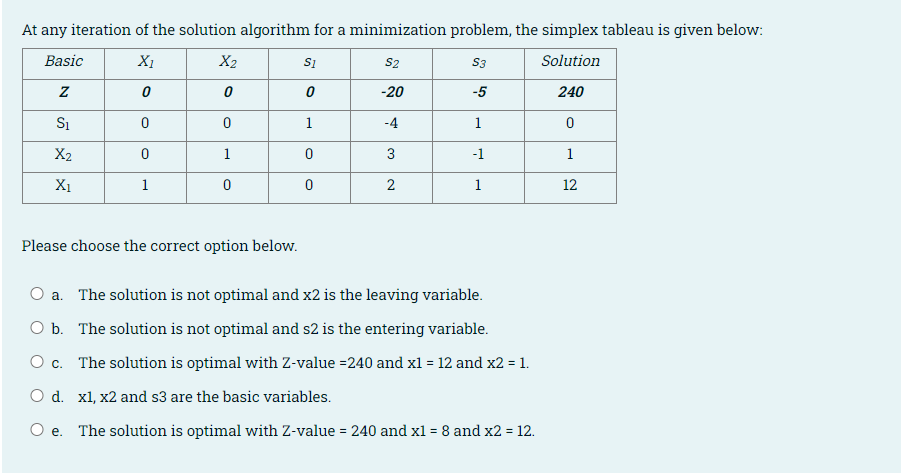
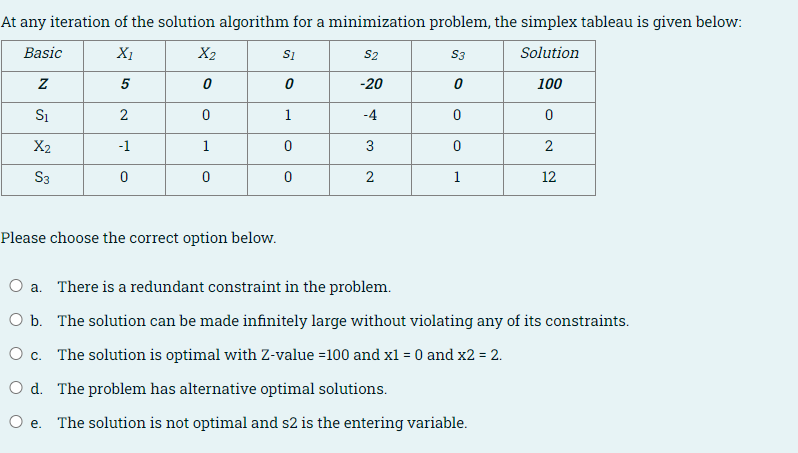
Question: At any iteration of the solution algorithm for a minimization problem, the simplex tableau is given below: Basic X1 X2 S2 S3 Solution Si Z



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


