Question: Background: Even though the Big-(0) will distinguish algorithms with different growth rates,it does so only for large input sizes. In other words, sometimes a worse
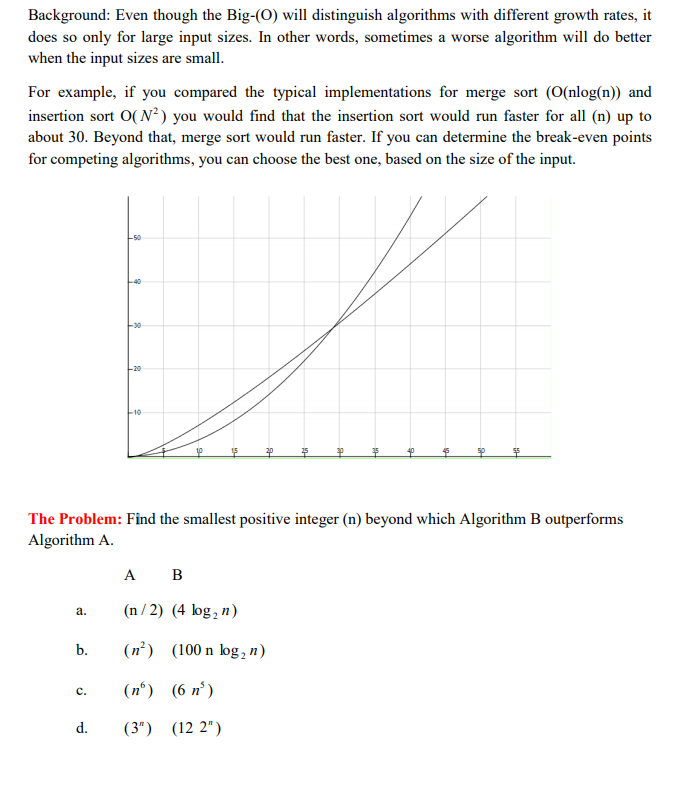
Background: Even though the Big-(0) will distinguish algorithms with different growth rates,it does so only for large input sizes. In other words, sometimes a worse algorithm will do better when the input sizes are small. For example, if you compared the typical implementations for merge sort (O(nlog(n)) and insertion sort O(N2) you would find that the insertion sort would run faster for all (n) up to about 30. Beyond that, merge sort would run faster. If you can determine the break-even points for competing algorithms, you can choose the best one, based on the size of the input. 50 30 10 The Problem: Find the smallest positive integer (n) beyond which Algorithm B outperforms Algorithm A. A B a. (n/2) (4 log2 n) b. ( (100 n log, n) c. (n) (6n) d. (3") (12 2")
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


