Question: solve the following Question : 3. As we have seen in class, hypothesis testing, and confidence intervals are the most common inferential tools used in
solve the following Question:
3. As we have seen in class, hypothesis testing, and confidence intervals are the most common inferential tools used in statistics. Imagine that you have been tasked with designing an experiment to determine reliably if a patient should be diagnosed with diabetes based on their blood test results. Create a short outline of your experiment, including all the following:??
??
??
a. A detailed discussion of your experimental design. Detailed experimental design should include the type of experiment, how you chose your sample size, what data is being collected, and how you would collect that data.??
??
???
b. How is randomization used in your sampling or assignment strategy? Remember to discuss how you would randomize for sampling and assignment, what type of randomization are you using???
??
??
??
c. The type of inferential test utilized in your experiment. Include type of test used, number of tails, and a justification for this choice.??
??
??
??
d. A formal statement of the null and alternative hypothesis for your test. Make sure to include correct statistical notation for the formal null and alternative, do not just state this in words.??
??
??
??
e. A confidence interval for estimating the parameter in your test. State and discuss your chosen confidence level, why this is appropriate, and interpret the lower and upper limits.??
??
??
??
d. An interpretation of your p-value and confidence interval, including what they mean in the context of your experimental design. Answer each part below. State your significance level, interpret your p-value, and make a decision on the null.??

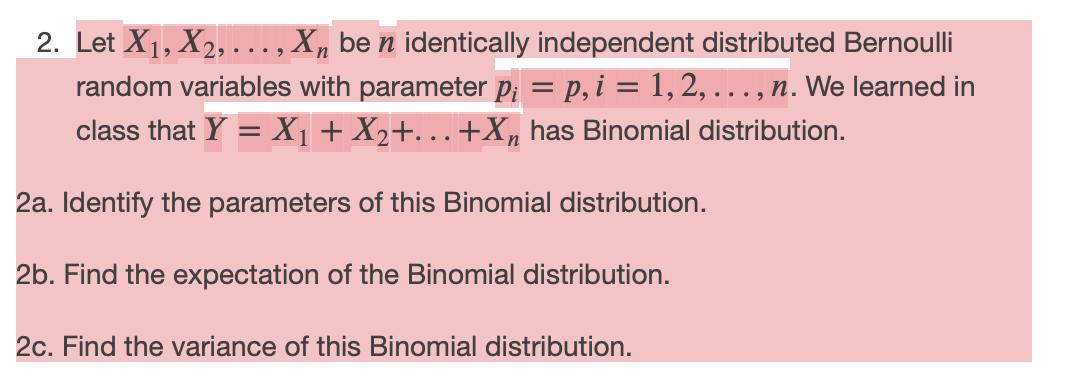


Which of the following statements regarding the Central Limit Theorem is FALSE? (a) The Central Limit Theorem assumes that the sample drawn from the population consists of i.i.d random variables. (b) The Central Limit Theorem states that, for large sample sizes, the sample mean has an approximately normal distribution. (c) The Central Limit Theorem states that, for large sample sizes, the random variable YLE has a H standard normal distribution where T, ,u,, and or are the sample mean, population mean, and population standard deviation respectively. ((1) The Central Limit Theorem assumes that the distribution of the population from which the sample is drawn must be normal. 2. Let X1, X2, ..., Xn be n identically independent distributed Bernoulli random variables with parameter pi = p, i = 1, 2, ..., n. We learned in class that Y = X1 + X2+...+X, has Binomial distribution. 2a. Identify the parameters of this Binomial distribution. 2b. Find the expectation of the Binomial distribution. 2c. Find the variance of this Binomial distribution.2 Understanding the central limit theorem Explain how the central limit theorem (WMS Theorem 7.4) can be used to show the following useful facts. If X1. ...; Xn are IID random variables with mean / and variance o', then , X, is approximately normal with mean nu and variance no', and X = 1 ). X, is approximately normal with mean / and variance o?, as n gets large.QUESTION 12 Select the comect statement concerning the Law of Total Probability and conditional probability. The Law of Total Probability defines unconditional probability of an event P(E) using known conditional probabilities P(BB) given that independent events Bk have occurred, each Bk with a unknown probability itself. Conditional probability P(E F) defines the probability of an event E given that an event F has occurred. Ob. The Law of Total Probability defines unconditional probability of an event P(E) using known conditional probabilities P(E B) given that mutually exclusive events B& have occurred, each BA with a known probability itself. Conditional probability P(E) ) defines the probability of an event F given that an event E has occurred. The Law of Total Probability defines unconditional probability of an event P(E) using known conditional probabilities P(E)By) given that independent events BA have occurred, each BK with a known probability itself. Conditional probability P(E F) defines the probability of an event F given that an event E has occurred. The Law of Total Probability defines unconditional probability of an event P(2) using known conditional probabilities P(FB) given that mutually exclusive events By have occurred, each By with a known probability itself. Conditional probability P(EA) defines the probability of an event E given that an event F has occurred
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


