Question: 1. Criticize the attached article Your project work is based on a research work (case studies done using system analysis technique). Read the paper carefully






1. Criticize the attached article
- Your project work is based on a research work (case studies done using system analysis technique).
- Read the paper carefully and understand the intent of the research work!
- Re-work the problem based on available information (if required, assume realistic values).
- Identify if any variations in the formulation and solution of the problem.
- Criticize the article based on your results.
- Draw your own conclusions and recommendations.
- Prepare a report using standard reporting format (Presentation of the report with clear and necessary steps will be credited)
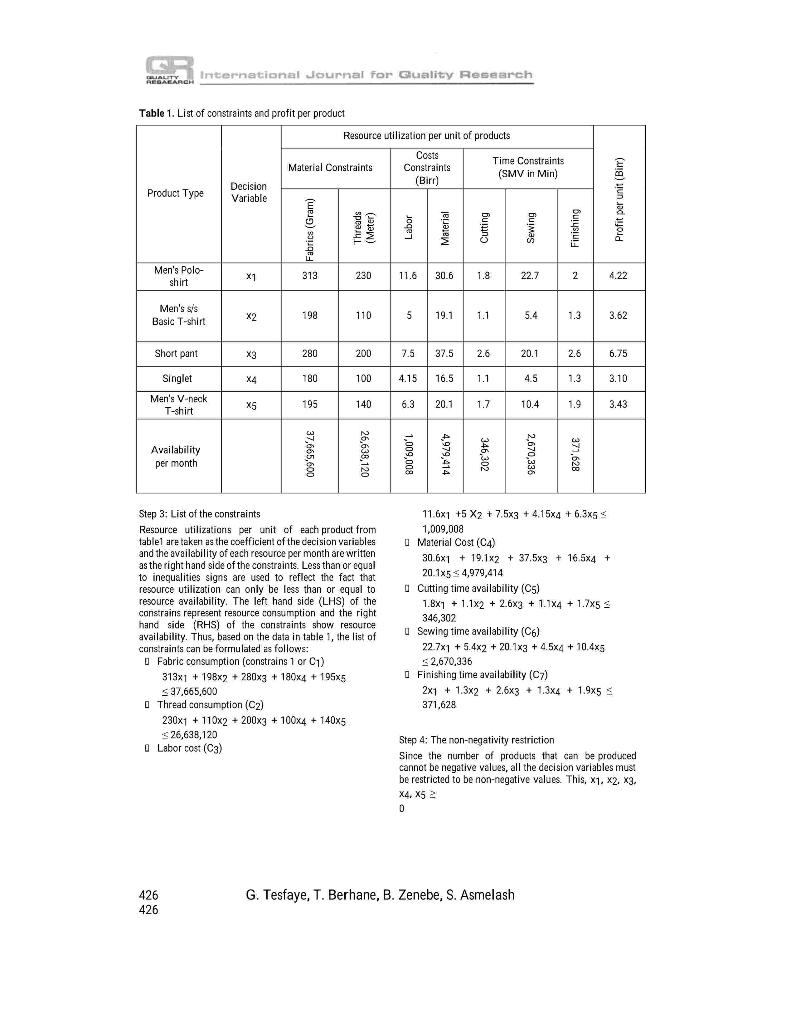
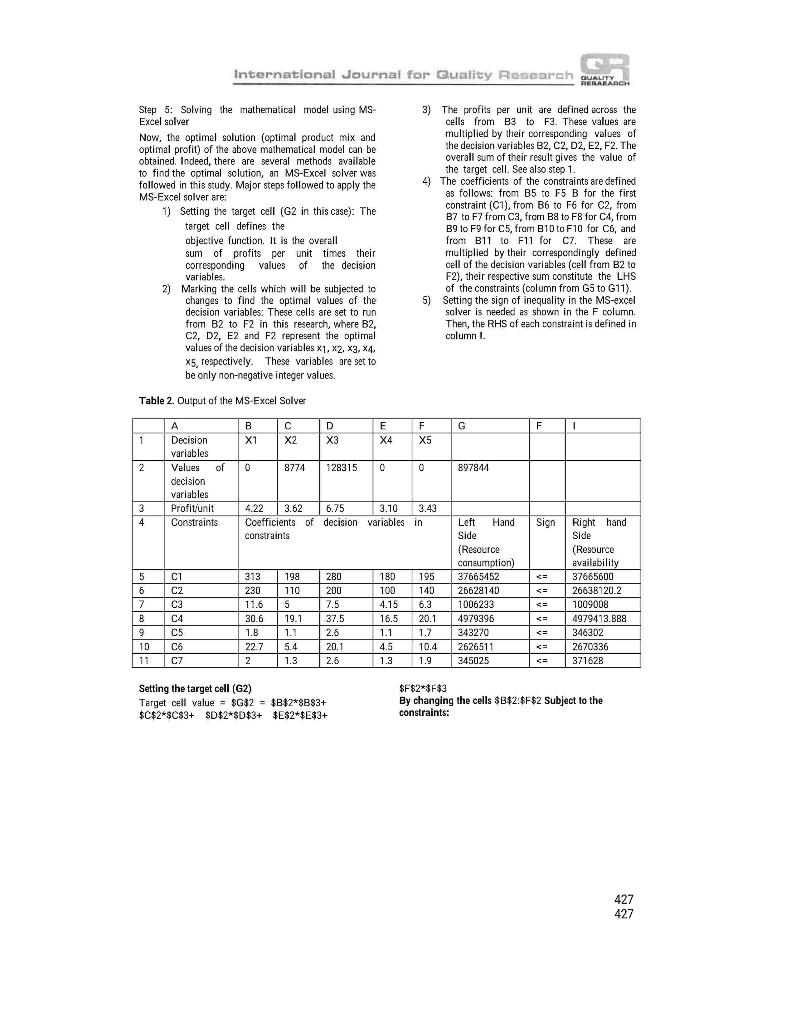
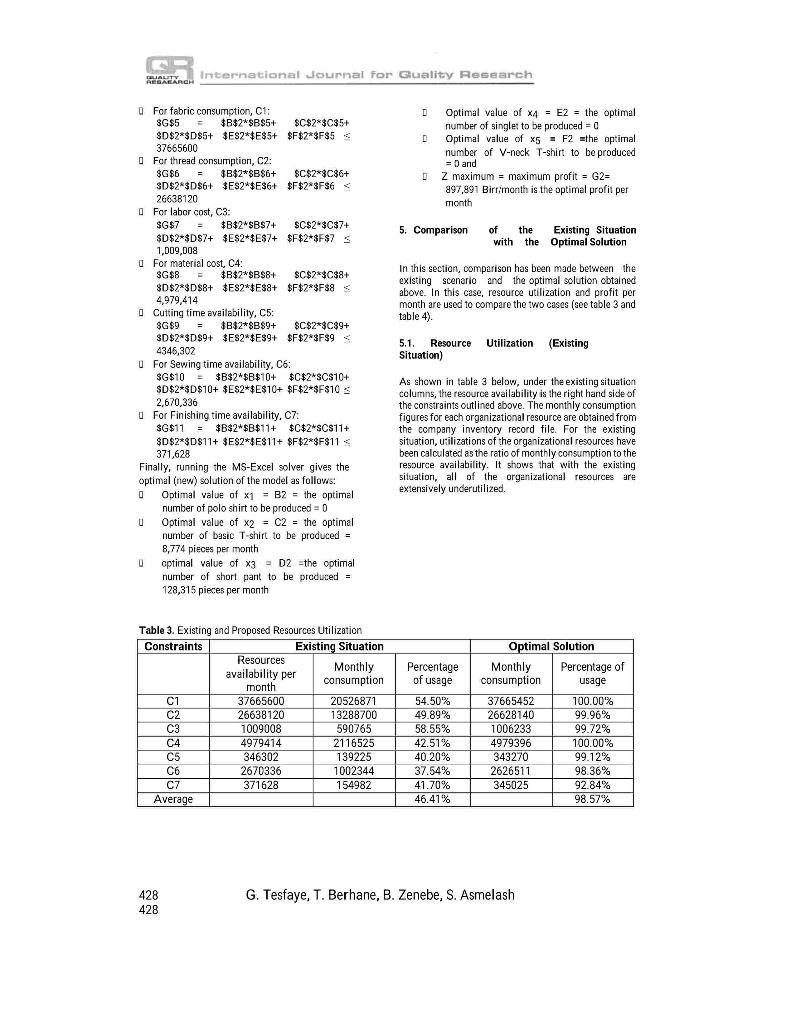
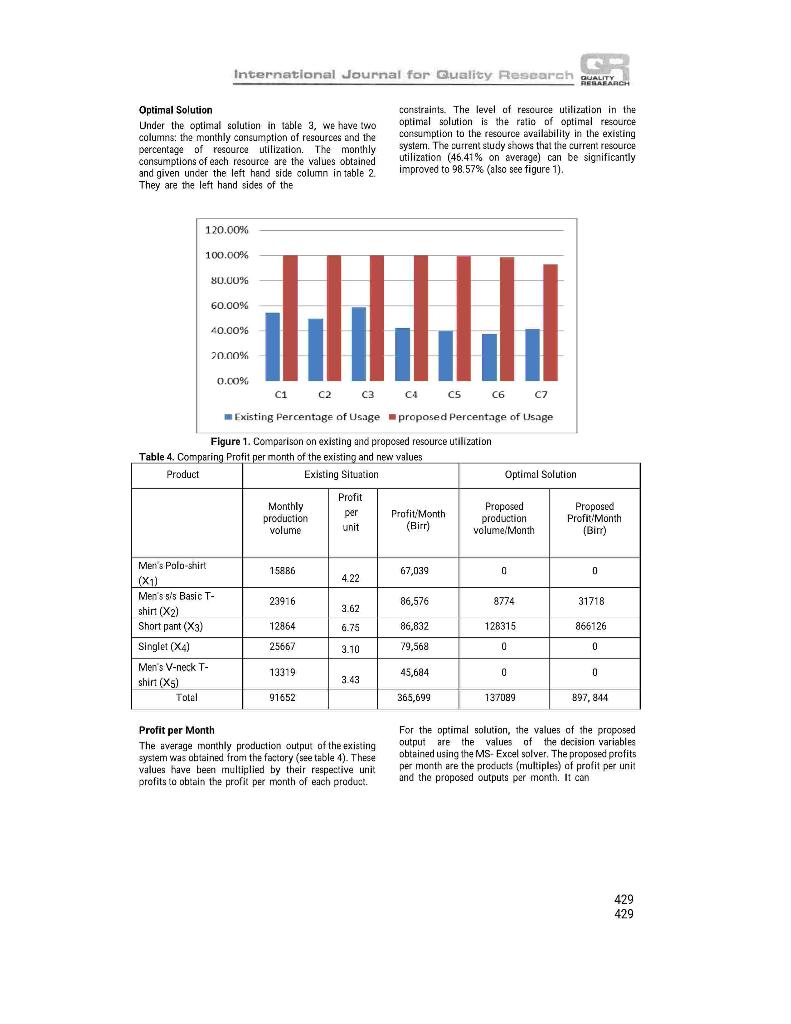
International Journal for Quality Research 10(2) 421 432 ISSN 1800-6450 A LINEAR PROGRAMMING METHOD TO ENHANCE RESOURCE UTILIZATION CASE OF ETHIOPIAN APPAREL SECTOR Gezahegn Tesfaye Tesfu Berhane Berihu Zenebe Senait Asmelash Article info: Received 20.07.2015 Accepted 09.02.2016 UDC 638.124,8 DOI 10.1842 VIJQR10.02-12 Abstract: The Ethiopian industrial development strategy is characterized by export-led and labor intensive industrialization. The count e country is energing as the most important investment destination in its apparel sector. Thought this sector is expected to generate more income from the export market, its export earnings remain trivial mainly due to the inefficient organizational resource utilization. One of the competent techniques that help companies to efficiently improve the use of their resources to increase their profit is linear programming. In apparel manufacturing fims, efficient use of materials such as fabrics and sewing threads and processing time at different stages of production as well as minimization of labor and materials cost are necessary to enhance their profitability. Cutting, sewing, and finishing operations deserve more attention for apparel process optimization. However, the issue of proper resource allocation remains an unsolved problem within the Ethiopian apparel industry. The aim of this research is to devise efficient resource utilization mechanism for Ethiopian apparel sector to improve their resource utilization and profitability, taking one of the garment factories engaged in the export market as a case study. Five types of products the company is currently producing the amount of resources employed to produce each unit of the products, and the value of pro'it per unit from the sale of each products have been collected from the case company. The monthly availability of resources utilized and the monthly production volume of the five products have also been collected from the company. The data gathered was mathematically modeled using a linear programming technique, and solved using MS-Excel solver. The findings of the study depicts that all of the organizational resources are severely underutilized. This research proved that the resource utilization of the case company can be improved from 46.41% of the current resource utilization to 98.57% This indicates that the new solution provides very significantly improvement in organizational resource utilization. At the same time, with the new solution, the total profit per month of the case company can be increased from 365,699 birr per month to 897,844 birr per month (ie, with an increment of 145.5%). Finally, it is concluded that this remarkable profil incrernent of the company can certainly enhance its global competitiveness. Keywords: apparel sector, linear programming technique, resource utilization, optimal solution 421 421 LALITY REABARCH International Journal for Guality Research 1. Introduction As the consequence of globalization and technological developments, the worldwide business environment has turned out to be highly competitive (Momaya, 2009). A manufacturing company's survival in an increasingly competitive market closely depends upon its ability to produce highest quality products at lowest possible cost (Kumar, 2010). More specifically Ezeme and Amakom (2012) asserted that organizations in the world are challenged by shortages of production inputs which can consequently lead to low capacity utilization and low production outputs. The authors stated that either cast minimization or output maximization is necessary to enhance the growth and competitiveness of organizations. Thus, companies have to create mechanisms that can support the improvement of their performances both in the national and international markets. Companies need to be aware of their internal processes, resource utilization and management to be competitive. Hence organizational resources are limited; every manufacturing corripany must use their resources optimally to increase their profit (Yalcinsay et al., 2014). However, a key challenge faced by these organizations is how to allocate scarce resources among activities. Linear programming is a method of allocating resources in an optimal way. It is one of the most widely used operations research tools (Reeb and Leavengood, 1998) to determine optimal resource utilization (Candes and Tao, 2005). Different products require different amount of production resources at several stages of production. They also have different selling prices and therefore, have different unit profits. The production process may also be subjected to different conditions. The linear programming technique will be used to determine the product mix that will maximize the total profit. It is the most flexible and extensively applied quantitative techniques. It is an efficient method for determining an optimal solution from a large number of alternatives to meet a specified objective functions subject to various constraints and restrictions (Shaheen and Ahmad, 2015) Using a linear programming method, we find the optimal, or most efficient, way of using limited resources to achieve the objective of the situation. Furthermore, as Oliver (2012) stated, linear programming refers to the problem of optimizing a linear objective function of several variables subject to a set of linear equality or inequality constraints. Linear programming is a mathematical technique and an aspect of operations research whose primary function is to allocate limited resources of the firm (Andawei, 2014). It refers to planning process that allocates resources labor, materials, machines, and capital in the best possible (optimal) way so that costs are minimized or profits are maximized (Reeb and Leavengood, 1998). One of the application areas of LPP is the optimization of the product mix of organizations (Ezema and Amakom, 2012). After citing the work of Kortler (1993), the authors define product mix as the set of all product lines and items that a particular seller or producer offers for sale to buyers". Model Components of a LPP Like many other kinds of optimization problems, LPP is mathematical model which has different components. The most important components of a LPP model are: D Defining key decision variables D Setting objective functions D Writing mathematical expressions for constraints Non-negativity Restriction D Solving the mathematical model Corresponding author: Gezahegn Tesfaye email: tesfmastera@gmail.com Defining key - decision variables They are the set of quantities that need to be 422 422 G. Tesfaye, T. Berhane, B. Zenebe, S. Asmelash International Journal for Quality Research QUALITY HERRARCH determined in order solve the problem. The decision variables represent unknown decisions to be made. This is in contrast to problem dala, which are values that are either giver or can be simply calculated from what is given. In this research, the decision variables are the number of products of each type to be produced. In general, the problem is said to be solved only when the best values of the variables have been identified. Typically, the variables represent the amount of resources to employ. the number of decision variables is 2. However, most real world linear programming problems have more than two decision variables and thus are too complex for graphical solution. Among the various methods of solving a linear programming problem the simplex method is one of the most powerful (Andawei, 2014). Computer programs and spreadsheets are available to handle the simplex calculations (Online Tutorial). 2. The Problem Statement Setting objective functions Every linear program has an objective. The objective of a LPP is either to maximize or to minimize the objective function. This objective has to be linear in the decision variables, which means it must be the sum of constants multiplied by decision variables. The objective function shows how each variable contributes to the value to be optimized in solving the problem. The coefficients of the objective function indicate the contribution to the value of the objective function of one unit of the corresponding variable. Writing mathematical expressions for constraints As a condition, linear programming problem must operate within the limits of restrictions placed upon the problem, which the decision maker must always take into consideration (Andawei, 2014). Constraints are the limitations such as available resource capacity, daily working hours, raw material availability, etc. In its economic reform program, the Ethiopian government has formulated a clear industrial development strategy (ETIDI, 2014). The strategy mainly focuses on export-led and labor intensive industrialization (Tesfaye et al, 2014), The country is emerging as one of the most important investment destinations in Africa. The apparel sector is considered as one of the priority areas by the Government's Industrial Development Strategy (ETIDI. 2014). As a result many European and Asian organizations began production and sourcing apparels from Ethiopia. The investment on apparel products and hence the export market of the country has relatively shown minimal increments over the past years. Though there are many challenges facing the apparel sector of the country at the current time, many studies revealed that the country has a good potential to be a center for apparel manufacturing and sourcing, but only when the existing business conditions are improved. Demisse et al. (2015) noted that garment manufacturing companies can make considerable contribution to national economies mainly for the developing world. The apparel sector is the area that can generate more income from the export market. However, studies shown that the performance of the Ethiopian apparel sector is much below the world standard (Razvan, 2008; Yisihak et al., 2011; Tesfaye et al. 2014; Demisse et al., 2015). According to these studies, the export earning of the Non-negativity Restriction In the many of the linear programming problems, and particularly in the product problems, the values of decision variables must be non-negative numbers. Solving the mathematical model A graphical method is a simplest method to solve a linear programming problem when 423 423 BALIKE International Journal for Quality Research finishing and packaging Currently, the products the case company produces are basic t-shirt, polo shirt, short pant, V-neck t-shirt and singlet. It is a challenging task for the decision makers of the company to identify the type of products (product mix) that ensure efficient resource utilization and maximum profit for the organization. The problem addressed here is to determine the proper product mix to be adopted by the company for efficient resource utilization that can enhance the global competitiveness of the corripany through the application of a linear programming technique. The following general assumptions have been made in this research: There is sufficient demand for every product produced as a result of a bigger domestic and international market for apparel products. D The omission of fixed cost of production does not affect the finding of the research Ethiopian apparel sector remains trivial. Apart from the great ambition of the government to modernize the apparel sector with the objective of attracting foreign investors, the efforts made so far to improve the performance of the sector was insignificant (Ethiopia Trade and Investment, 2010; Samuel, 2012). The low global competitiveness of the Ethiopian apparel sector is mainly due to the inefficient use of their organizational resources (Project profile on garment industry; Abebe, 1997; Assefa, 2008; Arefayne and Pal, 2014). In general terms, the country is challenged by inefficient use of manufacturing resources. Due to this fact, the Ethiopian apparel manufacturing companies must apply LPP in order to enhance resource utilization and increase their profit. In apparel manufacturing firms, production time, cost of labor and material, and material utilization significantly affect their profit (Arefayne and Pal, 2014). In this industrial sector cutting, sewing, and finishing operations are the major ones which deserve more attention for resource optimization. In general, in the context of Ethiopian apparel industry, it can be inferred that organizational resources are not utilized properly to the best level and the current work of the companies is only targeted towards fulfilling the production orders. As to the knowledge of the authors of this research, the issue of proper resource allocation remains the unsolved problem within the Ethiopian apparel industry. Thus, this paper focuses on how effective resource utilization can be established for Ethiopian apparel sector to increase their profit, taking a case study of one of the garment factories currently engaged in the export market. The study attempts to identify the existing resource utilization level and the profit per month of the case company and compare the results with the optimal solution obtained using a linear programming method. The case company has flaw of work starting from receiving customer orders to packaging the finished products through the entire process of designing, sampling, cutting, sewing, 3. Methodology Related literatures were surveyed to understand the industrial development strategy and the priority areas in the economic development process of Ethiopia. To bring national economic development via prioritized economic sectors of the country, a linear programming technique was suggested to arrive at effective resource utilization and optimal profit. To show how the methodology suggested can be applied, one of the apparel manufacturing carpa hiopia was considered as a case company. From this case company. five types of products the company is producing at the current time, the amount of resources (material, cost, and time) employed to produce each unit of the products and a profit per unit that can be generated from the sale of each product have been obtained. The monthly availability of each of these organizational resources (material, cost, and time) and the monthly production volume of 424 424 G. Tesfaye, T. Berhane, B. Zenebe, S. Asmelash International Journal for Quality Research QUALITY RERARRCH each of the five products have also been collected from the case company. A general methodology of a linear programming procedure (setting of objective function, constraints and non-negativity restriction) has been applied to set the data gathered from the company into its mathematical model. In order to solve the mathematical expression (ie, the mathematical model developed for the case company), the MS-Excel solver for a linear programming technique was used. The optimal solution generated by the MS-Excel solver was compared against the existing company's performance of resource utilization and profit making. Finally, conclusions have been made regarding the findings of the study. threads are shown in meter per product. Materials and labor costs per product are given in the sth and 6th columns of the table respectively. The time constrain in minutes per product, which is another most critical factor, is given for the cutting, sewing and finishing operations as indicated in the 7th, oth and oth columns of the table. Finally, in the 10th column of the table, we get unit profit in birr (Ethiopia currency) for the five products. Now, having the types of products the company is producing, the list of decision variables and constraints, and the unit profits, we can formulate the mathematical model using a linear programming technique and solve it to arrive at optimal solution. As stated in section 1, a linear programming procedure with the following steps has been applied to solve the resource allocation problem of the case company. Step 1: defining key - decision variables Step 2: setting objective functions to maximize the total profit Step 3: writing mathematical expressions for the material, cost and time constraints, and Step 4: restricting the key decision variables not to be negative values Step 5: Solving the mathematical model developed through step 1 to step 4 4. Results and Discussion 4.1. Optimal solution of the Existing System Materials, financial and time resources are the most critical organizational resources in apparel industry. Among the direct materials utilized in the production process of the company, fabrics and sewing threads are the decisive elements. The aim here is to determine the optimal material utilization. In the cost category, labor cost and materials cost constitutes the major proportion of the cost of finished apparels. The time required to process a unit of each product type have been estimated based the company's recent five year historical data (see table 1). The company currently manufactures Men's Polo-shirt Men's s's Basic T-shirt, Short pant, Singlet, and Men's V-neck T shirt. Each of these products are denoted by decision variables x1, x2...., 5 respectively. For the two materials considered in this study (fabrics and threads), their consumptions per unit have been given 3rd and the columns of the table. Fabrics are given in gram per product and sewing in the Step 1: definition of decision variables The optimal quantities of each type of product required to be produced by the company are denoted as follows: x1 = the number of polo shirt to be produced x2 = the number of basic T-shirt to be produced x3 = the number of short pant to be produced x4 = the number of singlet to be produced X5 = the number of V-neck T-shirt to be produced Step 2: setting the objective function The objective here is to maximize the total profit. It can be expressed as: 425 425 HAWTH International Journal for Guality Research Table 1. List of constraints and profit per product Resource utilization per unit of products Costs Time Constraints Material Constraints Constraints (SMV in Min) (Birr) Decision Product Type Variable Fabrics (Gram) Profit per unit (Bir) speanul Labor Material - Bugung Sewing Finishing Men's Polo- shirt X1 313 230 11.6 30.6 1.8 22.7 2 4.22 Men's s's Basic T-shirt X2 198 110 5 19.1 1.1 5.4 1.3 3.62 Short pant x3 280 200 7.5 37.5 2.6 20.1 2.5 6.75 Singlet 780 100 4.15 16.5 1.1 4.5 1.3 3.10 Men's V-neck T-shirt X5 195 140 6.3 20.1 1.7 10.4 3.43 Availability per month 37,665,600 26,638,120 1,009,00 4,979,414 246302 2.670.336 371,628 Step 3: List of the constraints Resource utilizations per unit of each product from tablel are taken as the coefficient of the decision variables and the availability of each resource per month are written as the right hand side of the constraints. Less than or equal to inequalities signs are used to reflect the fact that resource utilization can only be less than or equal to resource availability. The left hand side (LHS) of the constrains represent resource consumption and the right hand side (RHS) of the constraints show resource availability. Thus, based on the data in table 1, the list of coristraints can be formulated as follows: Fabric consumption (constrains 1 or C1) 313x1 + 198x2 + 280x3 + 180x4 + 195x5 37,665,600 Thread consumption (C2) 230x1 + 110x2 + 200x3 + 100x4 + 140x5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


