Question: B C D E F H I 2 3 Excel Basic Skills and Formula Tutorials 4 5 Cell Reference: Allows you to refer to data
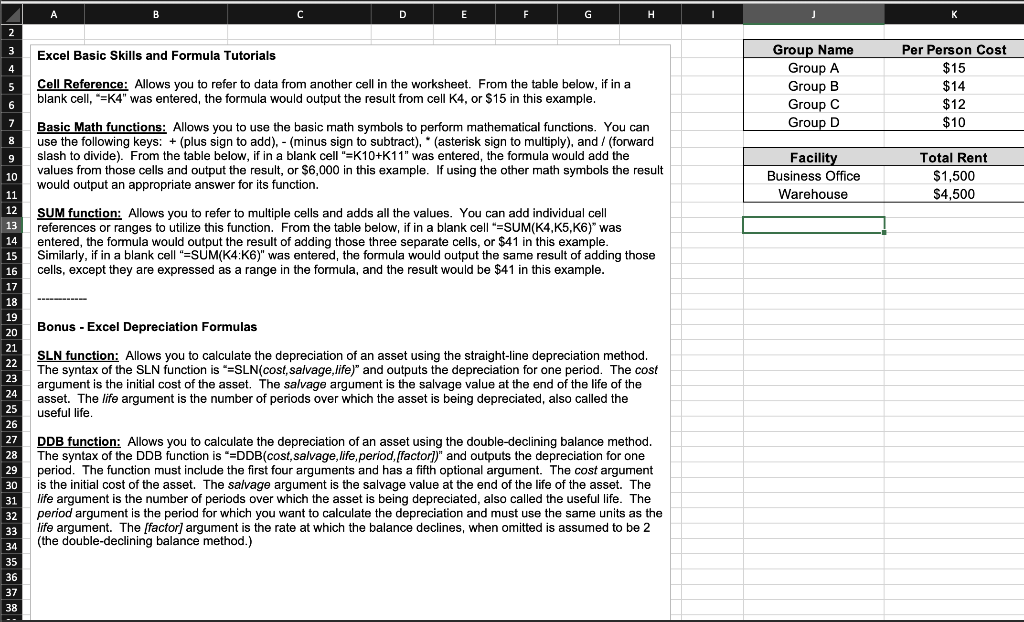
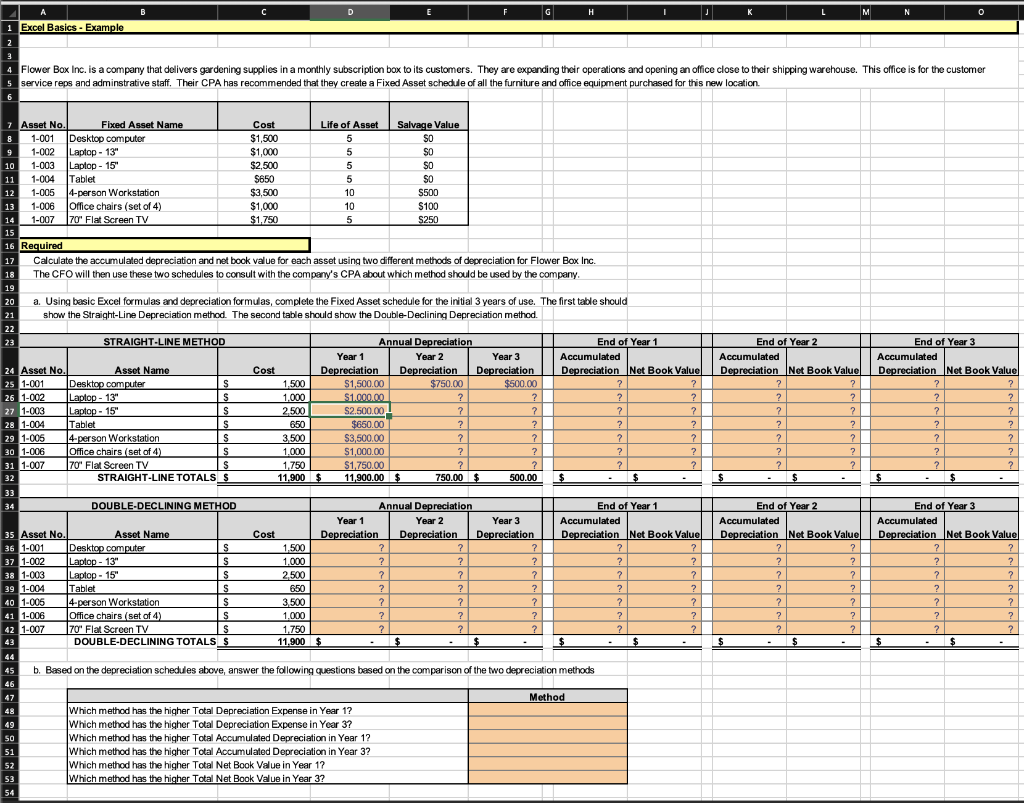
B C D E F H I 2 3 Excel Basic Skills and Formula Tutorials 4 5 Cell Reference: Allows you to refer to data from another cell in the worksheet. From the table below, if in a blank cell, "=K4" was entered, the formula would output the result from cell K4, or $15 in this example. Group Name Group A Group B Group C Group D Per Person Cost $15 $14 $12 $10 6 7 8 9 Basic Math functions: Allows you to use the basic math symbols to perform mathematical functions. You can use the following keys: + (plus sign to add),- (minus sign to subtract), * (asterisk sign to multiply), and / (forward slash to divide). From the table below, if in a blank cell "=K10+K11" was entered, the formula would add the values from those cells and output the result, or $6,000 in this example. If using the other math symbols the result would output an appropriate answer for its function. Facility Business Office Warehouse Total Rent $1,500 $4,500 SUM function: Allows you to refer to multiple cells and adds all the values. You can add individual cell references or ranges to utilize this function. From the table below, if in a blank cell"=SUM(K4, K5, K6)" was entered, the formula would output the result of adding those three separate cells, or $41 in this example. Similarly, if in a blank cell"=SUM(K4:K6)" was entered the formula would output the same result of adding those cells, except they are expressed as a range in the formula, and the result would be $41 in this example. ---- Bonus - Excel Depreciation Formulas 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 SLN function: Allows you to calculate the depreciation of an asset using the straight-line depreciation method. The syntax of the SLN function is "=SLN(cost, salvage,life)" and outputs the depreciation for one period. The cost argument is the initial cost of the asset. The salvage argument is the salvage value at the end of the life of the asset. The life argument is the number of periods over which the asset is being depreciated, also called the useful life. DDB function: Allows you to calculate the depreciation of an asset using the double-declining balance method. The syntax of the DDB function is "=DDB(cost, salvage,life, period, (factor])" and outputs the depreciation for one period. The function must include the first four arguments and has a fifth optional argument. The cost argument is the initial cost of the asset. The salvage argument is the salvage value at the end of the life of the asset. The life argument is the number of periods over which the asset is being depreciated, also called the useful life. The period argument is the period for which you want to calculate the depreciation and must use the same units as the life argument. The (factor] argument is the rate at which the balance declines, when omitted is assumed to be 2 (the double-declining balance method.) H . N 1 Excel Basics - Example 2 Flower Box Inc. is a company that delivers gardening supplies in a monthly subscription box to its customers. They are expanding their operations and opening an office close to their shipping warehouse. This office is for the customer s service reps and adminstrative staff. Their CPA has recommended that they create a Fixed Asset schedule of all the furniture and office equipment purchased for this new location . . 1-002 7 Asset No. Fixed Asset Name Cost Life of Asset Salvage Value 8 1-001 Desktop computer $1,500 5 SO Laptop - 13" $1,000 5 SO 10 1-003 Laptop - 15" $2,500 5 SO 11 1-004 Tablet $650 5 SO 12 1-005 4-person Workstation $3,500 10 $500 13 1-006 JOffice chairs (set of 4) $1,000 10 $100 14 1-007 70 Flat Screen TV $1.750 5 S250 15 16 Required 17 Calculate the accumulated depreciation and net book value for each asset using two different methods of depreciation for Flower Box Inc. 18 The CFO will then use these two schedules to consult with the company's CPA about which method should be used by the company 19 20 a. Using basic Excel formulas and depreciation formulas, complete the Fixed Asset schedule for the initial 3 years of use. The first table should 21 show the Straight-Line Depreciation method. The second table should show the Double-Declining Depreciation method. 22 23 STRAIGHT-LINE METHOD Annual Depreciation End of Year 1 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Accumulated 24 Asset No. Asset Name Cost Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Net Book Value 25 1-001 Desktop computer S S 1.500 $1,500.00 $750.00 $500.00 ? ? 26 1-002 Laptop - 13" S S 1.000 $1.000.00 ? ? ? ? ? ? 27 1-003 Laptop - 15" S 2500 $2,500.00 ? ? ? ? ? 28 1-004 Tablet S S 650 $650.00 ? ? ? ? ? ? 29 1-005 14-person Workstation $ 3,500 $3,500.00 ? ? ? 2 ? ? 30 1-006 Office chairs (set of 4) S 1.000 $1,000.00 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 31 1-007 70' Flat Screen TV IS 1,750 $1,750.00 ? ? 7 32 STRAIGHT-LINE TOTALS S 11.900 $ 11.900.00 $ 750.00 $ 500.00 $ $ 33 DOUBLE-DECLINING METHOD Annual Depreciation End of Year 1 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Accumulated 35 Asset No. Asset Name Cost Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Net Book Value 36 1-001 Desktop computer S 1,500 ? ? ? ? ? 371-002 Laptop - 13" S 1.000 ? ? ? ? ? 38 1-003 Laptop - 15" $ 2500 7 ? 7 2. ? ? 39 1-004 Tablet S 650 ? ? ? ? ? ? 40 1-006 4-person Workstation $ S 3,500 ? ? ? ? ? ? 2 41 1-006 Office chairs (set of 4) s 1.000 ? ? ? ? ? ? 42 1-007 70' Flat Screen TV S 1,750 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 43 DOUBLE-DECLINING TOTALS S 11.900 $ $ $ $ . $ 44 45 b. Based on the depreciation schedules above, answer the following questions based on the comparison of the two depreciation methods 46 47 Method 48 Which method has the higher Total Depreciation Expense in Year 1? 49 Which method has the higher Total Depreciation Expense in Year 3? 50 Which method has the higher Total Accumulated Depreciation in Year 1? 51 Which method has the higher Total Accumulated Depreciation in Year 3? 52 Which method has the higher Total Net Book Value in Year 1? 53 Which method has the higher Total Net Book Value in Year 3? 54 End of Year 2 Accumulated Depreciation Net Book Value ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 1 ? ? 21 $ $ End of Year 3 Accumulated Depreciation Net Book Value ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? S $ 34 End of Year 2 Accumulated Depreciation Net Book Value ? ? 2 ? 2 ? ? ? ? 2 ? 2 ? ? ? ? $ - $ $ End of Year 3 Accumulated Depreciation Net Book Value ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? $ $ B C D E F H I 2 3 Excel Basic Skills and Formula Tutorials 4 5 Cell Reference: Allows you to refer to data from another cell in the worksheet. From the table below, if in a blank cell, "=K4" was entered, the formula would output the result from cell K4, or $15 in this example. Group Name Group A Group B Group C Group D Per Person Cost $15 $14 $12 $10 6 7 8 9 Basic Math functions: Allows you to use the basic math symbols to perform mathematical functions. You can use the following keys: + (plus sign to add),- (minus sign to subtract), * (asterisk sign to multiply), and / (forward slash to divide). From the table below, if in a blank cell "=K10+K11" was entered, the formula would add the values from those cells and output the result, or $6,000 in this example. If using the other math symbols the result would output an appropriate answer for its function. Facility Business Office Warehouse Total Rent $1,500 $4,500 SUM function: Allows you to refer to multiple cells and adds all the values. You can add individual cell references or ranges to utilize this function. From the table below, if in a blank cell"=SUM(K4, K5, K6)" was entered, the formula would output the result of adding those three separate cells, or $41 in this example. Similarly, if in a blank cell"=SUM(K4:K6)" was entered the formula would output the same result of adding those cells, except they are expressed as a range in the formula, and the result would be $41 in this example. ---- Bonus - Excel Depreciation Formulas 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 SLN function: Allows you to calculate the depreciation of an asset using the straight-line depreciation method. The syntax of the SLN function is "=SLN(cost, salvage,life)" and outputs the depreciation for one period. The cost argument is the initial cost of the asset. The salvage argument is the salvage value at the end of the life of the asset. The life argument is the number of periods over which the asset is being depreciated, also called the useful life. DDB function: Allows you to calculate the depreciation of an asset using the double-declining balance method. The syntax of the DDB function is "=DDB(cost, salvage,life, period, (factor])" and outputs the depreciation for one period. The function must include the first four arguments and has a fifth optional argument. The cost argument is the initial cost of the asset. The salvage argument is the salvage value at the end of the life of the asset. The life argument is the number of periods over which the asset is being depreciated, also called the useful life. The period argument is the period for which you want to calculate the depreciation and must use the same units as the life argument. The (factor] argument is the rate at which the balance declines, when omitted is assumed to be 2 (the double-declining balance method.) H . N 1 Excel Basics - Example 2 Flower Box Inc. is a company that delivers gardening supplies in a monthly subscription box to its customers. They are expanding their operations and opening an office close to their shipping warehouse. This office is for the customer s service reps and adminstrative staff. Their CPA has recommended that they create a Fixed Asset schedule of all the furniture and office equipment purchased for this new location . . 1-002 7 Asset No. Fixed Asset Name Cost Life of Asset Salvage Value 8 1-001 Desktop computer $1,500 5 SO Laptop - 13" $1,000 5 SO 10 1-003 Laptop - 15" $2,500 5 SO 11 1-004 Tablet $650 5 SO 12 1-005 4-person Workstation $3,500 10 $500 13 1-006 JOffice chairs (set of 4) $1,000 10 $100 14 1-007 70 Flat Screen TV $1.750 5 S250 15 16 Required 17 Calculate the accumulated depreciation and net book value for each asset using two different methods of depreciation for Flower Box Inc. 18 The CFO will then use these two schedules to consult with the company's CPA about which method should be used by the company 19 20 a. Using basic Excel formulas and depreciation formulas, complete the Fixed Asset schedule for the initial 3 years of use. The first table should 21 show the Straight-Line Depreciation method. The second table should show the Double-Declining Depreciation method. 22 23 STRAIGHT-LINE METHOD Annual Depreciation End of Year 1 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Accumulated 24 Asset No. Asset Name Cost Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Net Book Value 25 1-001 Desktop computer S S 1.500 $1,500.00 $750.00 $500.00 ? ? 26 1-002 Laptop - 13" S S 1.000 $1.000.00 ? ? ? ? ? ? 27 1-003 Laptop - 15" S 2500 $2,500.00 ? ? ? ? ? 28 1-004 Tablet S S 650 $650.00 ? ? ? ? ? ? 29 1-005 14-person Workstation $ 3,500 $3,500.00 ? ? ? 2 ? ? 30 1-006 Office chairs (set of 4) S 1.000 $1,000.00 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 31 1-007 70' Flat Screen TV IS 1,750 $1,750.00 ? ? 7 32 STRAIGHT-LINE TOTALS S 11.900 $ 11.900.00 $ 750.00 $ 500.00 $ $ 33 DOUBLE-DECLINING METHOD Annual Depreciation End of Year 1 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Accumulated 35 Asset No. Asset Name Cost Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation Net Book Value 36 1-001 Desktop computer S 1,500 ? ? ? ? ? 371-002 Laptop - 13" S 1.000 ? ? ? ? ? 38 1-003 Laptop - 15" $ 2500 7 ? 7 2. ? ? 39 1-004 Tablet S 650 ? ? ? ? ? ? 40 1-006 4-person Workstation $ S 3,500 ? ? ? ? ? ? 2 41 1-006 Office chairs (set of 4) s 1.000 ? ? ? ? ? ? 42 1-007 70' Flat Screen TV S 1,750 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 43 DOUBLE-DECLINING TOTALS S 11.900 $ $ $ $ . $ 44 45 b. Based on the depreciation schedules above, answer the following questions based on the comparison of the two depreciation methods 46 47 Method 48 Which method has the higher Total Depreciation Expense in Year 1? 49 Which method has the higher Total Depreciation Expense in Year 3? 50 Which method has the higher Total Accumulated Depreciation in Year 1? 51 Which method has the higher Total Accumulated Depreciation in Year 3? 52 Which method has the higher Total Net Book Value in Year 1? 53 Which method has the higher Total Net Book Value in Year 3? 54 End of Year 2 Accumulated Depreciation Net Book Value ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 1 ? ? 21 $ $ End of Year 3 Accumulated Depreciation Net Book Value ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? S $ 34 End of Year 2 Accumulated Depreciation Net Book Value ? ? 2 ? 2 ? ? ? ? 2 ? 2 ? ? ? ? $ - $ $ End of Year 3 Accumulated Depreciation Net Book Value ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? $ $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


