Question: Bayesian binary decision (detection) rule, probability of error, optimal detector Consider a communication system where a transmitter sends one of two symbols denoted a, and
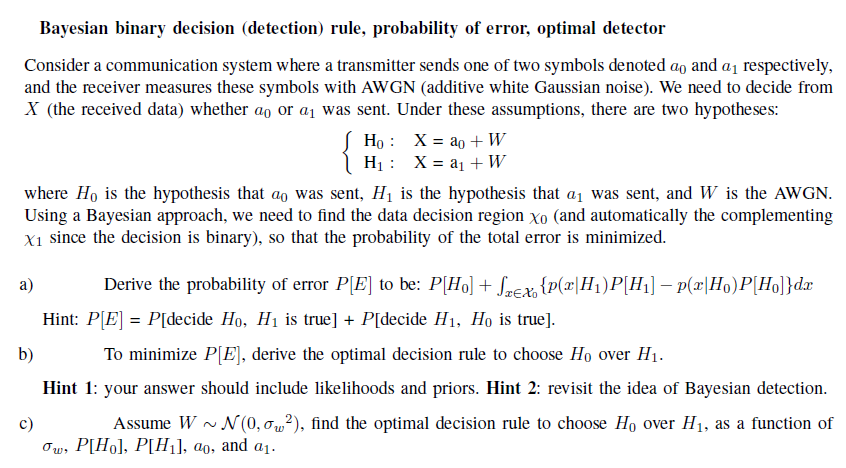
Bayesian binary decision (detection) rule, probability of error, optimal detector Consider a communication system where a transmitter sends one of two symbols denoted a, and a, respectively, and the receiver measures these symbols with AWGN (additive white Gaussian noise). We need to decide from X (the received data) whether ag or a, was sent. Under these assumptions, there are two hypotheses: Ho: X = ao + W H1 : X = al + W where Ho is the hypothesis that ao was sent, H1 is the hypothesis that a, was sent, and W is the AWGN. Using a Bayesian approach, we need to find the data decision region xo (and automatically the complementing x1 since the decision is binary), so that the probability of the total error is minimized. a) Derive the probability of error P[E] to be: P[Ho] + Srex. {p(@[H1)P[Hi] -P(x|Ho)P[Ho}}de Hint: P[E] = P[decide Ho, H1 is true] + P[decide H1, Ho is true]. b) To minimize PJE] , derive the optimal decision rule to choose Ho over H1. Hint 1: your answer should include likelihoods and priors. Hint 2: revisit the idea of Bayesian detection. C) Assume W~N(0, ow?), find the optimal decision rule to choose Ho over H1, as a function of Ow, P[Hol, P[Hil, co, and a1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


