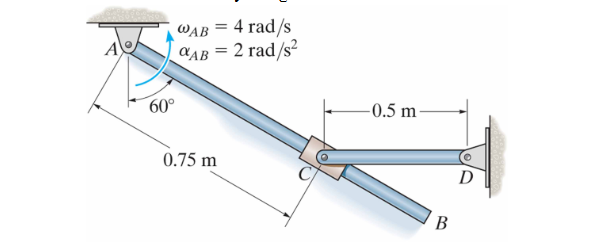
Question: At the instant shown, rod AB has an angular velocity of 4 rad / s and an angular acceleration of 2 rad / s .
At the instant shown, rod AB has an angular velocity of rads and an angular acceleration of rads Determine the angular velocity and acceleration of rod CD at this instant. The collar at C is pin connected to CD and slides freely along AB Please solve with MATLAB code template provided the acceleration is correct but I cant figure out what to change in order to make the velocity to be which should be the correct answer unless I am mistaken. Clear memory and screen
clear all;
clc;
Define unknown quantities in xy system
abc Acceleration of B wrt C on beam CD in i direction
vbc Velocity of B wrt C on beam CD in i direction
xacd Angular acceleration of beam CD in k direction
xvcd Angular velocity of beam CD in k direction
syms abc vbc xacd xvcd;
Create Unit Vectors in xy coordinates
i ;
j ;
k ;
Create Unit Vectors in XY coordinates R is rotation Matrix
Theta ; Angle from Xaxis to xaxis
R cosdThetasindTheta;
sindTheta cosdTheta; ;
XYZ Ri;j;k;
I XYZ:;
J XYZ:;
K XYZ:;
Set known quantities for Beam AB no slider connection
xVab k; Angular Velocity of Beam AB
xAab k; Angular Acceleration of Beam AB
Rba i; Vector from A to B in XY coordinates
Calculate velocity and acceleration of point B
due to rotation of Beam AB no slider connection
Vb crossxVabRba;
Ab crossxAabRba dotxVabxVabRba;
Set Motion of moving reference frame xy wrt XY
xV xvcdk;
xA xacdk;
Set Motion of B wrt moving frame xy
Rbc ij;
Vbc vbci;
Abc abci;
Calculate velocity and acceleration of point B
due to rotation of beam CD slider connection
Vb crossxVRbc Vbc;
Ab crossxARbc crossxVcrossxVRbccrossxVVbc Abc;
Set velocity and acceleration equations equal for point B and solve.
Z VbVbVbVbAbAbAbAb;
abcvbcxacd,xvcd solveZZZZ;
abc evalabc
vbc evalvbc
xacd evalxacd
xvcd evalxvcd
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


