Question: Answer all questions 2. -/1 points My Notes . Ask Your Teacher The figure below shows, in cross section, three solid cylinders, each of length
Answer all questions
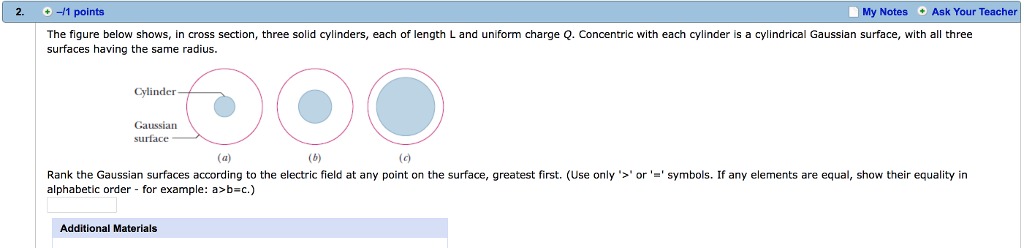
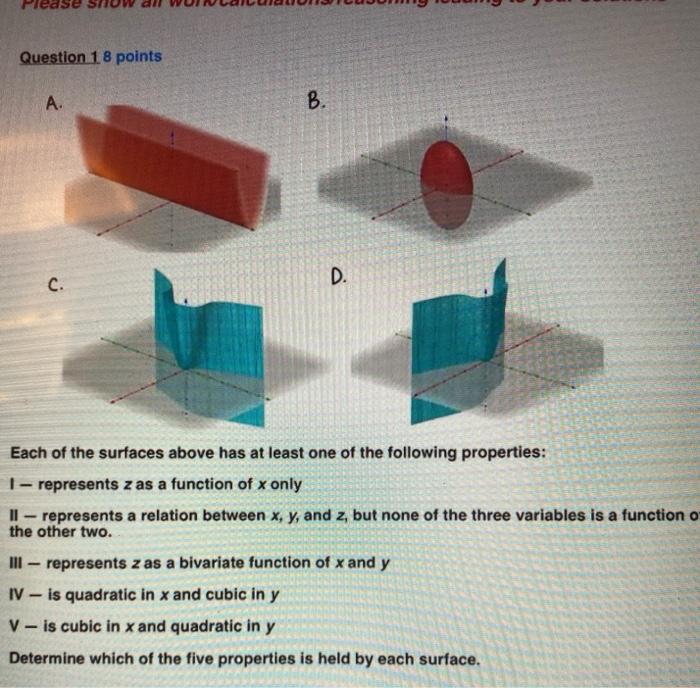


2. -/1 points My Notes . Ask Your Teacher The figure below shows, in cross section, three solid cylinders, each of length L and uniform charge Q. Concentric with each cylinder is a cylindrical Gaussian surface, with all three surfaces having the same radius. Cylinder Gaussian surface (a) (6) (c) Rank the Gaussian surfaces according to the electric field at any point on the surface, greatest first. (Use only '>' or '=' symbols. If any elements are equal, show their equality in alphabetic order - for example: a>b=c.) Additional MaterialsQuestion 1 8 points A. C. D. Each of the surfaces above has at least one of the following properties: I - represents z as a function of x only Il - represents a relation between x, y, and z, but none of the three variables is a function o the other two. Ill - represents z as a bivariate function of x and y IV - is quadratic in x and cubic in y V - is cubic in x and quadratic in y Determine which of the five properties is held by each surface.(2) 12. Some species of animals are censused by "rounding them all up" using a: a) linear transect and point count b) drive count and corral c) thermal infrared scanner and radar seine net and plastic bucket e) track and trail index (2) 13. Detecting radio signals from a radio-collared polar bear using a satellite makes detection of location more challenging because the frequency changes as the satellite approaches and leaves the North Pole. This phenomenon is known as: a) Dipole pause b) White noise c) Doppler shift d) Frequency modulation e) Amplitude damping (2) 14 A home range method that relies on the distribution of locations along the two directional axes (N-S, E-W) and the exclusion of outlying points improves the estimate of area used by an animal. It is called a) minimum convex polygon method b) 95% bivariate normal distribution c) minimum harmonic mean method d) fixed kernel density estimator e) shotgun scatter method(17) 1. Consider a random experiment that consists of throwing a dart at a triangle-shaped target with vertices at the (x, y) positions (-1, -1), (2, -1), and (-1, 2), resulting in outcome (x, y), the point where the dart hits. Assume that the dart always hits the target and that the probability distribution is uniform over the surface of the target. That is, the bivariate probability density function (pdf), fxy(x, y), has constant value C over the triangle and value 0 outside the triangle. Let the corresponding bivariate cumulative distribution function (CDF) be FXY(x, y). a. Sketch a bird's-eye view, looking straight down from above, showing the borders and "footprint" of pdf fxy(x, y) on the x-y plane. b. Find the numeric value of pdf fxY(x, y) for x = 0, y = 0. Explain your work. c. Find the numeric value of CDF FxY(x, y) for x = 0, y - 0. Explain your work
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


