Question: Assignment - 1 Multiprocessing Problem 1 Using the multiprocessing module, write a simple python program as follows: Create a pool of workers to run parallel
Assignment - 1 Multiprocessing
-
Problem 1
Using the multiprocessing module, write a simple python program as follows:
-
Create a pool of workers to run parallel tasks.
-
The pool size should be 4.
-
Write a simple function to be run in parallel, call it def my_pid(x):. The function should receive as
input an integer x identifying the task. When called, the function will print to the screen a message in the form: Hi, Im worker ID (with PID) Where ID should be replaced with the argument x and PID with the process ID of the running worker. Note: the PID of the current Python process can be found using the getpid() function in the os module.
-
Run tasks in parallel using the map function, for arguments x ranging from 0 through 9.
-
Problem 2
It is always easy to start with something tractable. Here we will compute an approximation to from one of the many available series:
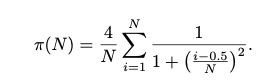
The accuracy increases with larger N, which denotes the number of terms to include in the expansion. For
the rest of the exercise, you may refer to exact value as returned from NumPy:
import numpy as np
print(np.pi)
Your goal is to compute an approximation to using the above formula for different values of N. Using the multiprocessing module, write a Python program as follows:
-
Create a pool of workers to run parallel tasks.
-
The pool size should be 4.
-
Write a function to run in parallel, call it py_pi.The function should receive on input a number N
specifying how many terms to include in the expansion. When called, the function will compute the approximation to , print the result to the screen along with difference from the exact value of . A typical output can be in the form: Pi(N) = XXX (Real is XXX, difference is XXX) Where N is the number of terms given as input and each XXX refers to the approximated value, exact, and difference, respectively.
-
Run tasks in parallel using the map function, starting with N = 10 for the first worker and increasing 5 times for each subsequent worker until reaching N = 3906250 (e.g. N =10,50,250,1250,. . . ).
-
Print the total runtime it took to compute each (N).
Problem 3
The above method of computing an approximation to is clearly inefficient since work is not evenly distributed between workers. Here we will modify the above procedure such that the expansion will be computed in parallel. Fix N and each worker will get a subset of the expansion to compute. Then, the main caller will collect the results and summarize them to get the final answer.
Using the multiprocessing module, extend the python program from Problem 2 as follows:
1. Write a function to be running in parallel, call it py_pi_better. The function should receive on input three parameters: N, i_start, and i_stop that denote the subset the worker should compute from the expansion. For example:
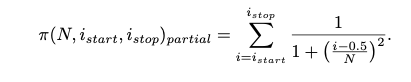
The function will return the partial result to the caller.
-
Run tasks in parallel using the map function, such that the work distribution scheme should be to divide
the expansion N as evenly as possible between the workers.
-
After receiving all the results, the caller should add them together and multiply by 4/N to get the final
answer and print it to the screen as before.
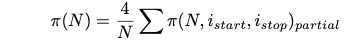
A typical output could be in the form:Pi(N) = XXX (Real is XXX, diff XXX) 4.Compute an approximation to using this procedure for N=100,500,1000,2000,10000,50000 and see if there is any performance benefit compared to trivial version from previous task.
N 4 (N) | N 1+ (1-0:5) istop 1 7 (N, i start, i stop)partial i=istart 1+(1-0.5)? 4 * (N) = i +(N, i start, i stop) partial N 4 (N) | N 1+ (1-0:5) istop 1 7 (N, i start, i stop)partial i=istart 1+(1-0.5)? 4 * (N) = i +(N, i start, i stop) partial
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


