Question: answer two blanks. NPV (000) Problem 9-33 Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple


 answer two blanks. NPV (000)
answer two blanks. NPV (000)
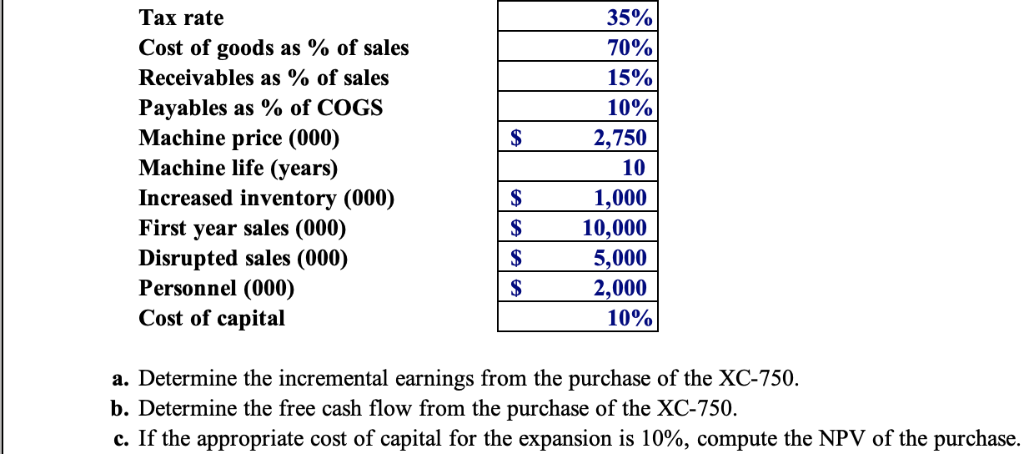
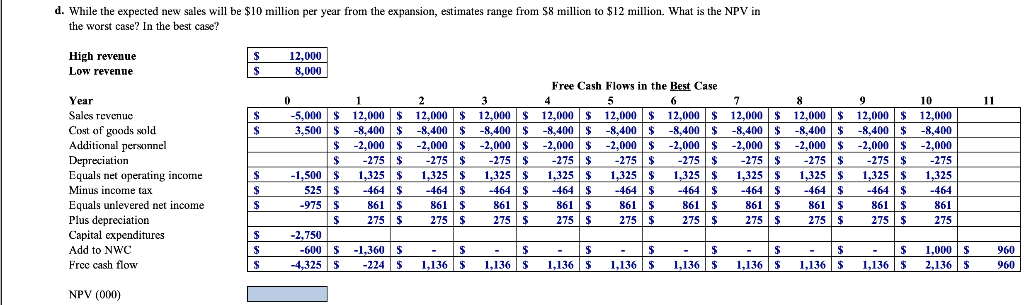
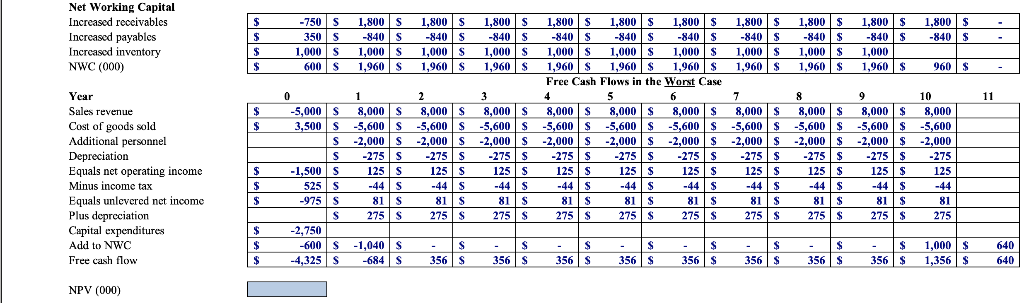
Problem 9-33 Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. Billingham Packaging is considering expanding its production capacity by purchasing a new machine, the XC-750. The cost of the XC-750 is $2.75 million. Unfortunately, installing this machine wll take several months and will partially disrupt production. The firm has just completed a S50,000 feasibility study to analyze the decision to buy the XC-750, resulting in the following estimates: Marketing: Once the XC-750 is operating next year, the extra capacity is expected to generate $10 million per year in additional sales, which will continue for the ten-year life of the machine Operations: The disruption caused by the installation will decrease sales by $5 million this year. As with Billingham's existing products, the cost of goods for the products produced by the XC-750 is expected to be 70% of their sale price The increased production will also require increased inventory on hand of $1 million during the life of the project. Human Resources: The expansion will require additional sales and administrative personnel at a cost of $2 million per ear Accounting: The XC-750 will be depreciated via the straight-line method over the ten-year life of the machine. The firm expects receivables from the new sales to be 15% of revenues and payables to be 10% of the cost of goods sold. Billingham's marginal corporate tax rate is 35% a. Determine the incremental earnings from the purchase of the XC-750 b. Determine the free cash flow from the purchase of the XC-750 c. If the appropriate cost of capital for the expansion is 10%, compute the NPV of the purchase d. While the expected new sales will be S10 million per year from the expansion, estimates range from $8 million to S12 million. What is the NPV in the worst casc? In the best casc? e. What is the break-even level of new sales from the expansion? What is the break-even level for the cost of goods sold? Billingham could instead purchase the XC-900, which offers even greater capacity. The cost of the XC-900 is $4 million. The extra capacity would not be useful in the first two years of operation, but would allow for additional sales in years 3-10. What level of additional sales (above the S10 million expected for the XC-750) per year in those years would justify purchasing the larger machine? Tax rate Cost of goods as % of sales Receivables as % of sales Payables as % of COGS Machine price (000) Machine life (years) Increased inventory (000) First year sales (000) Disrupted sales (000) Personnel (000) Cost of capital 35% 70% 15% 10% 2,750 10 1,000 10,000 5,000 2,000 10% a. Determine the incremental earnings from the purchase of the XC-750. b. Determine the free cash flow from the purchase of the XC-750 C. If the appropriate cost of capital for the expansion is 10%, compute the NPV of the purchase d. While the expected new sales will be $10 million per year from the expansion, estimates range from S8 million to $12 million. What is the NPV in the worst case? In the best case? High revenue Low revenue 12,000 Free Cash Flows in the Best Case Year Cost of goods sold Additional personnel Depreciation Equals net operating income Minus income tax Equals unlevered net income Plus depreciation Capital expenditures Add to Nwc Free cash flow 5,000 12,000 12,00012,000 12,00012,00012,000 12,00012,000 12,00012,000 3,500$ 8,4008,400-8.400 $8,400-8,400-8,400 8,400-8,400$ -8,4008,400 275 $ -2,000| $ -2.000|$ 2.000| $ -2,000|$ -2,000|$ -2,000|$ -2,000|$ -2,000|$ -2,000|$ -2,000 1.500 1325 S13251,325 $ 13251,325 1,3251,325 13251,3251325 861 525$ 4-464 464$-464464$-464464$ -46$464$-464 275 275$ 275$ 275$ 275$ 275$ 275$ 275$ 275$ 275$ 861 $ 861 275 $ 975 S 861 S 861S 861S 275$27 861S 861$ 275 $ 861$ 275 $ 861$ 275 $ 750 -600-1,3 1,000 S 960 960 325 5 -224 1,136 5 1,136 1,1361,136 1,1361,136 1,1361,136 ,136 NPV (000) Net Working Capital Increased receivables Incrcased payables Incrcasod inventory NWC (000) -750 S 1,800 | S 1,800 | S ,800 |$ ,800 | $ ,800 |$ 350 S840 S -840 S-840 S840 S 840S 1,800 |$ 840 S 1,800 | $ 840 S 1,800 | $ 840 S i,800 | $ 840 S 1,800 | $ 840S 1,000 S 1,000 S 1,000 S 1,000 S1,000 S 1,000 1,000S 1,000 1,000 1,9601,960S 1,9601,960 1,000 600 S ,960S 1,960 1,960 S 1,9601,960 960 S Free Cash Flows in the Worst Case Year Sales revenue Cost of goods sold Additional personnel 10 5,000 S 8,000 S8,000 S 8,0008,000S 8,000 S8,0008,000S8,000 8,000$8,000 3,500 S-5,600 S -5,600 S-5,600 S-5,600 S-5,600 -5,600 -5,600 $-5,600 $-5,600-5,600 S -2,000 S -2,000 S 2,000 S -2,000 S 2,000-2,000 2,000 -2,0002,000-2,000 125 275 Equals net operating income Minus income tax Equals unlevcred nct incomc Plus deprcciation Capital expenditures Add to NWC Free cash flow 275 S 125 S 44 S 81S 275 S 275 S 125 S -44 S 81S 275 S 275 S 125 S -44 S 81 S 275 S 275 S 125 S 44 S 81 S 275 S 275S 125 S 44 S 81S 275 S 275 S 125 S -44 S 81S 275 275 S 125 S -44S 81 S 275 275 S 125 S -44S 81 S 275 S 275 $ 125 S -44S 81S 275 1,500 S 525 S 975 S 275 2,750 -600 -1,040 S -4,325 S-684 S - $1,000 3561,356 640 640 356 S 356 S 356 S 356 S 356 S 356 S 356 S NPV (000) Net Working Capital Incrcased receivables Increased payables Increased inventory NWC (000) 50 S 1.200 i s 1.200 |S 1.200 | S 1.200 | S 1,200 |S 1.200 | S 1,200 |S 1,200 1.200 l s 1.200 s 350 -560 S-560 S560 S -560 S-560 S560 S-560 S 560 S-560 560 S 1,000 S 1,000S1,000 1,000 S 1,000 S 1,000 S 1,000S 1,000 S 1,000S1,000 600 S 1.640 i s i,640 | S 1,640 | S 1,640 | S i,640 i s 1,640 IS 1.640 | S ,640 ,640 | $ 640 s
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


