Question: Answer all questions .,,, Problem 5 Let X1, . . . ,Xn be i.i.d random variables with cumulative distribution function F. In other words, Vi
Answer all questions .,,,



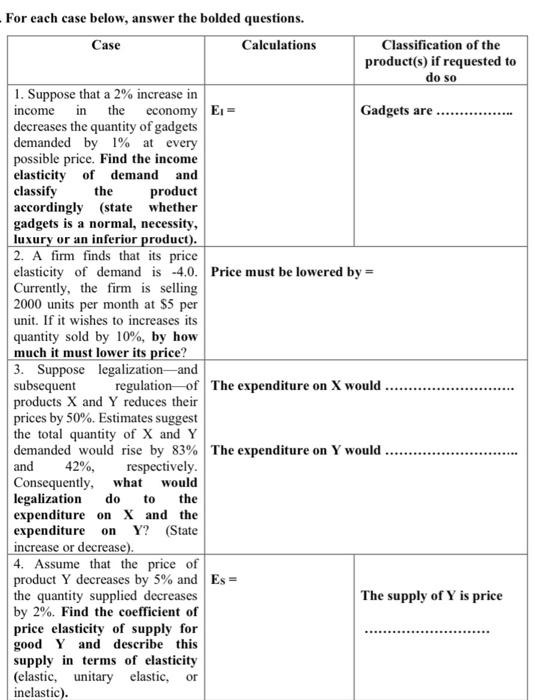

Problem 5 Let X1, . . . ,Xn be i.i.d random variables with cumulative distribution function F. In other words, Vi ,P(X,- 5 rs) = F(:r) . Call X0) 5 X9) 5 . . . 5 X0\") the order statistics of the sample. Fbr simplicity, we assume that F is continuous. 1. Call 14(3) the random variable K(m)_{11fX.:5:r 0 otherwise . Show that {Xm g 1:} if and only if Bad Ym(m) 2 3' . 2. What is the distribution of 8,;(3) = 22:1 Ym(m), if a: is xed? (Le to what family does. it belong, and with what parameters?) What is the cdf of max X;? What is its density? What is the cdf of min Xi? What is its density? . What is the cdf of XU) for any 3'? What is its density? . What is E (X07) if Xg's are uniform on [0,1]? racemes Explain how you could check this last result with R/with a small program. (You do not have to do it - just explain what you would do.) Three researchers are estimating the relationship between expenditure on cinema tickets (Ci) and total monthly expenditure (Y() using a cross-sectional survey of 1500 households in England during May 2014. All three have also been asked to look at the effect of children on cinema attendance and they have been given data on the number of children Ki in each household from which a dummy variable D; has been constructed taking the value 1 if Ki>0 and 0 otherwise. The variable E; is the years of education of the head of household, and residuals for each of the three researchers' models are denoted 21 22,1 23, respectively, i is the household identifier. Researcher 1 estimates the following relationship: (1) Ci = 5.48 + 2.48 Y; - 0.25 Y; 2 - 1.328 Di + 1, (1.24) (2.41) (2.16) (4.21) Number of observations = 1500 Researcher 2 estimates: (2) In Ci = 1.22 + 0.72 Yi - 0.38 Yi*Di - 0.42 Di + 2,i (0.26) (5.13) (3.28) (2.72) Number of observations = 1320Researcher 3 estimates: (3) In Ci = 1.32 + 1.38 In Y; - 0.11 K; + 0.28 E; + E3, (0.54) (6.56) (1.09) (1.10) Number of observations =1280 In all the above regressions, the numbers in brackets are absolute values of t-ratios. a) For each regression, discuss the effect of total monthly expenditure on cinema tickets expenditure. b) Researcher 3 claims to be able to reject the hypothesis that the income elasticity of spending on cinema tickets is equal to 1. Do you agree? Explain your reasoning.For each case below, answer the bolded questions. Case Calculations Classification of the product(s) if requested to do so 1. Suppose that a 2% increase in income in the economy Gadgets are ................ decreases the quantity of gadgets demanded by 1% at every possible price. Find the income elasticity of demand and classify the product accordingly (state whether gadgets is a normal, necessity, luxury or an inferior product). 2. A firm finds that its price elasticity of demand is -4.0. Price must be lowered by = Currently, the firm is selling 2000 units per month at $5 per unit. If it wishes to increases its quantity sold by 10%, by how much it must lower its price? 3. Suppose legalization-and subsequent regulation of The expenditure on X would . products X and Y reduces their prices by 50%. Estimates suggest the total quantity of X and Y demanded would rise by 83% The expenditure on Y would .. and 42%, respectively. Consequently, what would legalization do to the expenditure on X and the expenditure on Y? (State increase or decrease) 4. Assume that the price of product Y decreases by 5% and Es = the quantity supplied decreases The supply of Y is price by 2%. Find the coefficient of price elasticity of supply for good Y and describe this supply in terms of elasticity (elastic, unitary elastic, or inelastic).1. a. Use formula for variance os a security which return follows a single index model: o? = Boy, + o(e;)? to find: o' = 1250%%, ' = 2125%2 b. For a well-diversified portfolio which follows a single-index model the variance is given by o? = B-0%. Hence, 03 = 625%%, 0? = 900%2 E(RA) = 12.5%, E(RA) = 12% c. Slope of security A is 10, slope of security B is 8. Arbitrage strategy: short portfolio B and buy portfolio C in which wa = 1.2 and wT-bill = -.2. d. There are no arbitrage strategies since security-specific risk of A will affect any strategy which includes security A, portfolio B and T-bills
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


