Question: Assessment + 4 3 4 pts Resources Al Tutor 1 8 0 0 Question 7 of 8 Monetary Policy: End of Chapter Problem Milton Friedman
Assessment
pts
Resources
Al Tutor
Question of
Monetary Policy: End of Chapter Problem
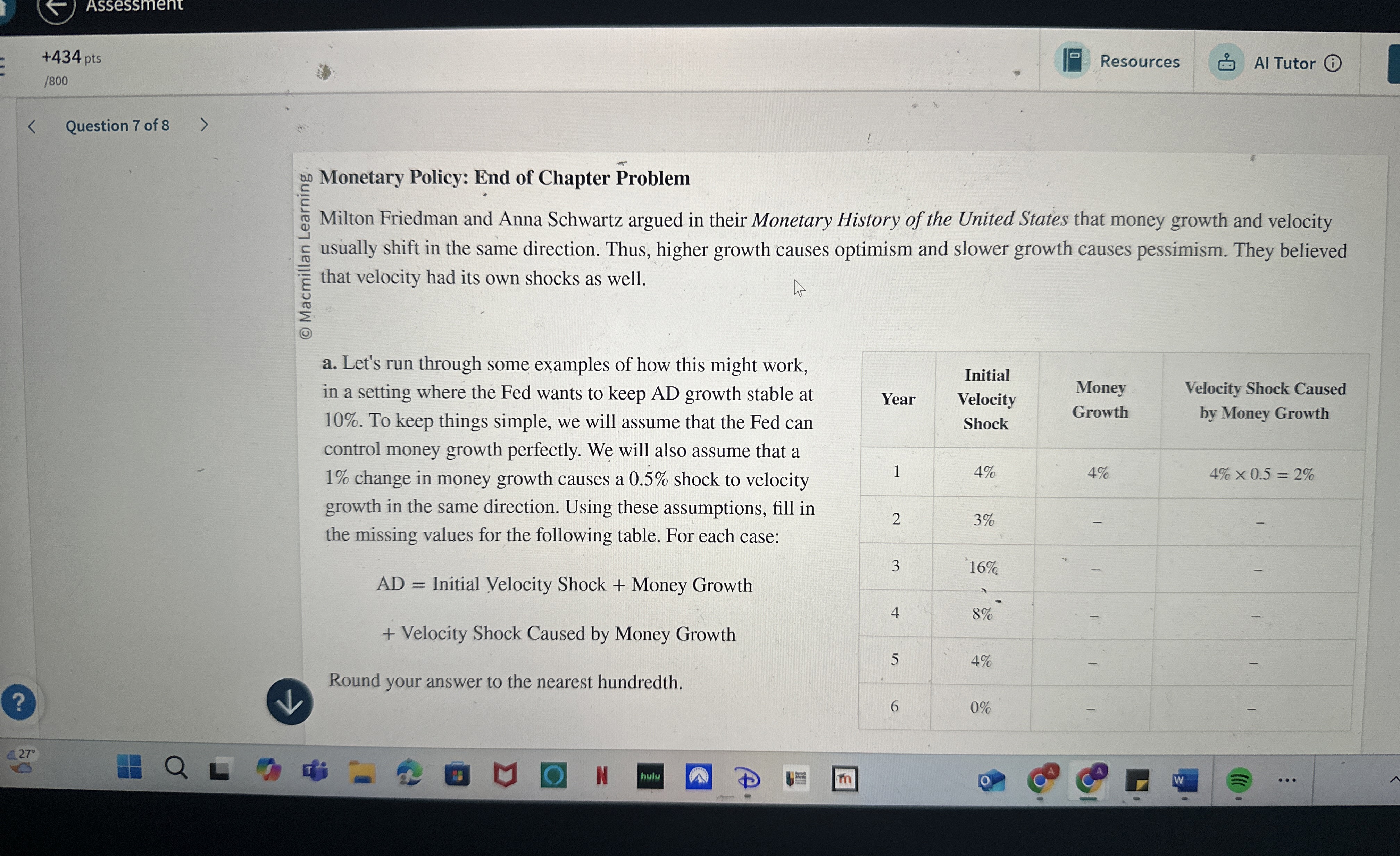
Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz argued in their Monetary History of the United States that money growth and velocity usually shift in the same direction. Thus, higher growth causes optimism and slower growth causes pessimism. They believed that velocity had its own shocks as well.
a Let's run through some examples of how this might work, in a setting where the Fed wants to keep AD growth stable at To keep things simple, we will assume that the Fed can control money growth perfectly. We will also assume that a change in money growth causes a shock to velocity growth in the same direction. Using these assumptions, fill in the missing values for the following table. For each case:
Initial Velocity Shock Money Growth
Velocity Shock Caused Money Growth
Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
tableYeartableInitialVelocityShocktableMoneyGrowthtableVelocity Shock Causedby Money Growth
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


