Question: Answer all the questions. QUESTION 6 USC is a listed company based in the USA. It is in the process of acquiring a French company,
Answer all the questions.
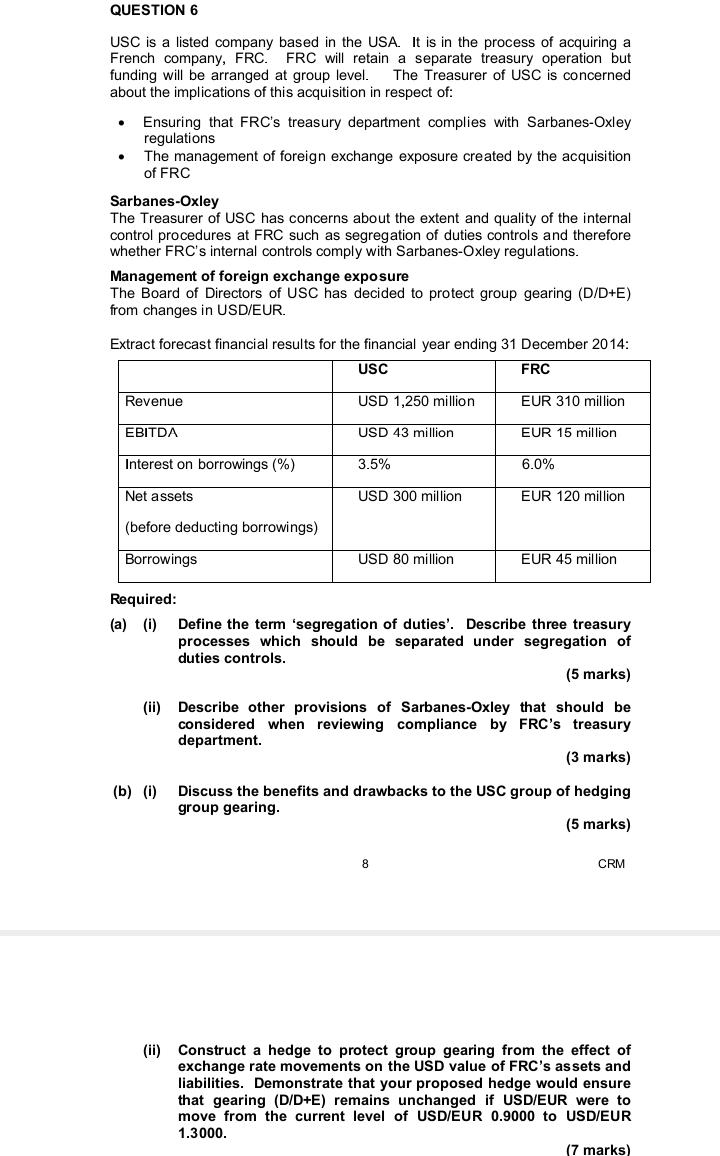
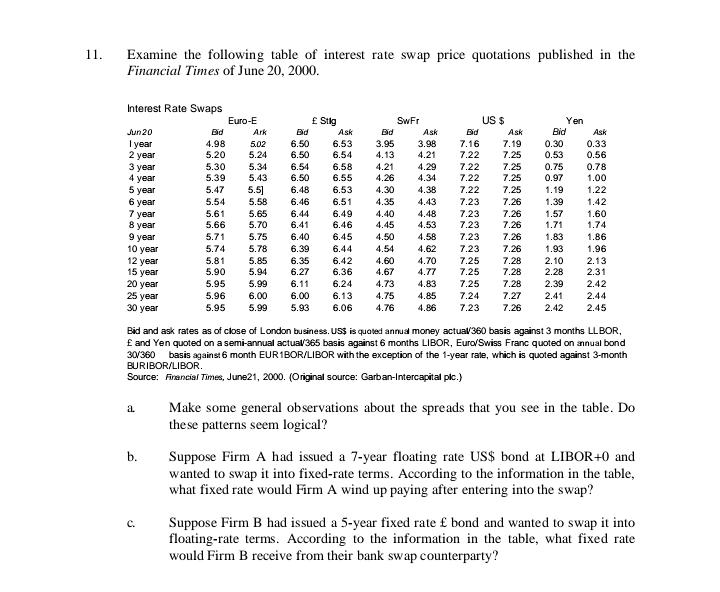



QUESTION 6 USC is a listed company based in the USA. It is in the process of acquiring a French company, FRC. FRC will retain a separate treasury operation but funding will be arranged at group level. The Treasurer of USC is concerned about the implications of this acquisition in respect of: . Ensuring that FRC's treasury department complies with Sarbanes-Oxley regulations The management of foreign exchange exposure created by the acquisition of FRC Sarbanes-Oxley The Treasurer of USC has concerns about the extent and quality of the internal control procedures at FRC such as segregation of duties controls and therefore whether FRC's internal controls comply with Sarbanes-Oxley regulations. Management of foreign exchange exposure The Board of Directors of USC has decided to protect group gearing (D/D+E) from changes in USD/EUR. Extract forecast financial results for the financial year ending 31 December 2014: USC FRC Revenue USD 1,250 million EUR 310 million EBITDA USD 43 million EUR 15 million Interest on borrowings (%) 3.5% 6.0% Net assets USD 300 million EUR 120 million (before deducting borrowings) Borrowings USD 80 million EUR 45 million Required: (a) (i) Define the term 'segregation of duties'. Describe three treasury processes which should be separated under segregation of duties controls. (5 marks) (ii) Describe other provisions of Sarbanes-Oxley that should be considered when reviewing compliance by FRC's treasury department. (3 marks) (b) (i) Discuss the benefits and drawbacks to the USC group of hedging group gearing. (5 marks) CO CRM (ii) Construct a hedge to protect group gearing from the effect of exchange rate movements on the USD value of FRC's assets and liabilities. Demonstrate that your proposed hedge would ensure that gearing (D/D+E) remains unchanged if USD/EUR were to move from the current level of USD/EUR 0.9000 to USD/EUR 1.3000. marks)11. Examine the following table of interest rate swap price quotations published in the Financial Times of June 20, 2000. Interest Rate Swaps Euro-E f Stig SWFr US $ Yen Ark Ask Ask Bid Ask Bid Ask Jun 20 Did I year 4.98 5.02 6.50 6.53 3.95 3.98 7.16 7.19 0.30 0.33 2 year 5.20 5.24 6.50 6.54 4.13 4.21 7.22 7.25 0.53 0.56 3 year 5.30 5.34 6.54 6.58 4.21 4.29 7.22 7.2 0.75 0.78 4 year 5.39 5.43 6.50 6.55 4.26 4.34 7.22 7.2 0.97 1.00 5 year 5.47 5.5] 6.48 6.53 4.30 4.38 7.22 7.25 1.19 1.22 6 year 5.54 5.58 6.46 6.51 4.35 4.43 7.23 7.26 1.39 1.42 7 year 5.61 5.65 6.44 6.49 4.40 4.48 7.23 7.26 1.57 1.60 1.71 1.74 8 year 5.66 5.70 6.41 6.46 4.45 4.53 7.23 7.26 9 year 5.71 5.75 6.40 6.45 4.50 4.58 7.23 7.26 1.83 1.86 10 year 5.74 5.78 6.39 6.44 4.54 4.62 7.23 7.26 1.93 1.96 12 year 5.81 5.85 5.35 6.42 4.60 4.70 7.25 7.28 2.10 2.13 15 year 5.90 5.94 6.27 6.36 4.67 4.77 7.25 7.28 2.28 2.31 5.95 5.09 6.11 6.24 4.73 4.83 7.25 7.28 2.39 2.42 20 year 2.44 25 year 5.96 6.00 6.00 6.13 4.75 4.85 7.24 7.27 2.41 30 year 5.95 5.99 5.93 6.06 4.76 4.86 7.23 7.26 2.42 2.45 Bid and ask rates as of close of London business. US$ is quoted annual money actual/360 basis against 3 months LLBOR, E and Yen quoted on a semi-annual actual/365 basis against 6 months LIBOR, Euro/Swiss Franc quoted on annual bond 30/360 basis against 6 month EUR1BOR/LIBOR with the exception of the 1-year rate, which is quoted against 3-month BURIBOR/LIBOR. Source: Financial Times, June21, 2000. (Original source: Garban-Intercapital pic.) a. Make some general observations about the spreads that you see in the table. Do these patterns seem logical? b. Suppose Firm A had issued a 7-year floating rate US$ bond at LIBOR+0 and wanted to swap it into fixed-rate terms. According to the information in the table, what fixed rate would Firm A wind up paying after entering into the swap? C. Suppose Firm B had issued a 5-year fixed rate f bond and wanted to swap it into floating-rate terms. According to the information in the table, what fixed rate would Firm B receive from their bank swap counterparty?4. Capital Inflows, Monetary Policy and the Yield Curve (Total: 14 Points). In recent months, capital inflows to Brazil have appreciated its currency. Capital is attracted by high interest rates (the Central Bank interest rate is 12.25%). These capital inflows increase the foreign reserves of the central bank as the foreign currency is exchanged by the local currency (Real). So far inflation has been contained but there is a risk that it will go up, even more because of what they see in other countries. Therefore, the central bank of Brazil is worried about increases in inflation. The president of the central bank of Brazil Henrique Meirelles said in a recent interview in Sao Paolo: "The biggest concern over the next 12 months for Brazil and the rest of the world is inflation. The risk is that prices for food and raw materials will continue to rise. If every central banker decides that this is a problem for other countries, nobody will do anything and there will be [faster] worldwide inflation." a. How do these capital flows that Brazil is experiencing influence the ability of the central bank to run monetary policy? Is the appreciation of the currency consistent with their interest rates? (7 points)Hedging policy RRR does not have a formal hedging policy, although, in the past, occasional hedging deals have been entered into if it was considered that the spot rate was at a favourable level historically. RRR's Board has delegated responsibility for hedging policy to its Risk Management Committee (RMC). Two Directors sitting on the RMC have expressed reservations about carrying out any hedging for foreign exchange risk. CRM Director A considers that the USD/NZD spot rate is equally likely to move up or down and that, over the longer term, such movements are likely to cancel out and therefore there is unlikely to be any long term financial benefit from hedging foreign exchange exposures. Director B is of the opinion that shareholders should have been aware of the foreign currency profile of the company when they invested in it and would expect to benefit from favourable exchange rate movements. Therefore the company should not carry out any foreign exchange hedging so that it can still benefit from favourable rate movements. Required: (c) Respond to the views expressed by Directors A and B, concluding with a recommendation of an appropriate risk response for RRR. (9 marks) (Total 30 marks)QUESTION 4 PENSK is a defined benefit pension scheme located in the UK. Company PK is the sponsor company for PENSK. PENSK's investments have a total value of GBP 900 million, of which 60% is invested in equities and 40% in bonds. Pension payment liabilities are estimated to be approximately GBP 88 million a year for the next 15 years. The bonds have an AA credit rating and range in maturity from 2 to 20 years, with a modified duration of 9.3 years and modified convexity of 123.0. The yield to maturity on the bonds is currently 4%. PENSK's Trustees are currently reviewing the risk profile of both the scheme assets and liabilities. The Trustees are aware that Quantitative Easing (QE) programmes can negatively affect pension schemes. Advisers to PENSK expect a QE programme to be announced shortly and that this would lead to a fall in interest rates, coupled with an increase in the value of equities. Equity values are expected to rise by approximately 2% for each 1% fall in interest rates. Bond yields can be assumed to move in line with interest rates. Required: (a) Explain the following risk factors and their potential impact on a defined pension scheme value (no calculations are required): Changing interest rates . A credit rating downgrade of a corporate bond held as an investment (4 marks) (b) (1) Calculate the PENSK scheme surplus or deficit. (3 marks) (ii) Calculate the expected impact on the PENSK scheme surplus or deficit of a QE programme that causes interest rates to fall from 4% to 3%. (6 marks) (ili) Explain the implications for sponsor PK of a large PENSK scheme deficit. (3 marks) (iv) Describe methods that can be used by pension schemes to reduce their interest rate exposure. (4 marks) (Total 20 marks) CRM QUESTION 5 Assume that you are the newly appointed Treasurer of INT, a transport infrastructure company based in Malaysia. INT is financed by equity plus floating rate bank borrowings. Interest is charged on the borrowings at 12 month KLIBOR plus 150 bp (where KLIBOR is the interbank rate in Malaysia). The Managing Director has become aware that other companies tend to have a mix of fixed and floating rate debt finance and has asked you to consider the implications of changing the interest profile of INT's debt. Three derivatives have been identified that could be used to adjust the interest profile of MYR 100 million of INT's floating rate bank borrowings. Each derivative has a 4 year term. Current market prices are as follows: 4.0% cap at an upfront premium of 0.8% of the notional principal Interest rate swap at 3.5% fixed against 12 month KLIBOR Zero cost collar with a cap of 4.0% and a floor of 3.0% Required: (a) Explain the potential benefits and challenges for INT of changing the interest profile of debt
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


