Question: ASAP new please dont copy pasted previous answer Exercise 3. Consider the open network of two queues shown in Figure 2. Customers enter the network
ASAP
new please dont copy pasted previous answer
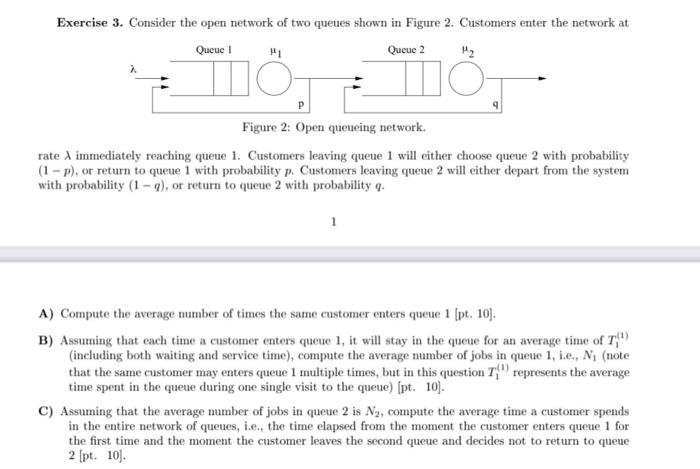
Exercise 3. Consider the open network of two queues shown in Figure 2. Customers enter the network at Queue 1 H1 Queue 2 M2 - Figure 2: Open queueing network. rate immediately reaching queue 1. Customers leaving queue 1 will either choose queue 2 with probability (1 - p), or return to queue 1 with probability p. Customers leaving queue 2 will either depart from the system with probability (1), or return to queue 2 with probability q. 1 A) Compute the average number of times the same customer enters queue 1 (pt. 10). B) Assuming that each time a customer enters queue 1, it will stay in the queue for an average time of T/" (including both waiting and service time), compute the average number of jobs in queue 1, i.e., N. (note that the same customer may enters queue 1 multiple times, but in this question represents the average time spent in the queue during one single visit to the queue) [pt. 10). C) Assuming that the average number of jobs in queue 2 is Ng, compute the average time a customer spends in the entire network of queues, i.e., the time elapsed from the moment the customer enters queue 1 for the first time and the moment the customer leaves the second queue and decides not to return to queue 2 (pt. 10) Exercise 3. Consider the open network of two queues shown in Figure 2. Customers enter the network at Queue 1 H1 Queue 2 M2 - Figure 2: Open queueing network. rate immediately reaching queue 1. Customers leaving queue 1 will either choose queue 2 with probability (1 - p), or return to queue 1 with probability p. Customers leaving queue 2 will either depart from the system with probability (1), or return to queue 2 with probability q. 1 A) Compute the average number of times the same customer enters queue 1 (pt. 10). B) Assuming that each time a customer enters queue 1, it will stay in the queue for an average time of T/" (including both waiting and service time), compute the average number of jobs in queue 1, i.e., N. (note that the same customer may enters queue 1 multiple times, but in this question represents the average time spent in the queue during one single visit to the queue) [pt. 10). C) Assuming that the average number of jobs in queue 2 is Ng, compute the average time a customer spends in the entire network of queues, i.e., the time elapsed from the moment the customer enters queue 1 for the first time and the moment the customer leaves the second queue and decides not to return to queue 2 (pt. 10)





