Question: Background: Linear Programming is used to inform business decisions. It involves constructing a Linear Programming model then solving the model to find the optimum choices
Background: Linear Programming is used to inform business decisions. It involves constructing a Linear Programming model then solving the model to find the optimum choices for the decision variables. Mathematically the optimal choice for the set of decision variables is the choice that masimizes or minimizes depending on the type of problem addressed while satisfying all of the constraints that apply.
EXCEL offers a practical way of finding the optimal solution even if the number of decision variables andor constraints is larger than can be handled by graphical methods. The EXCEL tool Solver is used for this.
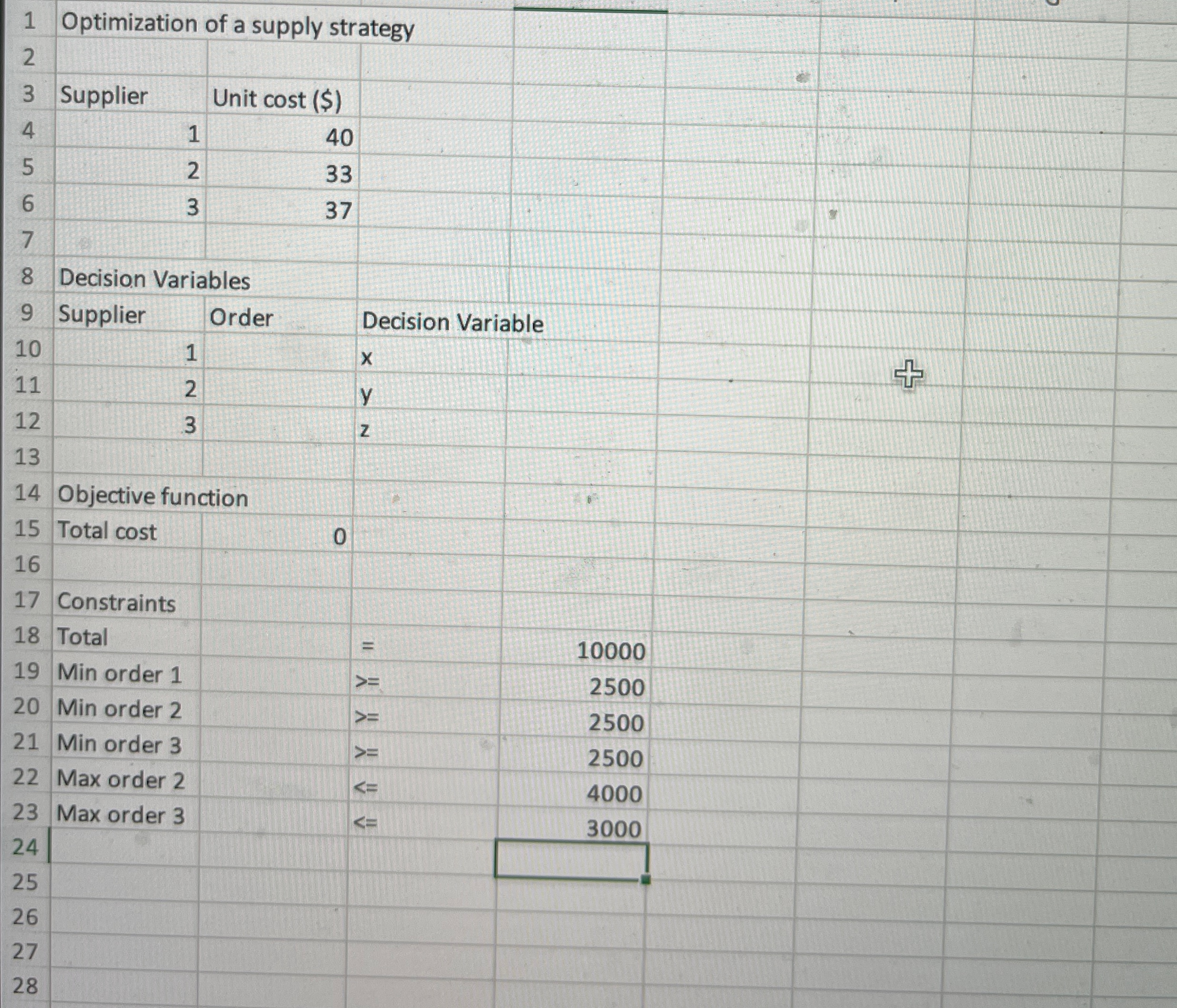
About the lab: In this Lab, Linear Programming LP is used to optimize a supply strategy for a manufacturer who needs to order units of a component part. There are three possible suppliers of the component. Each supplier has a set price per unit for the component and two of the suppliers have limits on the number of units they can supply in the required time, as shown in the table below
tableSupplierPrice per unit $Maximum number of units.Supplier Unlimited greater than Supplier Supplier
Also, the manufacturer wants to maintain each of the suppliers as a possible supplier for future orders; so the manufacturer decides to order at least of the total number of units from each supplier.
In the LP model, the decision variables are the number of units ordered from each of the manufacturers. The manufacturer wants to minimize the cost of the total order of units subject to the constraints described above.Directions
Let and represent the order number of units to be placed with Suppliers and respectively. Before programming in the EXCEL worksheet, write out the formula for the total cost of the order in mathematical equation form and write each constraint as an equality or inequality. Write the constraints in such a way that only a number appears on the righthandside. In each case write the number on the righthandside of the constraint as a number of units eg of the total order is
In Cells B to B place the initial guesses for the order from each supplier, ie units from Supplier and units from each of Supplier and Supplier
In Cell B construct a formula to calculate the total cost of the order. Be sure to use cell references for the numbers of units and the cost per unit
In Cells B to B type a formula to calculate the quantity that is being limited by the constraint.
Open the Solver dialogue box by clicking on the Solver icon in the Data ribbon. Complete the required information including the constraints. Dont forget any implicit constraints Run Solver and accept the solution it finds.
Save your completed workbook and submit it via the Moodle page.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


