Question: Back Project 4 TwoDTree.pdf goal is to implement a data structure, Two - dimensional ( 2 D ) Trees, that let us use both orderings.
Back Project TwoDTree.pdf
goal is to implement a data structure, Twodimensional D Trees, that let us use both orderings.
Twodimensional trees are a data structure very similar to binary search trees. They divide up geometric space in a manner convenient for use in range searching and other problems.
The idea is to build a binary tree using both the and coordinates of the points as keys. The levels of the tree can split either on the or the y coordinate; typically, the splits alternate between the two dimensions.
At every node in the twodimensional tree that splits on the following invariant holds:
all the points that have an coordinate value less than or equal to the nodes value are found in the left child;
all the points with a greater value are in the right child.
Nodes that split on y are similar: less than or equal to y values go on the left, larger on the right.
Searching in the tree
Like binary search trees, a D tree can be used to find elements it contains, by walking recursively from the root of the tree downward, making leftright choices at each node depending on the value of the point being searched for relative to the split value and axis of the current node.
In a D tree, it is also possible to search for all elements found within some spatial extent, such as a rectangle in the D space. To implement this kind of search, the rectangle is compared against the split value at each point. If the rectangle overlaps the split value, the algorithm must search both children of the current node.
Creating a tree
To create the tree each point is inserted into the tree. The algorithm walks down the tree to find the location that would contain the point if it were in the tree. When this leaf is reached, a new node containing the
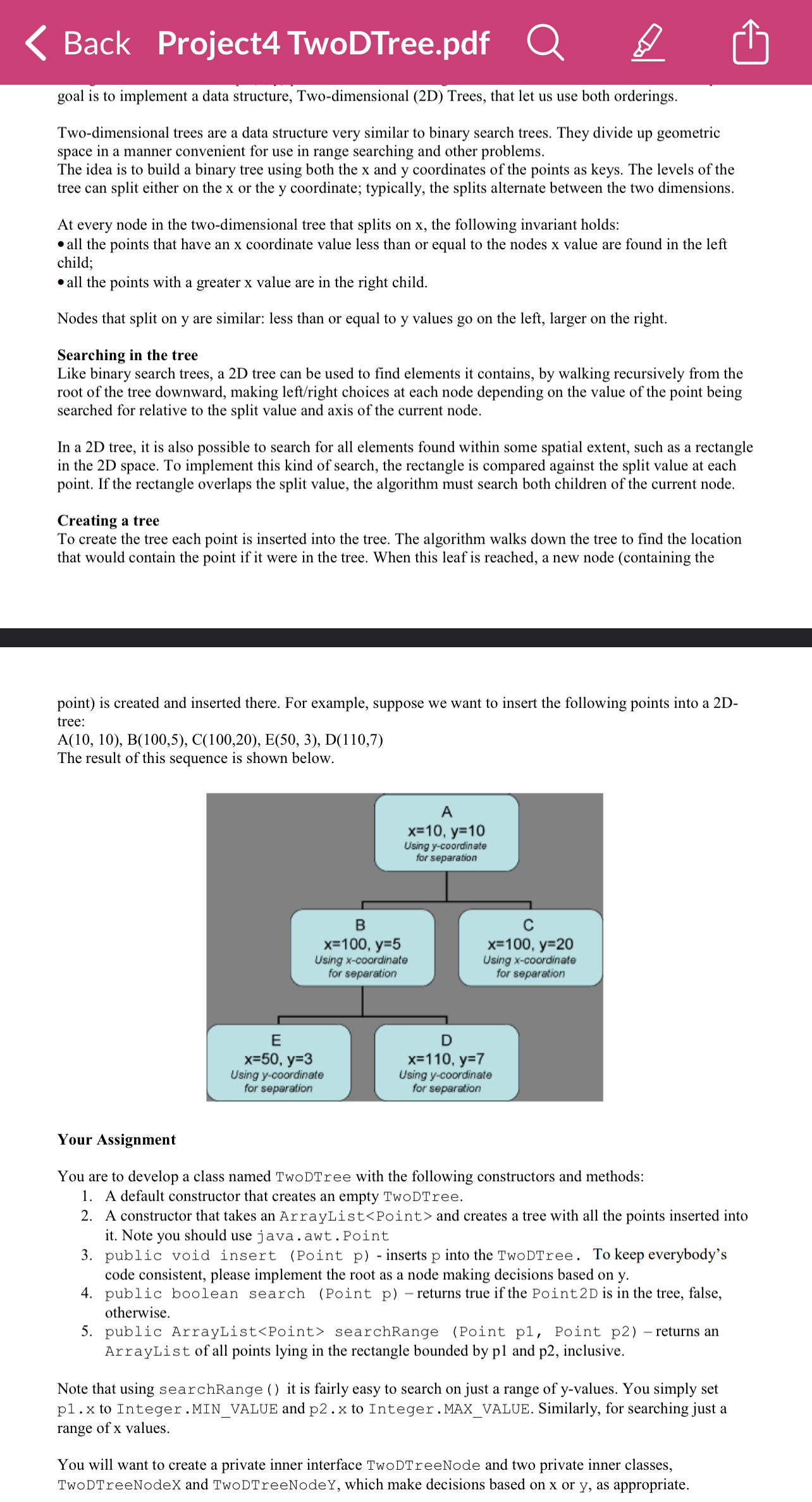
point is created and inserted there. For example, suppose we want to insert the following points into a Dtree:
The result of this sequence is shown below.
Your Assignment
You are to develop a class named TwoDTree with the following constructors and methods:
A default constructor that creates an empty TwoDTree.
A constructor that takes an ArrayListyp
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


