Question: Answer all.,,, 1. a. Use formula for variance os a security which return follows a single index model: o? = Boy, + o(e;)? to find:




Answer all.,,,



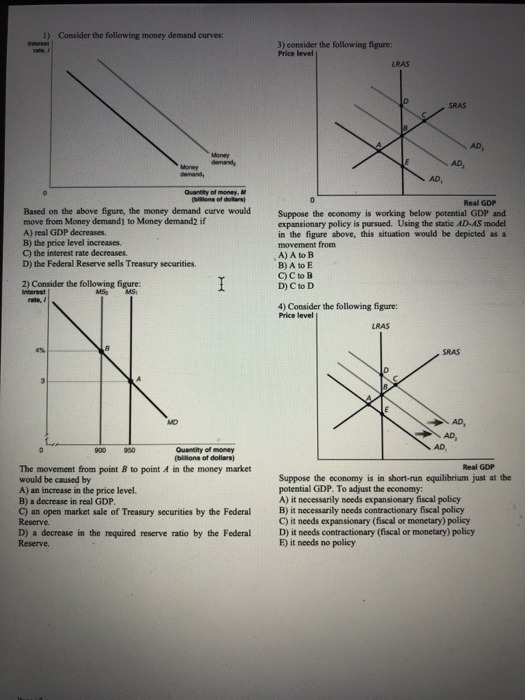

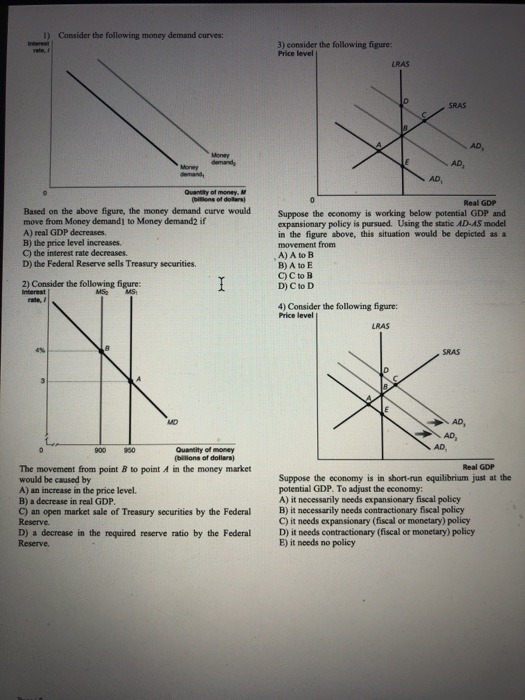
1. a. Use formula for variance os a security which return follows a single index model: o? = Boy, + o(e;)? to find: o' = 1250%%, ' = 2125%2 b. For a well-diversified portfolio which follows a single-index model the variance is given by o? = B-0%. Hence, 03 = 625%%, 0? = 900%2 E(RA) = 12.5%, E(RA) = 12% c. Slope of security A is 10, slope of security B is 8. Arbitrage strategy: short portfolio B and buy portfolio C in which wa = 1.2 and wT-bill = -.2. d. There are no arbitrage strategies since security-specific risk of A will affect any strategy which includes security A, portfolio B and T-bills.Consider a two period model, populated by a representative consumer and a govern- ment. The consumer's preferences can be described by the utility function: u(co, C1) = Vco + BVCI, where B = 0.95 captures the consumer's preference for the future. The consumer has an income yo-20 in the current period and expect a future income y1 = 25. The government plans to spend Go = 5 in the current period and G1 = 7. The interest rate is r = 10% in the economy. (a) If the government decides to impose a tax of To = 7, what will be the value of 71? (b) Is it optimal for the consumer to consume his disposable income in each period? Explain. (c) Solve the consumer's problem and find the optimal consumption in each period when r = 10%. Is the consumer a borrower or a lender? (d) Is the goods market in the equilibrium in the two periods when r = 10%? Explain. (e) What are the equilibrium values of (Co, ci) using goods market equilibrium? (f) Compute the equilibrium interest rate r*. (g) What would happen to the equilibrium interest rate if the government were to raise its expenditures in the future? (h) In the equilibrium, which income stream is more beneficial for the consumer, the initial one we started with or yo = 25 and y1 = 20?1. What does a positive linear relationship between x and y in a simple regression imply? (a) Increases in the independent variable are usually accompanied by increases in the regressor (b) The relationship between x and y cannot be explained by a straight line (c) Decreases in the independent variable is usually accompanied by increases in the regressors (d) Increases in the regressor are usually accompanied by increases in the dependent variable.Consider the following money demand curves: 3) consider the following figure: Price level LRAS SRAS AD AD, AD, Quantity of money. Real GDP Based on the above figure, the money demand curve would Suppose the economy is working below potential GDP and move from Money demand] to Money demand? if expansionary policy is pursued. Using the static AD-45 model A) real GDP decreases. in the figure above, this situation would be depicted as a Bj the price level increases movement from C) the interest rate decreases. A) A to B D) the Federal Reserve sells Treasury securities. B) A to E OC to B 2) Consider the following figure: D) Clo D Internal 4) Consider the following figure: Price level LRAS SRAS AP, AD, 900 Ounntity of money AD (billions of dollars] The movement from point & to point A in the money market Real GOP would be caused by Suppose the economy is in short-run equilibrium just at the AJ an increase in the price level. potential GDP. To adjust the economy: B) a decrease in real GDP. A) it necessarily needs expansionary fiscal policy () an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal B) it necessarily needs contractionary fiscal policy Reserve. C) it needs expansionary (fiscal or monetary) policy D) a decrease in the required reserve ratio by the Federal Dj it needs contractionary (fiscal or monetary) policy Reserve. EJ it needs no policyAssume that security returns are generated by the single-index model R1 = a, + BIRM + ev where R, is the excess return for security i, and Ry is the market's excess return. The risk-free rate is 3%. Suppose that there are three securities, A and B characterized by the table below Security E(R.). % o(e,). % Stock A |1.25 12.5 25 Stock B 1.5 12 35 a. If OM = .20, calculate the variance of returns of securities, A and B. b. Now assume that there is an infinite number of assets with return characteristics identical to those of A and B, respectively. If one forms a well-diversified portfolio of type A securities, what will be the mean and variance of the portfolio excess returns? What about portfolios composed only of type B stocks? c. Are there arbitrage opportunities in the market of question b? If so, what would be an arbitrage strategy? d. Now consider a single security A from question a and a well diversified portfolio B from question b. Are there arbitrage opportunities in this market? If so, what would be an arbitrage strategy
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


