Question: Assembly Operations A very simple microcontroller has one register, X, which is initialised to 0, and supports only 3 types of microinstructions: LDI v: Load
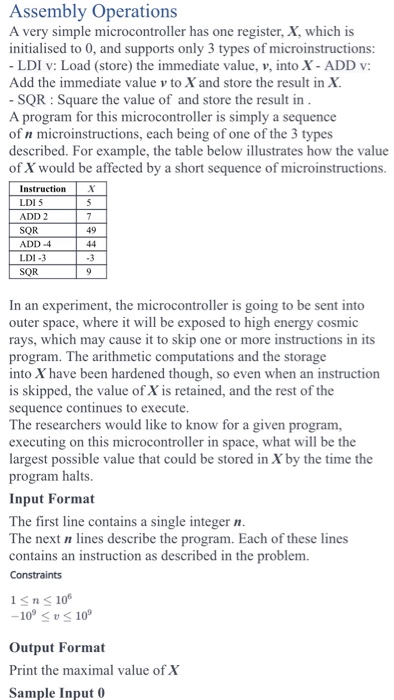
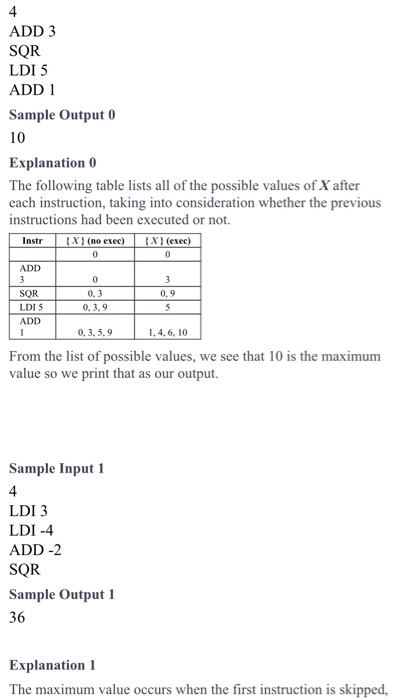

Assembly Operations A very simple microcontroller has one register, X, which is initialised to 0, and supports only 3 types of microinstructions: LDI v: Load (store) the immediate value, v, into X - ADD v: Add the immediate value v to X and store the result in X. SQR: Square the value of and store the result in A program for this microcontroller is simply a sequence of n microinstructions, each being of one of the 3 types described. For example, the table below llustrates how the value of X would be affected by a short sequence of microinstructions. LDI 5 ADD 2 SQR ADD-4 LDI-3 SQR 49 In an experiment, the microcontroller is going to be sent into outer space, where it will be exposed to high energy cosmic rays, which may cause it to skip one or more instructions in its program. The arithmetic computations and the storage into X have been hardened though, so even when an instruction is skipped, the value of X is retained, and the rest of the sequence continues to execute The researchers would like to know for a given program, executing on this microcontroller in space, what will be the largest possible value that could be stored in X by the time the program halts. Input Format The first line contains a single integer m The next n lines describe the p contains an instruction as described in the problem. rogram. Each of these lines n10 -10 U10 Output Format Print the maximal value of X Sample Input 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


