Question: Atter reedinglvewing the article, Bite Ninja Uses Remote Gig Workers to Take Faster Fast Food Orders and the related Bile Ninja Product Video (as noted



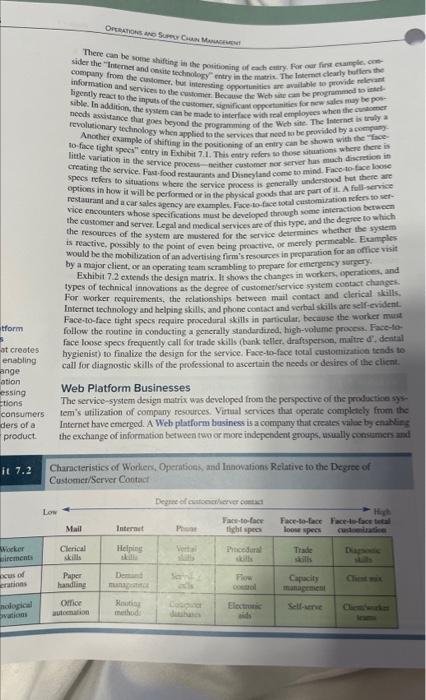
Atter reedinglvewing the article, Bite Ninja Uses Remote Gig Workers to Take Faster Fast Food Orders and the related Bile Ninja Product Video (as noted in Week 7: Things to do), do an intlal post and dencribe where you think the Bite Ninja worker fits into the Service-System Design Matrix (pp. 205-206). What pain points does this address for the Bite Ninja worker? What problems does this approach address for the restaurant? Does it make the service experiance any better of worie for the cuatomer? Do you feel this model will have a life beyond the special circumstances of the current pandemic? Bite Ninja Uses Remote Gig Workers to Take Faster Food Orders During the pandemic, finding employees has become difficult. The fast food industry has been hit especially hard by a shortage of employees. Many restaurant workers have ieft the industry for rearons including better pay. fewer health risks, and more stability. Additionally, enhanced unemployment benefits in the US, thave kept many workers out of the workforce. Bite Ninja offers a new approach to help alleviate the employee shortage. This service uses technology to allow workers to take orders at drive-thru restaurants remotely. Workers do not need to be in the restaurant to take the orders. Workers are provided by Bite Ninja, and can work for a variety of Bite Ninjars customers on an as needed basis. The customer at the drive-thru may not even know that their order is being taken remotely. Video Spotiight: Bite Ninja Product Video (Blar 20, 2021, Bite Ninja) This post is based on the TechCrunch ardicle, Bite Ninjo scoops up pre-seed funding to reimagine restouront working environments, by Christine Hail August 11,2021 , the Restauronit Eusiness Onfine article, As stoffing woes continue some restourants tum to technology, by joe Guspkowski, Aprw 28,2021 ; the NSW articie Qite Ninje outsources Video Spotlight: Bite Ninja Product Video (Mar 20, 2021, Bite Ninja) This post is based on the TechCrunch article, Bite Ninja scoops up pre-seed funding to reimagine restaurant working environments, by Christine Hall, August 11, 2021; the Restourant Business Online article, As staffing woes continue, some restourants turn to technology, by Joe Guszkowski, April 28, 2021; the NRN article, Bite Ninjo outsources drive-thru operations to gig employees working from home, by joanna Fantozz, March 12, 2021; and the YouTube wideo in the Spotlight image source: leof/123RK Discussion Questions: 1. Why would workers want this type of job? Guidance: The biggest advantage is that workers can work from home, selecting from a variety of hours from different restaurants across the country. By working from home, they avoid any travel time to work, have options of working at restaurants that are not in their geographic area, and avoid exposure to COVD-19. 2. What are the benefits to fast food restaurants for using this service? Guidance: The biggest advantage is that you can now draw on a workforce 2. What are the benefits to fast food restaurants for using this service? Guidance: The biggest advantage is that you can now draw on a workforce that extends beyond the local community, and from workers that cant or prefer not to go to work at the restaurant. Also, it allows restaurants to hire workers on an "as-needed" basis. Restaurants don" have to deal with setting schedules. Another advantage: Bite Ninja can share workers across multiple restaurants. For example, a Bite Ninja worker could transfer from one restaurant to another as demand changes, possibly changing time zones. 3. Are there any drawbacks to this service? Guidance: As long as the customer doesn't see a degradation in order-taking performance, there are few drawbacks. The biggest issues will deal with the technology. Is the restaurant's internet reliable and fast enough to support remote order taking? Also, can the technology integrate with a restaurant's existing systems? And, of course, gig workers at Bite Ninja must be available when restaurants need them. 4. What are other alternatives to help fast food restaurants with their employee shortage? Guidance: One option is improving the systems used to hire employees: Many fast food restaurants are turning to online services such as Landed and Seasoned to assist. Landed uses Al to help identify potential employees. Some franchises are setting up special campaigns to recruit employees. Another option is to improve performance to reduce the number of workers. that it takes to fill orders. This has an additional advantage of cost savings. Sonics, McDonalds, and others are turning to voice automation using Al to take your order. Another approach is to change the order taking process by pushing orders to apps or online, thus eliminating the traditional order taking process at fast food restaurants. Although not ideal, some restaurants are reducing their hours, and using their available workforce to staff these reduced hours. Published On: August 31, 2021 - By Ross L. Fink, Ph.D. Tagsy capacity, gig economy, scheduling service design, service processes, technology, wating airfares, botel specials an weekends, and wo on. This is alwo a foed illustration of why it is difficult to seporate the of cekations manapenent fusctioes fmon macketistg in services. Waiting line models, which are discussed in this chapter, powide a powerfinl mudhematieal tool for analy ziege many commion senice situatians. Quenticas soch as how many tellers we should have in a bask or how many computer kevers we ncod in an Interner vervice operation can be analyzed with these modelk. Theve models an be casaly implentented using spreadsheets. Structuring the Service Encounter: Service-System Design Matrix Service encounters can be cockigured in a mamber of differeat ways. The service-system design matrix in Eathibit 7.1 identifes six common aliermatives. The top of the mutrix shoms the degree of castometherver coesact the bulentid care: which is physically scparated froen the cesomer, the permatle syatem, which is penctrable by the customer tia photic or face-1o-face ocotact and the andefrie sudem, which is both penctrable and reactive so the cultomer's requertats. The left side of the matrix shoas what we believe to be a logical marketing ogsetaniry namely, that the greater the amoint of eontace, the gremer the sales opportunity at the oime when the service is delivered; the right side.sbous the ampact oin froduction elfatich y as ahe custamer eierts more influeace on the opertion. The entrices withis the matrix liat the mays ie which servise cas be delivered: At one: the other extreme, custoreers. Thabe it their wuy" shrouph fuce-to-fose onnts. The remaining four estries in the exhllit contain varying degrots if inderation As one would guess, profuction stficieecy docimper as the cestomer has incre conas mail, allows the mystem in wock mone cfficiently becase the curanher is unable bo. sig: additional prodact sales. Face-fo-face eigld spows require procelleal the-lhs in purticular. because the wutker amat hygientat) to finalize the design for the icrvice. Face-to-fac bofal covenimatien teside to Web Platform Businesses Internet have emergod: A Webplatformi braiocos a a oungany thur creales value by enablim Caiometerver Contset There can be sotne shifting ia the poiticeing of each eatry, for our find cuang ie, oneneeds assidance that eoes beyool the propramining of the Web site. The Internet is trally a revolutionary tectinology when applicd to the srivices thar aced wo be peovided by a comifasAncelser example of shiftiang in the poriticeing of an eritry can be stown with the "ficecreating the service. Fast-food restarants ath Dispeyland come to mind. Face-to-face loose specs refers to situations where the service process is generally understood bet thete are options in herw it will be perfiomed or in the physical goods that are part of it. A full-service restaurant and a car sales agency are caamples. Face io-face total catsomisation refers to setvice encounters whose specifications mest be developed through wome interaction betwecn the custoaver and serves, Legal and medical services are of this type, and the degree to whech the resources of the system are nusered for the kervice determines whether the system is reactive, possibly to the point of even being preactive, of mercly permeable. Exanpples would be the mohilization of an advertising firm's reseures ia preparation for an office visit by a major client, or an operating team sctambliag so prepare for energetsy sarpery. Exhibit 7.2 extends the desiga matrix. It shoas the chatges in workers, operatices, and types of techinical innovations as the degree of custoenerfservice systeia cootact changeh. For worker requifements, the telationships betweed mail contact and clerical ikills, Internet technology and helping skills, and phone contact and verbal skills are self-evifent. Face-to-face tight specs reqaire procedural skitls in particular, because the worker mur follow the routine in conducting a gerserally standardured, hugh-volsme prosen. Face-taface loase specs frequently call foe trade skills (bank teflec. draftsperion, maitre d", deatal hygienist) to finalize the design for the service. Face-to-fece total custornizatica tends to call for diagnostic skills of the professional to ascertuin the needi or desires of ale elicat. Web Platform Businesses The service-system design matrix was developed from the perspective of the production syy tem's utilization of company resources. Virial services that operite complachy fman the Internet have emerged. A Web platform besiness is a company that creates valee by enaklin. the exchange of information between two or more independent groups, usually consumers as Chameteristics of Workens, Operatioes, and Inaovalions Relative to the Degree of Customet/Server Contacf
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


