formed as where d=-2 if b;= 0) and d=+2 if b; = 1 a) With t=lms, plot m(t) for k=-3...3. b) What is the DC (or average value) of m(t)? k=-00 c) Find the Fourier Series of m(t) and plot its amplitude spectrum. d) DSB-SC modulation is used to transmit m(t) with a carrier wave of carrier wave is c(t) = 10cos(21fc t) with fc = 100kHz. Plot the RF amplitude spectrum. [Hint: from the Fourier Series of m(t) apply the modulation theorem.] e) With t=lms find the average energy per bit. This form of digital modulation is called Phase Shift Keying (PSK) or binary PSK (BPSK). 5. Repeat problem 4 d) and e) using DSB-SC with d=0 if b; = 0 and d=+2 if b; = 1. This form of digital modulation is called On-Off Keying (OOK). t-(2k+1) 2 m(t) = direct( 2) 4. Consider a sequence of information bits bi {....0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1....}, That is, alternating 0's and ls. A baseband analog message signal m(t) is formed as where d=-2 if b;= 0) and d=+2 if b; = 1 a) With t=lms, plot m(t) for k=-3...3. b) What is the DC (or average value) of m(t)? k=-00 c) Find the Fourier Series of m(t) and plot its amplitude spectrum. d) DSB-SC modulation is used to transmit m(t) with a carrier wave of carrier wave is c(t) = 10cos(21fc t) with fc = 100kHz. Plot the RF amplitude spectrum. [Hint: from the Fourier Series of m(t) apply the modulation theorem.] e) With t=lms find the average energy per bit. This form of digital modulation is called Phase Shift Keying (PSK) or binary PSK (BPSK)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


