Question: Any programming language 2. (5 pts.) Suppose T is a BinaryTree ADT. Assume, as the book does, that T is a proper binary tree. That

Any programming language
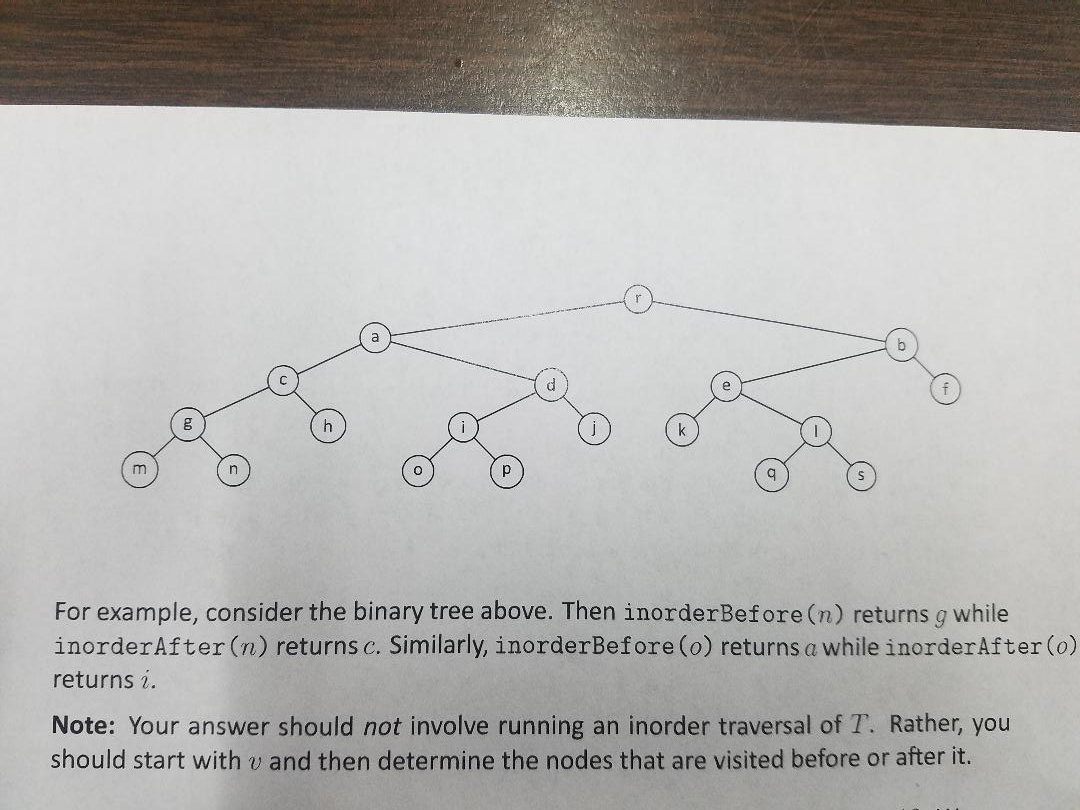
2. (5 pts.) Suppose T is a BinaryTree ADT. Assume, as the book does, that T is a proper binary tree. That is, if v is an internal node, then v has a left and a right child. Design algorithms for the following methods: inorderBefore(v): returns the node visited before v in an inorder traversal of T. inorder Next (v): returns the node visited after u in an inorder traversal of T. Explain why your algorithms are correct and determine their running times. aan For example, consider the binary tree above. Then inorderBefore(n) returns g while inorderAfter(n) returns c. Similarly, inorderBefore(o) returns a while inorderAfter(o) returns i. Note: Your answer should not involve running an inorder traversal of T. Rather, you should start with v and then determine the nodes that are visited before or after it. 2. (5 pts.) Suppose T is a BinaryTree ADT. Assume, as the book does, that T is a proper binary tree. That is, if v is an internal node, then v has a left and a right child. Design algorithms for the following methods: inorderBefore(v): returns the node visited before v in an inorder traversal of T. inorder Next (v): returns the node visited after u in an inorder traversal of T. Explain why your algorithms are correct and determine their running times. aan For example, consider the binary tree above. Then inorderBefore(n) returns g while inorderAfter(n) returns c. Similarly, inorderBefore(o) returns a while inorderAfter(o) returns i. Note: Your answer should not involve running an inorder traversal of T. Rather, you should start with v and then determine the nodes that are visited before or after it
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


