Question: Before programming the binomial tree it is a good idea to program the Black-Scholes solution for the European call option. This will give us a

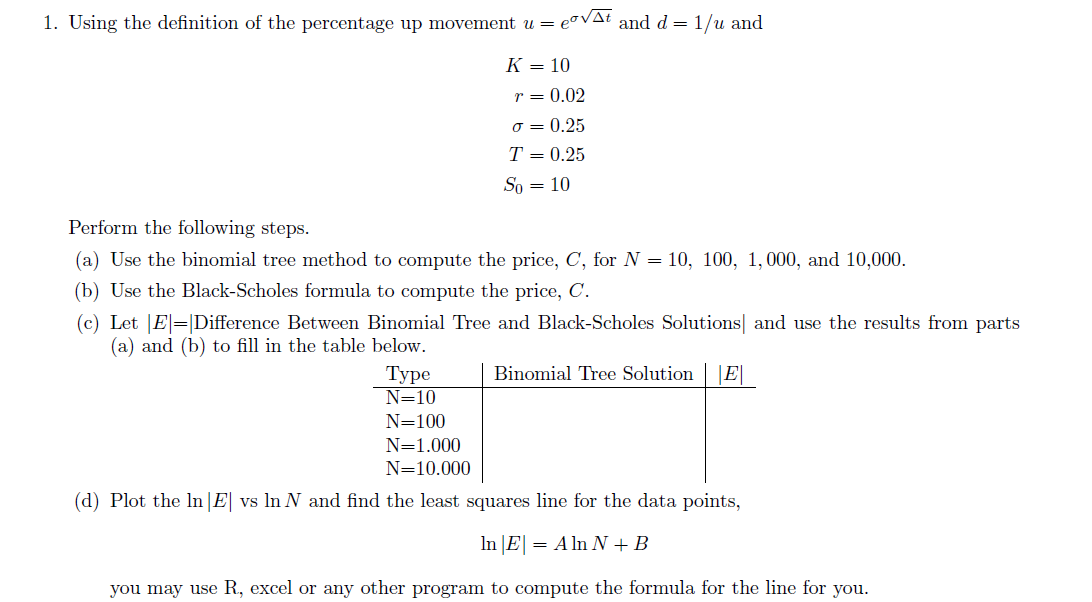
Before programming the binomial tree it is a good idea to program the Black-Scholes solution for the European call option. This will give us a a value to compare the binomial tree approximation against. Consider C = current price of a call option on a non-dividend-paying stock So = current stock price K = strike price of option r= constant risk-free interest rate o= constant volatility of the stock price T = time to maturity. Then according the The Black-Scholes formula?, covered in chapter 15.8 of our book, the price of a European call option is C = S,(di) - Ke-T (d2), where di In(So/K) + (r + 02/2)T NT In(So/K) + (r 02/2)T = d - OVT. d2 = OVT is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution. The price for the put option can be found in our book or you can just use the put-call parity to find it. 1. Using the definition of the percentage up movement u = covat and d=1/u and K = 10 r= 0.02 O= 0.25 T = 0.25 So = 10 Perform the following steps. (a) Use the binomial tree method to compute the price, C, for N = 10, 100, 1,000, and 10,000. (b) Use the Black-Scholes formula to compute the price, C. (c) Let E=Difference Between Binomial Tree and Black-Scholes Solutions and use the results from parts (a) and (b) to fill in the table below. Type Binomial Tree SolutionE N=10 N=100 N=1.000 N=10.000 (d) Plot the In|E| vs In N and find the least squares line for the data points, In E = Aln N +B you may use R, excel or any other program to compute the formula for the line for you. Before programming the binomial tree it is a good idea to program the Black-Scholes solution for the European call option. This will give us a a value to compare the binomial tree approximation against. Consider C = current price of a call option on a non-dividend-paying stock So = current stock price K = strike price of option r= constant risk-free interest rate o= constant volatility of the stock price T = time to maturity. Then according the The Black-Scholes formula?, covered in chapter 15.8 of our book, the price of a European call option is C = S,(di) - Ke-T (d2), where di In(So/K) + (r + 02/2)T NT In(So/K) + (r 02/2)T = d - OVT. d2 = OVT is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution. The price for the put option can be found in our book or you can just use the put-call parity to find it. 1. Using the definition of the percentage up movement u = covat and d=1/u and K = 10 r= 0.02 O= 0.25 T = 0.25 So = 10 Perform the following steps. (a) Use the binomial tree method to compute the price, C, for N = 10, 100, 1,000, and 10,000. (b) Use the Black-Scholes formula to compute the price, C. (c) Let E=Difference Between Binomial Tree and Black-Scholes Solutions and use the results from parts (a) and (b) to fill in the table below. Type Binomial Tree SolutionE N=10 N=100 N=1.000 N=10.000 (d) Plot the In|E| vs In N and find the least squares line for the data points, In E = Aln N +B you may use R, excel or any other program to compute the formula for the line for you
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


