Question: Apply the steady-state approximation to the intermediate oxygen atom concentration [O] and use the equation you derive for [O] to substitute for [O] in #2
Apply the steady-state approximation to the intermediate oxygen atom concentration [O] and use the equation you derive for [O] to substitute for [O] in #2 to give the differential rate equation in the box below in terms of only k1, k-1, k2, [O2], and [O3] (i.e., use the SST to get rid of the [O] in #2 above). Show your algebra neatly and succinctly.
![Apply the steady-state approximation to the intermediate oxygen atom concentration [O] and](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f8e89d08b88_50866f8e89ca76cf.jpg)
Here is #2:
![use the equation you derive for [O] to substitute for [O] in](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f8e89db2658_50966f8e89d34565.jpg)
From the proposed mechanism, write down the equation for the rate of DISappearance of ozone in terms of k1, k-1, k2, [O], [O2], and [O3]. To help you get started, I wrote down one of the three terms in the equation for you.
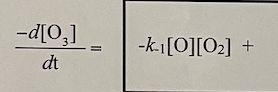
dtd[O3]= The experimentally determined rate law for the decomposition of ozone to oxygen molecules, 2O3(g) 3O2(g), is rate =k[O3]2[O2]1. The proposed mechanism is given below: O3k1k1O2+OO+O3k22O2 dtd[O3]=k1[O][O2]+
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


