Question: begin{tabular}{lcc} hline & multicolumn{2}{c}{ Expected return } cline { 2 - 3 } Year & Stock L & Stock M hline 2013 &
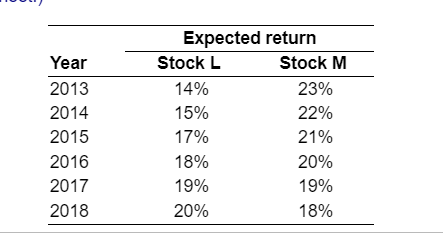
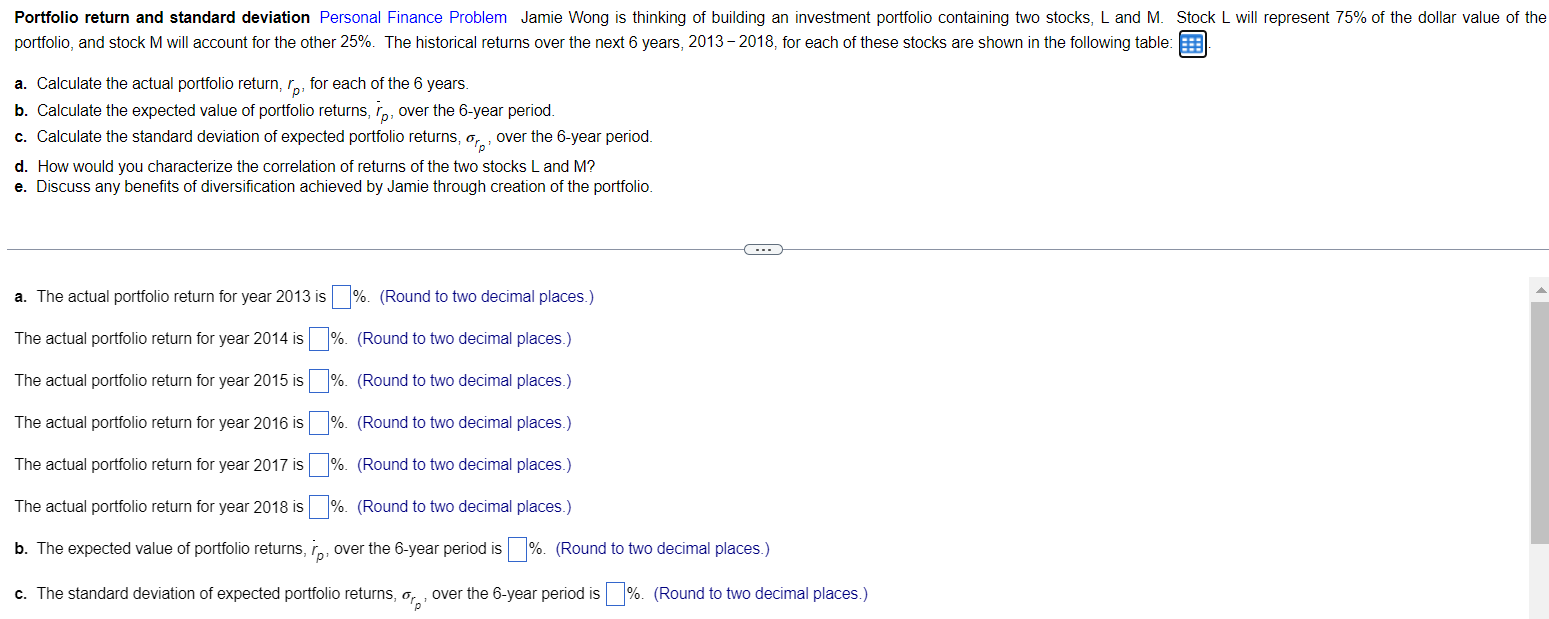
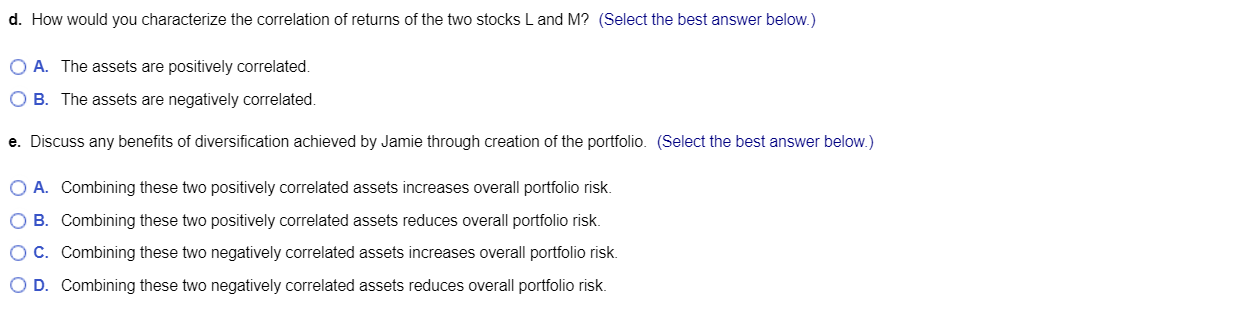
\begin{tabular}{lcc} \hline & \multicolumn{2}{c}{ Expected return } \\ \cline { 2 - 3 } Year & Stock L & Stock M \\ \hline 2013 & 14% & 23% \\ 2014 & 15% & 22% \\ 2015 & 17% & 21% \\ 2016 & 18% & 20% \\ 2017 & 19% & 19% \\ 2018 & 20% & 18% \\ \hline \end{tabular} portfolio, and stock M will account for the other 25%. The historical returns over the next 6 years, 2013 - 2018, for each of these stocks are shown in the following table: a. Calculate the actual portfolio return, rp, for each of the 6 years. b. Calculate the expected value of portfolio returns, rp, over the 6 -year period. c. Calculate the standard deviation of expected portfolio returns, rp, over the 6-year period d. How would you characterize the correlation of returns of the two stocks L and M ? e. Discuss any benefits of diversification achieved by Jamie through creation of the portfolio. a. The actual portfolio return for year 2013 is The actual portfolio return for year 2014 is The actual portfolio return for year 2015 is The actual portfolio return for year 2016 is The actual portfolio return for year 2017 is The actual portfolio return for year 2018 is The actual portfolio return for year 2018 is b. The expected value of portfolio returns, rp, over the 6-year period is c. The standard deviation of expected portfolio returns, rp, over the 6-year period is \%. (Round to two decimal places.) \%. (Round to two decimal places.) \%. (Round to two decimal places.) \%. (Round to two decimal places.) \%. (Round to two decimal places.) %. (Round to two decimal places.) %. (Round to two decimal places.) o. (Round to two decimal places.) A. The assets are positively correlated. B. The assets are negatively correlated. Discuss any benefits of diversification achieved by Jamie through creation of the portf A. Combining these two positively correlated assets increases overall portfolio risk. B. Combining these two positively correlated assets reduces overall portfolio risk. C. Combining these two negatively correlated assets increases overall portfolio risk. D. Combining these two negatively correlated assets reduces overall portfolio risk
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


